Blog Grid
- Home
- Blog Grid
The Importance of Comparing the Insurance Rates
It is a long established fact that a reader will be distra
by the readable content of a page when looking at its
layout. The point of using Lorem Ipsum is that it has
a more-or-less normal distribution of letters, as opposed
to using \’Content here, content here\’, making it look like
readable English. Many desktop publishing packages and
web page editors now use Lorem Ipsum as their default
model text, and a search for \’lorem ipsum\’ will uncover
many web sites still in their infancy. Various versions
have evolved over the years, sometimes by accident,
sometimes on purpose (injected humour and the like).
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum
available, but the majority have suffered alteration in
some form, by injected humour, or randomised words
don\’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to
passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn\’t
anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text.
5 Unbelievable Facts about Gas Stations
It is a long established fact that a reader will be distra
by the readable content of a page when looking at its
layout. The point of using Lorem Ipsum is that it has
a more-or-less normal distribution of letters, as opposed
to using \’Content here, content here\’, making it look like
readable English. Many desktop publishing packages and
web page editors now use Lorem Ipsum as their default
model text, and a search for \’lorem ipsum\’ will uncover
many web sites still in their infancy. Various versions
have evolved over the years, sometimes by accident,
sometimes on purpose (injected humour and the like).
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum
available, but the majority have suffered alteration in
some form, by injected humour, or randomised words
don\’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to
passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn\’t
anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text.
How to Save on Homeowners Insurance
How to Save on Homeowners Insurance
It is a long established fact that a reader will be distra
by the readable content of a page when looking at its
layout. The point of using Lorem Ipsum is that it has
a more-or-less normal distribution of letters, as opposed
to using \’Content here, content here\’, making it look like
readable English. Many desktop publishing packages and
web page editors now use Lorem Ipsum as their default
model text, and a search for \’lorem ipsum\’ will uncover
many web sites still in their infancy. Various versions
have evolved over the years, sometimes by accident,
sometimes on purpose (injected humour and the like).
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum
available, but the majority have suffered alteration in
some form, by injected humour, or randomised words
don\’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to
passage of Lorem Ipsum, you need to be sure there isn\’t
anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text.
How do you qualify for a loan in South Africa?
Qualifying for a loan in South Africa can seem daunting without proper guidance. Securing a loan can be a significant step towards achieving your financial goals, whether it’s purchasing a home, starting a business, or covering unexpected expenses. I’ll walk you through the essential steps and requirements to help you navigate the loan qualification process smoothly.
Qualification for a loan in South Africa
Qualifying for a loan in South Africa involves several factors that lenders consider before approving your application. These criteria are crucial for a successful loan application, from creditworthiness to income verification.
Credit Score and History
Your credit score plays a pivotal role in determining your eligibility for a loan. Lenders assess your credit history to evaluate your past repayment behavior and assess the risk associated with lending to you.
Income and Employment Verification
Lenders need assurance that you have a stable source of income to repay the loan. Providing proof of employment and income through payslips, bank statements, or tax returns is typically required during the application process.
Debt-to-Income Ratio
Your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio is another crucial factor that lenders consider. This ratio compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income. A lower DTI ratio indicates that you have more disposable income available to repay the loan, increasing your chances of approval.
Loan Amount and Term
Determining the loan amount and repayment term that aligns with your financial situation is essential. Consider factors such as your income, expenses, and long-term financial goals when deciding on the loan amount and duration.

Collateral and Guarantors
Some loans in South Africa may require collateral or a guarantor to secure the lender’s investment. Collateral could be in the form of property, vehicles, or other valuable assets that you own. A guarantor, on the other hand, is someone who agrees to take responsibility for the loan if you default on payments.
Interest Rates and Fees
The interest rates and fees associated with the loan are crucial for assessing its affordability. Compare offers from different lenders to find the most competitive rates and favorable terms.
Loan Application Process
Once you’ve gathered all the necessary documentation and information, it’s time to initiate the loan application process. Be prepared to fill out forms, undergo credit checks, and provide additional documentation as requested by the lender.

Tips for Improving Your Loan Eligibility
- Maintain a good credit score by paying bills on time and avoiding excessive debt.
- Reduce existing debt to improve your DTI ratio.
- Save for a down payment to reduce the loan amount and lower the lender’s risk.
- Consider enlisting a co-borrower or guarantor with a strong credit history to bolster your application.
FAQs
Can I qualify for a loan in South Africa with bad credit?
Yes, some lenders offer loans specifically designed for individuals with less-than-perfect credit. However, these loans may come with higher interest rates or stricter terms.
What documents do I need to apply for a loan in South Africa?
Required documents may vary depending on the lender and the type of loan in South Africa. Generally, you’ll need proof of identity, proof of income, bank statements, and details of any existing debts.
How long does it take to get approved for a loan in South Africa?
The approval timeline can vary depending on the lender, the complexity of your application, and other factors. Some lenders offer instant approval, while others may take several days to process your application.
Can I apply for multiple loans simultaneously?
While it’s possible to apply for multiple loans, doing so can negatively impact your credit score and raise red flags for lenders. It’s advisable to carefully consider your options and avoid overextending yourself financially.
What happens if I miss a loan payment?
Missing a loan payment can have serious consequences, including late fees, penalty interest rates, and damage to your credit score. Contact your lender immediately if you’re experiencing financial difficulties to explore alternative repayment options.
Is it possible to pay off a loan early?
Yes, many lenders allow early repayment of loans without penalty. Paying off your loan ahead of schedule can save you money on interest and improve your overall financial health.
Conclusion
Qualifying for a loan in South Africa requires careful planning, financial discipline, and a thorough of application process. By focusing on improving your creditworthiness, managing your finances responsibly, and exploring your options, you can increase your chances of securing the loan you need to achieve your goals.
How to Change Your Banking Details for Your SASSA R350 Grant
Through several grants, including the SASSA R350 Grant relief, the South African Social Security Agency (SASSA) offers qualifying residents vital financial support. If you’re a recipient of the SASSA R350 grant and need to update your banking details, you can do so through a straightforward process.
Here’s a guide on how to change your banking details for your SASSA R350 grant:
1. Contact SASSA: The first step is to get in touch with SASSA to initiate the process of changing your banking details. You can reach out to them through their toll-free helpline at 0800 60 10 11. Prepare to provide your ID number and other relevant information for verification purposes.
2. Request the Change: Inform the SASSA representative that you need to update your banking details for your R350 grant. They will guide you through the process and inform you of any required documentation or information.
3. Provide Necessary Information: Depending on SASSA’s requirements, you may need to submit certain documents to facilitate the change. These documents may include a certified copy of your ID, proof of residence, and proof of your new banking details (such as a bank statement or a stamped letter from your bank).

4. Complete Forms: SASSA may require you to fill out specific forms related to changing banking details. Ensure that you complete these forms accurately and follow any instructions provided by SASSA.
5. Submit Documentation: Once you have all the necessary documentation and forms filled out, submit them to SASSA through the designated channels. This could involve emailing the documents, faxing them, sending them via post, or visiting a SASSA office in person, depending on their procedures.
6. Follow-Up: After submitting your request, it’s essential to follow up with SASSA to confirm that your banking details have been successfully updated. You can do this by contacting them again through their helpline or visiting a SASSA office if necessary.
7. Confirmation: Once SASSA has processed your request and updated your banking details, they should provide confirmation. This confirmation may be sent to you via email, SMS, or letter. Be sure to retain this confirmation for your records.

By following these steps and ensuring that you provide accurate and complete information to SASSA, you can successfully change your banking details for your SASSA R350 grant. Timely updating of your banking details ensures that you continue to receive your grant payments without any interruptions.
Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups
Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups is a critical aspect of planning and strategizing.
In essence, it involves creating a dynamic representation of a company’s financial situation, projecting future performance, and analyzing potential outcomes.
For pre-seed startups navigating the challenging landscape of entrepreneurship, effective financial modeling is more than a tool; it’s a compass guiding them through the uncharted waters of business.
The pre-seed stage: exhilarating, chaotic, and, quite frankly, a little nerve-wracking. You’ve got a groundbreaking idea, a passionate team, and a caffeine drip that rivals Niagara Falls.
But amidst the hustle, investors beckon, asking the dreaded question: “Show me the money.” That’s where financial modeling comes in, but at this stage, forget complexity.
We’re talking lean, mean, storytelling machines, not crystal balls.
Think lean, not Lamborghini: Ditch the multi-sheet monsters. This early game requires agility, not spreadsheets the size of Texas.
A single page, focused on core metrics like customer acquisition cost, lifetime value, and burn rate, is your playground.
Remember, investors want to see your understanding of the business, not your Excel wizardry.
Assumptions? Keep it real: Forget five-year forecasts built on air. Use reasonable estimates based on market research and your gut instinct.
Think customer conversion rates, pricing models, and even napkin math. Transparency is key, so document your assumptions.
Scenario planning: the crystal ball slayer: The future’s a fickle beast. Build different scenarios with varying assumptions.
What if customer acquisition takes longer?
What if revenue explodes?
This shows investors you’re prepared for the rollercoaster ride (and hey, it forces you to think through potential roadblocks).
Iteration is queen (or king): Your business model is a living, breathing beast. As you learn, your model evolves. Don’t be afraid to tweak, update, and adapt.
This isn’t about predicting the future; it’s about understanding your present and navigating the twists and turns ahead.
Storytelling: where numbers sing: Let’s face it, spreadsheets can be snooze-inducing. Use your model to weave a compelling narrative about your business.
Highlight key insights, showcase your growth potential, and most importantly, convince investors you’re the Elon Musk of your niche (minus the Twitter meltdowns, hopefully).
Tools for the lean and mean: Ditch the bespoke consultants and fancy software. Tools like Pry and Google Sheets offer simple, accessible platforms to build your model.
Remember, it’s not about the bells and whistles; it’s about telling your story through numbers.
The bottom line: Pre-seed financial modeling isn’t about precision; it’s about painting a picture with a brush dipped in informed assumptions and sprinkled with strategic foresight.
It’s a tool to guide your decisions, attract investors, and most importantly, prove you’ve got the brains (and the hustle) to turn your dream into reality.
So, roll up your sleeves, grab your trusty spreadsheet, and start demystifying those dollars. The investors await your masterpiece.
Now, conquer the pre-seed stage, armed with your lean, mean, storytelling financial model! Remember, it’s not about predicting the future; it’s about shaping it.
And who knows your next model might just be the one that lands you on Forbes, not just in your dreams, but on the cover.
Importance of Financial Modeling for Pre-seed Startups
Attracting Investors
Investors look for startups with a clear and well-thought-out financial plan. A robust financial model instills confidence and demonstrates that the Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups has thoroughly considered potential challenges and opportunities.
Strategic Decision-Making
Financial models serve as decision-making tools. They enable startups to assess the financial implications of different strategies, helping them make informed choices that align with their long-term goals.
Risk Mitigation
By identifying potential financial risks through modeling, startups can implement mitigation strategies. Whether it’s adjusting spending habits or securing additional funding, proactive risk management is essential for survival.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

Overly Optimistic Projections
While optimism is crucial in entrepreneurship, overly optimistic financial projections can lead to unrealistic expectations. Pre-seed Startups should strike a balance between ambition and practicality.
Ignoring Market Trends
Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups should consider market trends and external factors. Ignoring these elements can result in a misalignment between projections and reality.
Neglecting Contingency Planning
Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups should always plan for the unexpected. Neglecting contingency planning can leave a business vulnerable to unforeseen challenges.
FAQs
What is the role of Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups’ success?
Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups is pivotal in startup success by providing a roadmap for financial decisions, attracting investors, and mitigating risks.
How frequently should a Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups update its financial model?
Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups should update their financial models regularly, especially in response to changes in the business environment or strategic shifts.
Are there specific industries where financial modeling is more crucial?
While financial modeling is important across industries, it’s particularly crucial in sectors with high uncertainty, rapid changes, and intense competition.
Can a Financial Modeling for Pre-Seed Startups succeed without a detailed financial model?
While success is possible, a detailed financial model enhances a startup’s chances by providing a structured approach to decision-making and risk management.
What are the potential risks of inadequate financial modeling?
Inadequate financial modeling can lead to unrealistic expectations, poor decision-making, and increased vulnerability to unforeseen challenges. It’s a crucial aspect of long-term planning for startups.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of pre-seed startups, financial modeling emerges as a linchpin for success.
By navigating the intricacies of revenue projections, expense forecasting, and cash flow analysis, startups can chart a course toward sustainable growth.
It’s not just about numbers; it’s about making informed decisions that lay the foundation for a resilient and thriving business.
How do you create a financial model for investors?
In this article, we’ll explore the intricacies of creating a financial model for investors that speaks to investors effectively. For entrepreneurs seeking investment, a polished financial model is the Rosetta Stone which translates potential into concrete value.
It’s not just about spreadsheets and formulas; it’s a compelling story about your business’s future, told in the language investors understand.
So, how do you craft a financial model that captivates them?
Steps to Create a financial model for investors
1. Define Your Purpose and Audience
Is your model for securing seed funding, attracting venture capitalists, or pitching a merger? Understanding the purpose dictates the level of detail and complexity.
Tailor it to your audience’s expectations and risk tolerance. Investors seeking high-growth startups can handle bolder assumptions, while banks might require conservative projections.
2. Gather and Organize Data create a financial model for investors
Think of data as your building blocks. Historical financial statements, industry benchmarks, and competitor analysis provide a solid foundation.
Ensure data accuracy and consistency, and present it in a way that’s easy to understand and navigate. Transparency builds trust and allows investors to delve deeper.
3. Choose the Right Tool to create a financial model for investors
Excel might be your comfortable go-to, but consider dedicated financial modeling software. Tools like FinPlan, Valuate, or Anaplan offer user-friendly interfaces, built-in templates, and robust functionalities for scenario testing and sensitivity analysis.
Choose a tool that suits your technical expertise and the model’s complexity.
4. Build the Core Statements create a financial model for investors
The Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement are the backbone of your model. Start with historical data and build projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability.
Use a bottom-up approach for detailed forecasting, or a top-down approach for broader strategic direction.
5. Layer on Assumptions and Sensitivities
Your model isn’t a crystal ball but informed assumptions fuel its engine. Document key assumptions like sales growth rates, marketing spending, or price changes.
Don’t shy away from sensitivity analysis, showing how the model reacts to different scenarios. This showcases your foresight and understanding of potential risks and rewards.
6. Make it Transparent and Easy to Use
Remember, clarity is your friend. Use clear labels, consistent formatting, and intuitive navigation.
Color coding, charts, and graphs can bring data to life and make complex relationships readily apparent. Investors shouldn’t need a decoder ring to understand your story.
7. Don’t Forget the Story
Numbers tell a story, but sometimes they need a narrator. Explain your assumptions, highlight key growth drivers, and emphasize the opportunities your business presents.
Connect the dots between financial projections and your broader vision, demonstrating how your company will create value for investors.
8. Review and Refine
Your model is a living document, not a static snapshot. Regularly review its accuracy, update assumptions based on new information, and be prepared to adapt to changing market conditions.
This demonstrates agility and responsiveness, attractive qualities for any investor.
Building a winning financial model for investors is about more than just formulas and calculations. It’s about crafting a compelling narrative, fueled by data, that paints a clear picture of your business’s potential.
By following these steps and focusing on clarity, transparency, and a compelling story, you can turn your financial model into a powerful tool that unlocks the door to investment and propels your business forward.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
A. Overcomplicating the model
While detail is important, avoid overcomplicating the model with unnecessary information. Keep it focused on the key metrics that matter.
B. Ignoring industry benchmarks
Benchmarking against industry standards provides context for your financial model. Ignoring these benchmarks can lead to misguided projections.
C. Neglecting risk factors
Identify and address potential risks. Ignoring these factors can result in an incomplete and unrealistic representation of the business.
FAQs
How often should I update my financial model?
It’s advisable to update your financial model regularly, especially when there are significant changes in your business, market conditions, or industry trends.
Can I use free financial modeling tools?
While free tools like Excel are widely used, specialized financial modeling software can offer advanced features and automation for more complex models.
What role does scenario analysis play in a financial model?
Scenario analysis helps assess how changes in variables impact the financial model, providing insights into potential outcomes under different conditions.
How important is industry benchmarking in financial modeling?
Industry benchmarking is crucial as it provides context for your financial model, allowing investors to compare your performance against industry standards.
Is it necessary to tailor financial models for different industries?
Yes, customizing financial models for specific industries ensures that the metrics and assumptions align with the unique characteristics of each sector.
Conclusion
A. Recap of key points
Creating a financial model for investors is a multifaceted process that involves meticulous planning, realistic projections, and transparent communication.
The key components, steps, and best practices outlined in this article serve as a comprehensive guide for entrepreneurs seeking to create investor-friendly financial models.
B. Emphasis on the role of financial model for investors
financial model for investors are not just numbers on a spreadsheet but a dynamic representation of a business’s potential.
When crafted with precision and presented effectively, these models instill confidence in investors, fostering a positive relationship between entrepreneurs and financiers.
Financial Modeling for Healthcare Startups
Financial modeling for healthcare startups involves creating a detailed representation of the company’s financial performance and projections. In the dynamic world of healthcare, innovation runs rampant.
From telemedicine apps to AI-powered diagnostics, startups are transforming how we deliver and experience healthcare.
But amidst the hustle and buzz, one element remains critical for success: a robust financial model.
For healthcare startups, financial modeling isn’t just about securing funding; it’s about building a roadmap for the future.
It’s understanding how your business will generate revenue, manage costs, and ultimately become profitable.
In a landscape marked by complex reimbursement mechanisms and evolving regulations, a well-constructed financial model becomes your guiding light.
Financial Modeling for Healthcare Startups Why is it Different for Healthcare?
Building a financial model for a healthcare startup presents unique challenges. Unlike traditional businesses, your revenue streams might involve a mix of patient payments, insurance reimbursements, and grants.
Moreover, the regulatory environment can be intricate, impacting everything from pricing to data privacy.

Here is a step-by-step guide to creating a financial model for a healthcare startup
- Market Analysis: Understand the size and growth potential of your target market. Identify key competitors and their pricing strategies.
- Revenue Model: Define how you’ll generate income. Will it be through subscriptions, per-service fees, or partnerships with healthcare providers?
- Cost Structure: Factor in operational costs like personnel, technology, and marketing. Don’t forget regulatory compliance expenses.
- Expense Projections:
Operating Expenses: Detail all operating costs, including salaries, rent, utilities, insurance, and other overhead expenses.
Capital Expenditures: Include any significant investments in assets like equipment or technology.
- Cash Flow Statement:
Cash Inflows: Consider all sources of cash, including investments, loans, and revenue.
Cash Outflows: Account for all expenses and investments that require cash.
- Balance Sheet:
Assets: List all the assets your startup owns, including cash, equipment, and intellectual property.
Liabilities: Include debts, loans, and other financial obligations.
- Financial Projections: Forecast future revenue, expenses, and cash flow. Be realistic, but not pessimistic. Remember, investors appreciate ambitious yet achievable goals.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Analyze how your model reacts to changes in key assumptions, such as market size or reimbursement rates. This helps you prepare for potential risks and opportunities.
- Valuation: Determine the valuation of your healthcare startup. This is crucial for fundraising and strategic decision-making.
- Risk Analysis: Identify potential risks and uncertainties impacting your financial projections. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks.
- Scenario Analysis: Model different scenarios to assess the impact of various market conditions on your startup’s financial health.
- Investor Presentation: Summarize your financial model in a clear and concise format suitable for investor presentations. Highlight key metrics and assumptions.
- Iterate and Update: Regularly update your financial model to reflect changes in the market, business strategy, or other relevant factors. This ensures that your projections remain accurate and useful.
Beyond the Numbers
Effective financial modeling for healthcare startups goes beyond mere spreadsheets. It’s about communicating your vision effectively.
Present your model clearly and concisely, highlighting key assumptions and potential scenarios.
Investors want to understand your thought process and see your passion for making a difference in healthcare.
Tools and Resources for Financial Modeling for Healthcare Startups
- Financial modeling software: Excel remains a popular choice, but specialized healthcare modeling tools can offer greater flexibility and accuracy.
- Industry reports and data: Research market trends, regulatory changes, and reimbursement rates. Reliable data strengthens your assumptions and adds credibility to your model.
- Mentors and advisors: Seek guidance from experienced healthcare professionals and financial experts. Their insights can be invaluable in navigating the complexities of the industry.
Remember: Your financial model is a living document. As your Financial Modeling for Healthcare Startups evolves, so should your model. Regularly update it with new data and adapt your assumptions to reflect changing market realities.
conclusion
In conclusion, building a robust Financial Modeling for Healthcare Startups is not just an obligation for healthcare startups; it’s an opportunity.
It’s a chance to showcase your potential, attract investors, and ultimately, achieve your vision of improving healthcare.
So, grab your spreadsheets, gather your data, and start building your roadmap to success.
The future of healthcare waits for no one, and a well-crafted Financial Modeling for Healthcare Startups will be your compass on the journey.
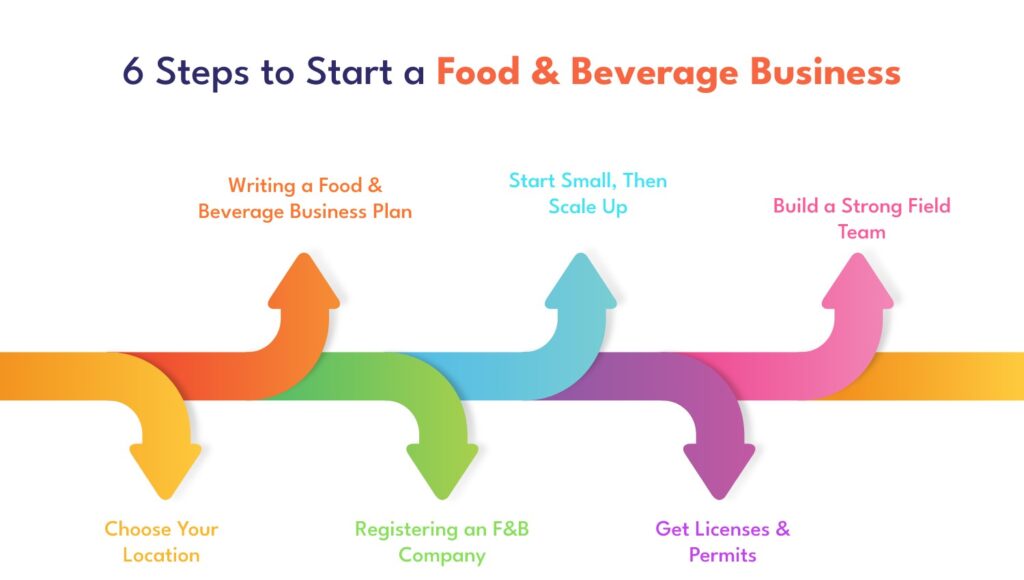
How do you write a business plan for food and beverage?
A well-written business plan for food and beverage is essential for any food and beverage business, whether you’re starting a new restaurant or expanding an existing one.
It will help you clarify your vision, identify potential challenges, and secure funding.
What is a business plan for food and beverage?
A business plan is a written document that outlines your business goals, strategies, and financial projections. It should be clear, concise, and persuasive.
What should be included in a business plan for food and beverage?
Your business plan should include the following sections.
Executive Summary
A brief overview of your business, including your concept, target market, and financial projections.
Company Description
A detailed description of your business, including your mission, values, and competitive advantage.
Market Analysis
An analysis of the food and beverage market, including your target market, competition, and industry trends.
Marketing Plan
How you will reach your target market and promote your business.
Operations Plan
How you will run your business, including your menu, staffing, and logistics.
Financial Projections
Your financial forecasts, including your revenue, expenses, and profit margin.
Management Team
A description of your management team and their experience.
Funding Request
If you are seeking funding, you will need to include a funding request in your business plan.
Tips for writing a business plan for food and beverage
Keep it concise: Your business plan should be no more than 20 pages long.
Use clear and concise language: Avoid using jargon or technical terms.
Focus on the financials: Make sure your financial projections are realistic and well-supported.
Get feedback: Ask friends, family, and mentors to review your business plan before you submit it.
Additional resources
The Small Business Administration (SBA) has several resources for food and beverage businesses, including a sample business plan template.
The SCORE organization provides free mentoring and business advice to entrepreneurs.
Writing a business plan can be a daunting task, but it is essential for any food and beverage business.
Conclusion
By following this guide and tailoring each section to your specific business, you’ll be well on your way to creating a comprehensive business plan for your food and beverage venture.
Remember to keep your plan clear, concise, and reflective of your passion for the culinary experience you aim to provide.
How to use financial modeling to make a social impact?
In this article, we’ll explore how to leverage financial modeling to make a social impact aligning financial strategies with positive change.
Financial modeling, often associated with corporate profits and Wall Street titans, can be a powerful tool for a different kind of ambition: making a social impact.
By harnessing the analytical power of numbers, individuals and organizations can design, evaluate, and scale initiatives that address pressing social and environmental challenges.
Why financial modeling to make a social impact?
Traditional impact assessment methods, while valuable, often lack the precision and clarity needed to attract investors, secure funding, and demonstrate real-world effectiveness.
Financial modeling provides a robust framework to
- Quantify the impact: Translate the qualitative goals of a social initiative into measurable metrics. This could be the number of lives improved, the amount of carbon emissions reduced, or the increase in educational attainment.
- Forecast outcomes: Predict the impact of different interventions and strategies, allowing for informed decision-making and resource allocation.
- Attract and manage funding: Secure grants and investments by demonstrating your social impact project’s financial viability and potential return on investment (ROI).
- Track progress and measure success: Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your initiative over time, allowing for course correction and continuous improvement.

Financial Modeling in Action
Here are some ways financial modeling can be applied to different areas of social impact:
- Microfinance: Modeling can assess the loan repayment capacity of low-income individuals and optimize loan terms to maximize both financial sustainability and social impact.
- Sustainable agriculture: Financial models can predict the economic feasibility of sustainable farming practices and quantify their environmental benefits.
- Education initiatives: Modeling can assess the cost-effectiveness of different educational programs and predict their impact on student outcomes.
- Renewable energy projects: Financial models can evaluate the financial viability of wind farms, solar installations, and other renewable energy projects, attracting investment and accelerating the transition to clean energy.
Building a financial modeling to make a social impact
- Define your goals and impact metrics: Clearly articulate your desired social outcome and identify measurable indicators to track progress.
- Gather relevant data: Collect historical, industry benchmarks, and impact-specific data to inform your model.
- Choose the right model: Select a financial model type (e.g., cost-benefit analysis, discounted cash flow) that aligns with your goals and data availability.
- Make realistic assumptions: Base your model on credible assumptions, acknowledging uncertainties and conducting sensitivity analyses to assess risk.
- Communicate effectively: Present your model in a clear and easy-to-understand manner, highlighting key findings and potential impact.
Beyond the Numbers
While financial modeling is a powerful tool, it’s important to remember that social impact goes beyond numbers.
Building relationships with stakeholders, understanding the local context, and adapting to changing circumstances are crucial for long-term success.
FAQs
How can financial modeling to make a social impact benefit social impact initiatives?
Financial modeling helps organizations plan, allocate resources, and measure the success of social impact projects, ensuring a more strategic and impactful approach.
What challenges do organizations face when implementing financial modeling to make a social impact?
Challenges include limited data availability, complex social dynamics, and external factors beyond an organization’s control. Overcoming these challenges requires adaptive strategies.
Are there specific tools recommended for financial modeling to make a social impact?
Yes, platforms like [Software A] and [Software B] offer features tailored to the unique needs of social impact initiatives, enhancing the efficiency of financial modeling.
How often should organizations update their financial modeling to make a social impact?
Regular updates are crucial to reflect changing circumstances, emerging trends, and evolving community needs.
Conclusion
Financial modeling is not just for Wall Street anymore. Individuals and organizations can create a more just and sustainable world by harnessing its power.
By quantifying the impact of their initiatives, attracting funding, and making informed decisions, social entrepreneurs can turn their passion into measurable change.
So, grab your spreadsheets, roll up your sleeves, and let’s use the language of numbers to speak the language of social good.
How To Create A Financial Model For A Green Tech Startup?
Starting a Financial Model For A Green Tech Startup is not just about innovative ideas and cutting-edge technology; it’s also about ensuring financial sustainability.
In the face of climate change and resource depletion, green tech startups are emerging as powerful solutions.
However, turning these innovative ideas into successful businesses requires a solid financial foundation.
A well-crafted financial model is a crucial tool for green tech startups to attract investors, secure funding, and navigate the path to profitability.
As the world pivots towards sustainable solutions, understanding the nuances of green tech becomes crucial for any startup.
To build a winning Financial Model For A Green Tech Startup
1. Define Your Revenue Model
How will your green tech solution generate revenue? Will it be through product sales, subscriptions, licensing fees, or a combination? Clearly define your revenue streams and forecast future sales based on market research, industry trends, and potential customer adoption.
2. Estimate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Accurately estimate the costs associated with producing and delivering your green tech solution. This includes material costs, manufacturing expenses, and any additional costs specific to your product or service.
3. Project Operating Expenses
Identify and categorize all ongoing expenses associated with running your business, such as salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative costs. Ensure your projections are realistic and account for potential growth in your operations.
4. Consider Capital Expenditures (CAPEX)
If your green tech solution requires significant upfront investments in equipment, technology, or infrastructure, include these costs in your model. Consider depreciation and amortization schedules for these assets.
5. Plan for Financing
Outline your funding strategy, whether it involves bootstrapping, angel investors, venture capital, or other sources. Define the amount of capital required, potential terms of investment, and repayment plans.
6. Build Your Model
Choose a suitable platform like Excel, Google Sheets, or specialized financial modeling software. Organize your model into clear tabs for each financial statement (income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement), and include relevant charts and graphs for visual representation.
7. Incorporate Flexibility
Your model should adapt to changing market conditions and unforeseen circumstances. Include sensitivity analyses to assess the impact of different assumptions on your financial projections.
8. Keep it Simple and Clear
While your model should be comprehensive, avoid unnecessary complexity. Prioritize clarity and transparency to allow investors and stakeholders to understand your financial forecasts and assumptions easily.
9. Regularly Review and Update
As your business evolves, so should your financial model. Regularly review and update your projections to reflect changes in your business plan, market dynamics, and financial performance.
10. Seek Expert Support
Consider seeking guidance from financial professionals or experienced advisors familiar with green tech funding and financial modeling. Our expertise can help refine our model and ensure its accuracy and effectiveness.
By following these steps and incorporating these key components, we can build a robust financial model to attract investors, secure funding, and propel our green tech startup toward a sustainable future. Remember, a well-built financial model is not just a static document; it’s a dynamic tool that allows us to assess our business’s potential, make informed decisions, and ultimately achieve success in the green tech landscape. If you want to know about the components of the financial model.
FAQs
What is the significance of a Financial Model For A Green Tech Startup?
Financial Model For A Green Tech Startup provides a roadmap for sustainable growth, balancing profit with environmental impact.
How can a Financial Model For A Green Tech Startup estimate its environmental impact?
Conduct an environmental impact assessment, calculating factors like carbon footprint and sustainable practices.
Are there specialized financial modeling tools for green tech?
Yes, there are tools designed to cater specifically to the unique needs of the Financial Model For A Green Tech Startup.
How do uncertainties in the green tech industry affect financial modeling?
Uncertainties require a flexible Financial Model For A Green Tech Startup, with contingency plans to adapt to changing circumstances.
Can financial models adapt to changing sustainability practices?
Regular updates and revisions ensure that financial models remain aligned with evolving sustainability practices.
Conclusion
Creating a financial model for a green tech startup is a meticulous yet rewarding process.
It’s not just about numbers; it’s about balancing financial success with environmental responsibility. Remember, a well-crafted financial model is a dynamic tool that evolves with your business.

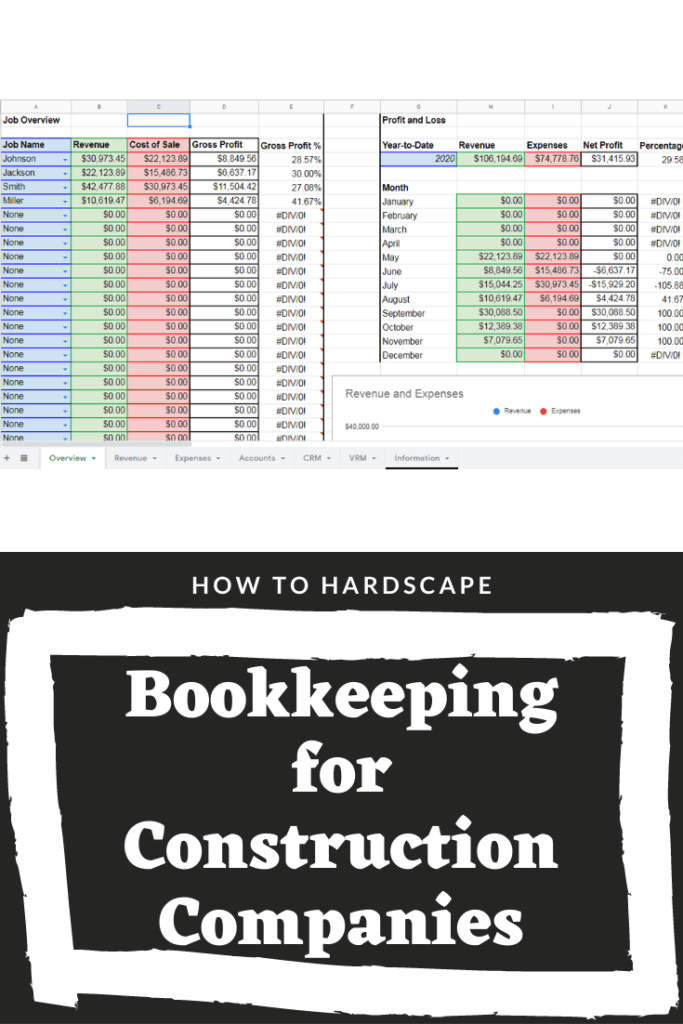
What is Bookkeeping in Construction?
Bookkeeping in Construction refers to the systematic recording, organizing, and managing of financial transactions and records within a construction company. It involves tracking and documenting income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity related to construction projects. By maintaining accurate financial records, construction companies can gain insights into their financial health, profitability, and project performance.
Importance of Bookkeeping in Construction
Effective bookkeeping is essential for construction companies due to the unique nature of the industry. Construction projects involve numerous financial transactions, including material purchases, subcontractor payments, equipment rentals, and labor costs. Proper bookkeeping ensures that all these transactions are recorded accurately, enabling companies to monitor costs, maintain cash flow, and comply with financial regulations.
Key Principles of Construction Bookkeeping
To maintain accurate and reliable financial records, Bookkeeping in Construction follows several key principles:
Accrual Accounting
Accrual accounting is widely used in Bookkeeping in Construction. It recognizes revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. This method provides a more accurate representation of a company’s financial position and performance.
Cost Tracking and Job Costing
Bookkeeping in Construction projects often has multiple cost elements. Effective bookkeeping involves tracking and allocating costs to specific projects or job sites. Job costing enables companies to monitor the profitability of individual projects and make informed decisions.
Separate Accounts for Each Project
To ensure proper project cost tracking and financial clarity, construction companies typically maintain separate accounts for each project. This segregation helps prevent the intermingling of funds and provides a clear overview of project-specific financials.
How do I choose the right bookkeeping software for my construction business?
To establish effective bookkeeping practices in the construction industry, consider the following best practices:
Regular Reconciliation
Perform regular bank reconciliations to ensure that financial records match with bank statements. This practice helps identify discrepancies and ensures accurate financial reporting.
Documenting and Categorizing Expenses
Maintain a well-organized system for documenting and categorizing expenses related to construction projects. This practice enables easy tracking of project costs and simplifies financial analysis.
Retaining Supporting Documentation
Keep all supporting documentation, such as invoices, receipts, and contracts, organized and easily accessible. These documents serve as evidence for transactions and provide necessary backup during audits or disputes.
Implementing Internal Controls
Establish robust internal controls to minimize the risk of fraud or errors. Segregate duties, implement approval processes, and regularly review financial records to maintain integrity and accuracy.
Do you need a bookkeeper for a construction business?
Selecting the appropriate bookkeeping software is vital for efficient construction bookkeeping. Look for software that offers features specifically designed for the construction industry, such as project tracking, job costing, and integration with other construction management systems.
What are the most common bookkeeping challenges faced by the Bookkeeping in Construction Industry?
Bookkeeping in the construction industry comes with its own set of challenges, including:
Tracking Costs Across Multiple Projects
Managing and tracking costs across multiple ongoing projects can be complex. Bookkeeping in Construction must provide accurate and detailed cost tracking to ensure project profitability.
Dealing with Change Orders and Variations
Bookkeeping in Construction projects often experiences change orders and variations that impact costs and revenue. Bookkeeping practices should account for these changes to maintain accurate financial records.
Managing Cash Flow
Cash flow management is critical in construction due to the timing of payments and expenses. Bookkeeping in Construction should focus on monitoring cash flow and ensuring sufficient funds for project operations.
What are the benefits of outsourcing Bookkeeping Services for Construction Companies?
Outsourcing bookkeeping services to specialized professionals can offer several advantages for construction companies, including:
Expertise and Industry Knowledge
Outsourced bookkeepers possess specialized knowledge of Bookkeeping in Construction practices and regulations, ensuring accurate and compliant financial reporting.
Time and Cost Savings
By outsourcing bookkeeping, construction companies can free up valuable time and resources, allowing them to focus on core business activities and reducing overhead costs.
Access to Advanced Technology
Outsourced bookkeeping services often utilize advanced accounting software and tools, providing construction companies with access to the latest technology without significant investments.
What accounting components affect the construction industry’s bookkeeping process?
Construction companies must comply with various financial regulations and reporting requirements. These may include tax obligations, labor regulations, and industry-specific regulations. Adhering to these regulations is essential for avoiding penalties and maintaining the company’s financial reputation.
Monitoring and Analyzing Financial Performance in Construction
Bookkeeping in Construction facilitates monitoring and analyzing financial performance by generating financial reports, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These reports help construction companies assess their profitability, identify areas for improvement, and make informed financial decisions.
Integrating Bookkeeping with Project Management in Construction
Integrating bookkeeping with project management systems enhances efficiency and accuracy in the construction industry. By integrating project data with bookkeeping records, companies can better track costs, manage budgets, and ensure project profitability.
Why is cash flow management important in construction?
Cash flow management is vital for construction companies to ensure uninterrupted project operations. Effective bookkeeping practices help monitor cash inflows and outflows, enabling timely payment of expenses and maximizing revenue generation.
Tax Considerations for Construction Companies
Construction companies must navigate various tax considerations, such as income tax, sales tax, and payroll tax. Adhering to tax regulations, maintaining proper records, and working with tax professionals can help companies optimize their tax positions and minimize potential liabilities.
Bookkeeping Tools and Resources for Construction Professionals
Several bookkeeping tools and resources are available to assist construction professionals in their financial management efforts. These tools offer features like expense tracking, invoicing, and financial reporting, streamlining bookkeeping processes for construction companies.
Key Takeaways and Conclusion
Bookkeeping is a vital aspect of construction management, ensuring accurate financial recording, cost tracking, and compliance with regulations. By implementing sound bookkeeping practices and utilizing appropriate software and resources, construction companies can optimize their financial operations, make informed decisions, and achieve long-term success.
Why is bookkeeping important in the construction industry?
Bookkeeping in Construction is important in the construction industry to track expenses, manage cash flow, and ensure compliance with financial regulations. It helps construction companies maintain accurate financial records and make informed business decisions.
How does bookkeeping benefit construction companies?
Bookkeeping benefits construction companies by providing financial accuracy, cost tracking, and insights into project profitability. It helps companies manage their finances effectively and make informed decisions.
Can construction companies outsource their bookkeeping services?
Yes, construction companies can outsource their bookkeeping services to specialized professionals. Outsourcing offers expertise, cost savings, and access to advanced technology, allowing companies to focus on their core business activities.
What are the key challenges in construction bookkeeping?
Some key challenges in construction bookkeeping include tracking costs across multiple projects, managing change orders and variations, and effectively managing cash flow due to timing differences in payments and expenses.
How does bookkeeping integrate with project management in construction?
Integrating bookkeeping with project management systems enhances efficiency and accuracy in the construction industry. It allows for better cost tracking, budget management, and project profitability analysis.
What are the 4 major components of financial modeling?
Whether you’re a business owner, an investor, or a financial analyst, understanding the four major components of financial modeling is essential for navigating the complex landscape of finance.
Financial modeling is a critical aspect of strategic decision-making for businesses and individuals alike.
In this article, we will delve into the key components of financial modeling that constitute effective financial modeling, providing insights into its purpose, building blocks, challenges, and real-world applications.
Financial modeling is a powerful tool used across various fields, from investment banking and corporate finance to business planning and entrepreneurship.
It allows users to project a company’s financial performance, assess risks, and make informed decisions.
But what are the core elements that make up a robust financial model?
Four major components of financial modeling
1. Income Statement
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a snapshot of a company’s financial health over a specific period.
It summarizes the revenues earned, expenses incurred, and ultimately, the net profit or loss generated. Key components of financial modeling include:
- Revenue: This represents the total income generated from selling goods or services.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This reflects the direct costs associated with producing the goods or services sold.
- Operating Expenses: These are indirect costs incurred in running the business, such as salaries, rent, and utilities.
- Taxes: This includes corporate income taxes and other applicable levies.
- Net Income: This is the final profit or loss after deducting all expenses from the revenue.
2. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet presents a company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
It captures the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity, providing a picture of its financial resources and obligations.
Key components of financial modeling include:
- Assets: This represents the resources owned by the company, including current assets (cash, inventory) and long-term assets (property, equipment).
- Liabilities: These are the company’s financial obligations, including current liabilities (accounts payable, accrued expenses) and long-term liabilities (loans, bonds).
- Shareholders’ Equity: This represents the residual ownership interest of shareholders, calculated by subtracting liabilities from assets.
3. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement details the inflow and outflow of cash within a specific period. It helps assess the company’s liquidity and ability to meet its financial obligations.
Key components of financial modeling include:
- Operating Activities: This includes cash inflows from sales and outflows for expenses related to running the business.
- Investing Activities: This includes cash inflows from selling assets and outflows for purchasing new assets.
- Financing Activities: This includes cash inflows from raising debt or issuing equity and outflows for repaying debt or paying dividends.
4. Debt Schedule
The debt schedule details the company’s outstanding debt obligations, including the principal amount, interest rate, maturity date, and repayment schedule.
It helps understand the company’s financial risk and ability to manage its debt burden.
These four components of financial modeling are dynamically linked and interdependent. Changes in one component can affect the others, highlighting the interconnectedness of a company’s financial health.
By understanding and analyzing these components, financial models provide valuable insights for decision-making, investment analysis, and strategic planning.

FAQs
What is the significance of financial modeling in startups?
Financial modeling is particularly crucial for startups as it helps in forecasting and planning, aiding them in securing funding and making strategic decisions for sustainable growth.
How often should financial models be updated?
Financial models should be updated regularly, especially when there are significant changes in the business environment, to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Can artificial intelligence replace traditional financial modeling?
While AI can enhance financial modeling, it’s unlikely to replace traditional modeling entirely. Human expertise is still essential for interpreting results and making strategic decisions.
What are the common mistakes to avoid in financial modeling?
Common mistakes include overlooking data quality, neglecting to update assumptions, and failing to consider external factors. Rigorous attention to detail is crucial to avoid these pitfalls.
Are there any free resources for learning financial modeling?
Yes, there are several free resources available online, including tutorials, webinars, and open-access courses, making financial modeling accessible to a broader audience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the four major components of financial modeling is crucial for individuals and businesses seeking to make informed decisions.
The evolving landscape of finance demands continuous learning and adaptation to leverage the full potential of financial modeling.
How to write a business plan for a startup?
A business plan for a startup is a roadmap for your startup, outlining your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s an essential tool for attracting investors, securing funding, and keeping your business on track.
key steps to writing a business plan for a startup
1. Identify your target audience
- Who are you trying to reach with your product or service?
- What are their needs and wants?
2. Define your value proposition
- What makes your product or service unique?
- Why should people choose you over your competitors?
3. Conduct market research
- Who are your competitors?
- What are their strengths and weaknesses?
- What is the size of the market?
- What is the growth potential?
4. Develop your marketing and sales strategy
- How will you reach your target audience?
- How will you convert leads into customers?
- What is your pricing strategy?
5. Create your financial projections
- What are your revenue projections?
- What are your cost projections?
- How much funding do you need?
6. Write your executive summary
- This is a brief overview of your business plan.
- It should be concise and compelling.
7. Put it all together
- Your business plan for a startup should be well-organized and easy to read.
- Use visuals like charts and graphs to make your data more digestible.
8. Get feedback
- Share your business plan for a startup with friends, family, and mentors.
- Get their feedback and make sure you’re on the right track.
9. Update your business plan for a startup regularly.
- Your business plan is a living document.
- As your business grows, you must update it to reflect your changing goals and strategies.
Tips
- Keep it concise: Your business plan should be no more than 20-30 pages long.
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid jargon and technical terms.
- Be realistic: Don’t overestimate your revenue or underestimate your costs.
- Be passionate: Your business plan should reflect your enthusiasm for your business.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a well-crafted business plan is the foundation for a successful startup. It attracts investors and serves as a guiding document for internal decision-making. Take the time to create a comprehensive plan that communicates your vision and sets your business on a path to success.
FAQs
Do I need a business plan if I’m not seeking funding?
Yes, a business plan is essential for internal clarity and strategic direction, even if you’re not seeking external funding.
How often should I update my business plan?
Regularly revisit and update your business plan, especially when there are significant changes in your market or business model.
What should I include in the appendix?
Include supporting documents like market research, financial statements, and other relevant data that add depth to your plan.
How can I make my executive summary stand out?
Focus on key differentiators, achievements, and the unique value your startup brings to the market.
Is it necessary to hire a professional to write my business plan?
While professional help can be valuable, many entrepreneurs successfully write their plans using online resources
BEST BOOKKEEPING SOFTWARE
<h3>II. Criteria for evaluating bookkeeping software</h3> <h4>A. User-friendly interface and ease of use</h4> When it comes to choosing the best bookkeeping software for your business, one crucial aspect to consider is the user-friendliness of the interface. A user-friendly interface ensures that you and your team can navigate the software easily and efficiently. Look for software that offers intuitive features, a clean design, and well-organized menus. A clear and logical layout can save you valuable time and minimize the learning curve for you and your staff.
Additionally, consider the ease of use in terms of data input and retrieval. The software should provide a streamlined process for entering financial information, generating reports, and accessing specific data. Features such as drag-and-drop functionality, autofill options, and customizable dashboards can greatly enhance the overall user experience.<h4>B. Features and functionalities</h4> Bookkeeping software should offer a comprehensive set of features and functionalities to effectively manage your financial records. Look for key features such as general ledger management, invoicing and billing, expense tracking, bank reconciliation, and financial reporting. These features will help you track income and expenses, reconcile accounts, and generate reports that provide valuable insights into your business’s financial health.
Furthermore, consider additional features that can streamline your bookkeeping processes. For example, integration with other business tools such as payroll software or CRM systems can facilitate data transfer and reduce manual entry. Automated features like recurring transactions, scheduled reporting, and data backup can save you time and ensure the accuracy and security of your financial data.<h4>C. Integration with other business tools</h4> Efficient bookkeeping often relies on the seamless integration of various business tools. When evaluating bookkeeping software options, consider how well they integrate with other software applications you use, such as payment processors, inventory management systems, or tax software.
Integration capabilities can streamline workflows and minimize duplicate data entry. For example, bookkeeping software that integrates with your e-commerce platform can automatically import sales data and update your financial records. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors associated with manual data entry.
Before making a decision, research the available integrations for each bookkeeping software option you are considering. Check if they offer pre-built integrations or have an open API that allows for custom integrations. The more seamless the integration possibilities, the more efficient and effective your overall business operations will be.<h4>D. Security and data protection</h4> As bookkeeping involves handling sensitive financial information, security and data protection should be top priorities. When evaluating bookkeeping software, consider the security measures in place to protect your data from unauthorized access, loss, or corruption.
Look for software that offers encryption protocols, secure data storage, and regular backups. Additionally, check if the software adheres to industry standards and regulations, such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance for handling credit card information.
Read reviews and testimonials from other users to gauge their experiences with the software’s security features. Pay attention to any incidents or breaches reported and how the software provider responded to them. Remember, robust security measures are crucial to safeguarding your business’s financial data and maintaining the trust of your clients and stakeholders.<h4>E. Pricing and affordability</h4> Pricing is an essential factor to consider when choosing the best bookkeeping software for your business. Take the time to understand the pricing structure of each software option and evaluate it in relation to your budget and needs.
Some software providers offer tiered pricing plans based on the number of users or the level of functionality required. Determine whether the pricing aligns with your business size and growth projections. It’s important to find a balance between affordability and the features and capabilities that are critical for your business
operations.
Consider not only the initial cost but also any additional fees or hidden charges that may be associated with the software. For example, some software providers may charge extra for customer support or for accessing advanced features. Take these factors into account when evaluating the overall affordability of the software.
Furthermore, consider the scalability of the pricing plans. As your business grows, you may need to upgrade to a higher-tier plan or add more users. Ensure that the software offers flexible pricing options that can accommodate your future needs without breaking the bank.
It’s also worth exploring if the software provider offers a free trial or a money-back guarantee. This allows you to test the software firsthand and assess its suitability for your business before making a financial commitment.
What is the SaaS 3 statement financial model?
This article delves into the intricacies of the SaaS 3 statement financial model unraveling its components and illuminating its significance in shaping strategic decisions.
In the dynamic world of Software as a Service (SaaS), financial modeling plays a pivotal role in steering businesses towards success.
Among the array of financial tools, the SaaS 3 statement financial model stands out as a comprehensive framework for evaluating and projecting a SaaS company’s financial health.
The Three Statements Model
The SaaS 3 statement financial model encompasses three fundamental financial statements that collectively portray a holistic picture of a SaaS company’s financial performance:
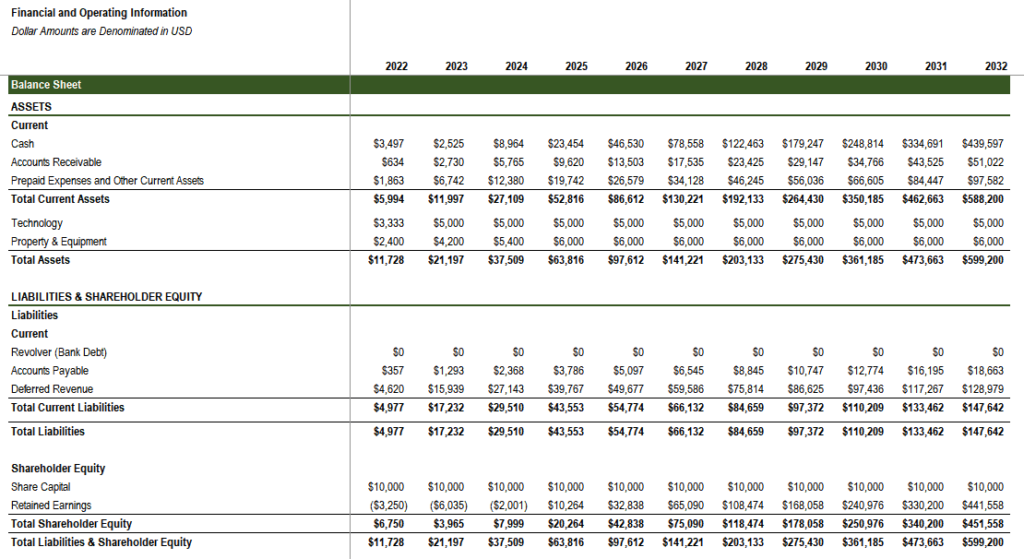
- Income Statement: This statement serves as a scorecard for a company’s operational performance, revealing its ability to generate revenue and manage expenses over a specified period. It depicts the company’s profitability or losses, providing insights into its core business activities.
- Balance Sheet: This statement serves as a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a particular point in time. It captures the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, providing a glimpse into its financial resources and obligations.
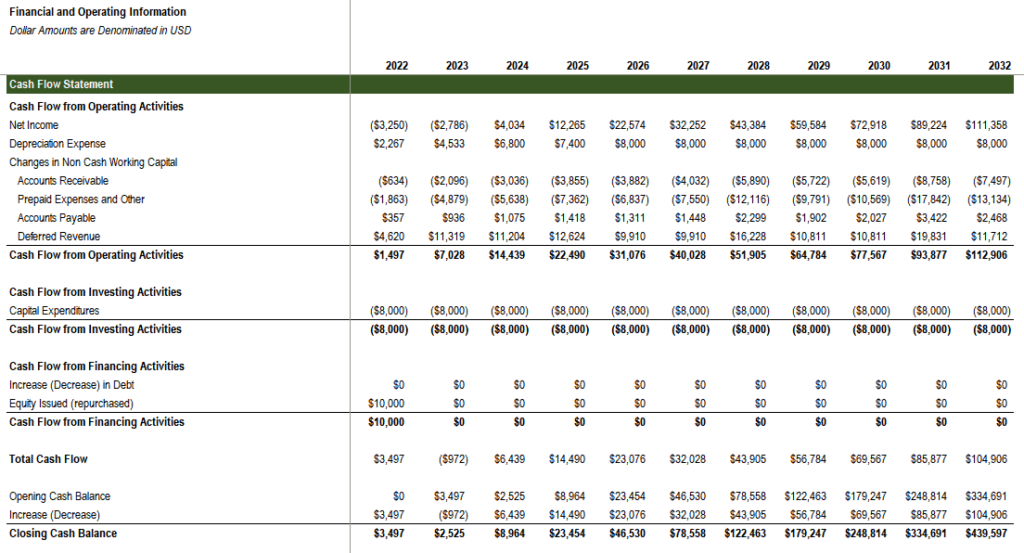
- Cash Flow Statement: This statement bridges the gap between the income and balance sheets, demonstrating how cash flows in and out of the company over a designated period. It tracks the cash movement, highlighting the company’s ability to generate cash from its operations.
Model to the Industry
While the SaaS 3 statement financial model forms a universal framework for financial analysis, SaaS companies face unique characteristics that necessitate adaptations to the model.
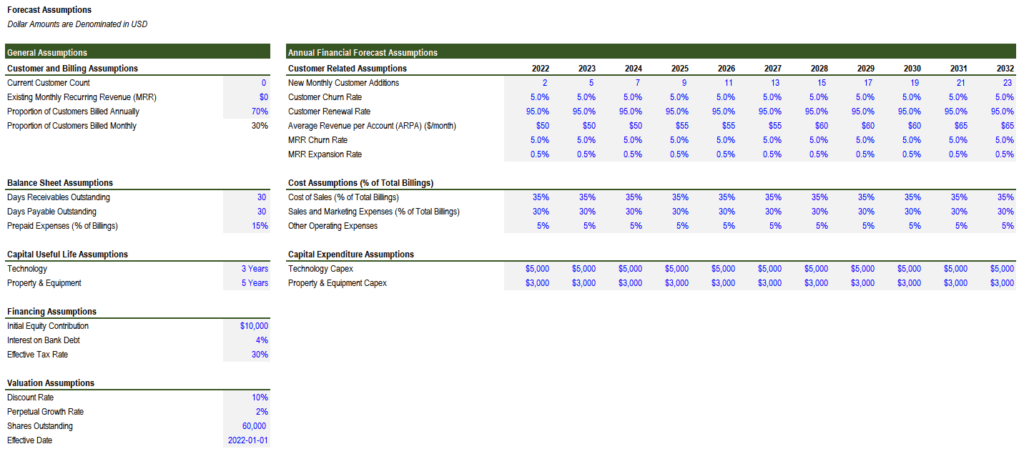
- Recurring Revenue Model: SaaS businesses typically operate on a subscription-based model, earning recurring revenue from customer contracts. This model necessitates adjustments to revenue recognition and subscription metrics.
- Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC): CAC represents the expense of acquiring new customers, a crucial metric for SaaS companies. Incorporating CAC into the model helps assess the effectiveness of customer acquisition strategies.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): CLTV represents the total revenue a company expects to generate from a customer over their lifetime. Modeling CLTV provides insights into customer profitability and retention.
Strategic Decisions for SaaS 3 statement financial model
The SaaS 3 statement financial model serves as an invaluable tool for strategic decision-making, empowering businesses to:
- Project Financial Performance: The model allows businesses to forecast future revenue, expenses, and cash flows, enabling informed financial planning and investment decisions.
- Assess Profitability: By analyzing metrics like gross margin, EBITDA, and net income, businesses can gauge their profitability and identify areas for improvement.
- Evaluate Capital Structure: The model provides insights into the company’s debt and equity financing, aiding in optimizing capital structure and managing financial risks.
- Monitor Financial Health: Continuous monitoring of key financial ratios, such as quick and debt-to-equity ratios, helps identify potential financial issues and promptly take corrective measures.
How do you do financial modeling for a fintech startup?
In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of financial modeling for fintech startups, offering insights and strategies to help you build a solid foundation for your business.
Financial modeling is the backbone of strategic decision-making for any business, and in the dynamic world of fintech startups, it becomes even more critical.
Financial modeling for a fintech startup involves developing a framework to assess the financial viability and potential growth of the business.
It serves as a tool for entrepreneurs to make informed decisions, secure funding, and communicate their plans to investors. Here’s a step-by-step guide to financial modeling for a fintech startup:
1. Define Clear Objectives and Assumptions
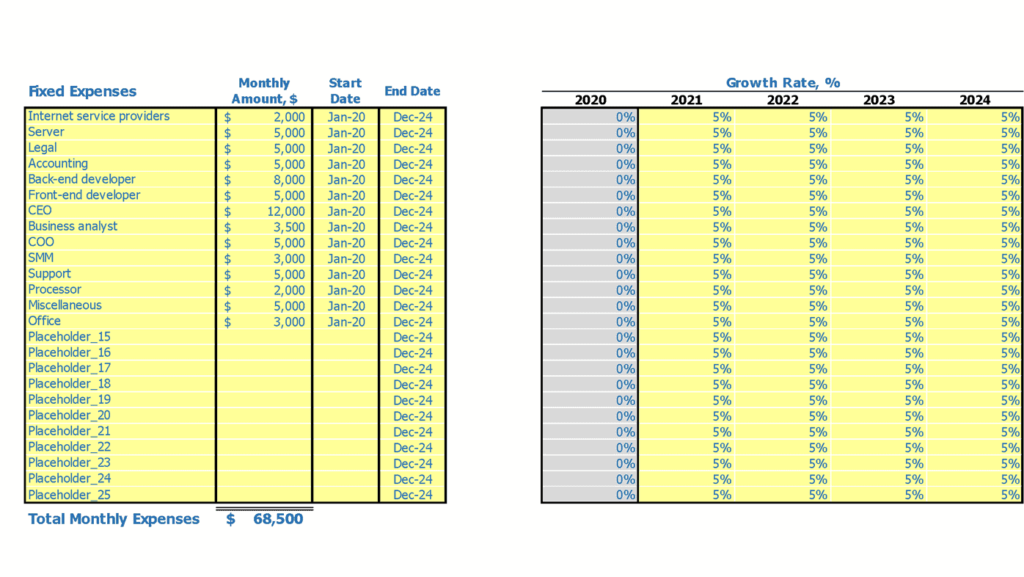
- Objectives: Clearly outline the purpose of the financial model, whether it’s for fundraising, internal planning, or evaluating new business opportunities.
- Assumptions: Identify and document all key assumptions underlying the financial projections, such as market growth rates, customer acquisition costs, and revenue streams.
2. Understand the Fintech Business Model for a Fintech startup
- Revenue Streams: Analyze the various sources of revenue, such as transaction fees, subscription charges, or interest income.
- Cost Structure: Break down the operational expenses, including salaries, marketing costs, technology infrastructure, and regulatory compliance.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Determine the relevant KPIs for the fintech business, such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), and gross margin.
3. Develop Financial Statements
- Income Statement: Project the revenue, expenses, and profit or loss for each period, typically monthly or annually.
- Balance Sheet: Forecast the assets, liabilities, and equity of the company at each financial reporting date.
- Cash Flow Statement: Model the inflows and outflows of cash, including operating cash flow, investing cash flow, and financing cash flow.
4. Sensitivity Analysis and Scenario Planning
- Sensitivity Analysis: Test the impact of changing key assumptions on the financial projections to assess the model’s robustness.
- Scenario Planning: Develop different scenarios, such as optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely, to consider the range of potential outcomes.
5. Visualize and Communicate Findings
- Charts and Graphs: Create clear and concise charts and graphs to present the financial projections and insights.
- Executive Summary: Prepare a concise executive summary that highlights the key financial findings and implications for the business.
6. Continuously Refine and Update
- Regular Review: Regularly review and update the financial model as market conditions, business strategies, or assumptions change.
- Adaptability: Ensure the financial model can adapt to new business lines, products, or partnerships as the fintech startup evolves.
How to do financial modeling for an e-commerce startup?
Financial modeling for an e-commerce startup involves creating a detailed representation of the business’s financial performance, projections, and potential outcomes.
Financial modeling is the process of creating a financial forecast for a company.
This can be done for a variety of purposes, such as raising capital, making investment decisions, or planning for the future.
Financial models are typically created using spreadsheets, such as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets.
To create a financial model for an e-commerce startup, you will need to gather a lot of information about the company, including:
- The company’s products or services
- The company’s target market
- The company’s pricing strategy
- The company’s marketing and sales plan
- The company’s operational costs
- The company’s financial statements
Once you have gathered this information, you can start to build your financial model. The first step is to create a revenue forecast. This will involve estimating how many sales the company will make each year. You will need to consider factors such as the company’s target market, its pricing strategy, and its marketing and sales plan.
The next step is to create an expense forecast. This will involve estimating all of the company’s costs, such as its cost of goods sold, its marketing and sales expenses, and its administrative expenses.
Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC): Estimate the cost of acquiring each customer through marketing and advertising.
Consider various channels such as social media, search engine marketing, and partnerships.
Customer Retention: Project customer churn rates (the rate at which customers stop buying from you).
Consider strategies for customer retention and repeat business.
Once you have created a revenue forecast and an expense forecast, you can create a profit and loss statement. This is a financial statement that summarizes the company’s revenues, expenses, and profit or loss.
Operating Expenses: Identify and estimate fixed and variable operating expenses.
Include costs for marketing, employee salaries, technology, and any other relevant expenses.
The next step is to create a cash flow statement. This is a financial statement that shows how cash flows into and out of the company. This is important for e-commerce startups, as they often need to manage their cash flow carefully.
Funding Requirements: Determine how much funding you’ll need to start and run the business until it becomes profitable.
Consider different funding sources such as equity investment, loans, or grants.
Scenario Analysis: Perform sensitivity analysis and scenario planning to understand how changes in key variables affect your financials.
Consider best-case and worst-case scenarios to assess the business’s resilience.
Use Financial Models and Tools: Leverage spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or financial modeling tools to create detailed financial models.
Utilize templates or build models from scratch, depending on your proficiency.
Investor Presentation: Summarize your financial projections and key assumptions for potential investors.
Clearly communicate your business model, growth strategy, and financial milestones.
Regularly Update the Model: Periodically update your financial model to reflect actual performance and adjust assumptions as needed.
Use real data to refine your projections and improve the accuracy of your financial model.
The final step is to create a balance sheet. This is a financial statement that shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. This is important for e-commerce startups, as it can help them to identify potential financial risks.
Financial modeling is a complex process, and it is important to get professional help if you are not familiar with it.
However, it can be a very valuable tool for e-commerce startups, as it can help them make informed decisions about their finances.
Here are some of the benefits of financial modeling for e-commerce startups:
- It can help you to identify potential financial risks.
- It can help you to make informed decisions about your pricing strategy.
- It can help you to make informed decisions about your marketing and sales plan.
- It can help you to make informed decisions about your staffing levels.
- It can help you to raise capital.
If you are an e-commerce startup, I encourage you to learn more about financial modeling. It can be a very valuable tool for helping you to achieve your business goals.
What are the assumptions of the SaaS financial model?
SaaS financial models are forecasting tools that software companies use to project future financial performance.
They are based on historical business performance, market dynamics, and assumptions about future growth.
These assumptions are crucial for understanding the potential financial viability of a SaaS company and for making informed business decisions.
Here are some of the key assumptions that are typically included in a SaaS financial model:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The amount of money it costs to acquire a new customer. This includes the costs of marketing, sales, and customer support.
- Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): The total amount of revenue that a customer is expected to generate over their lifetime. This is typically calculated based on the average monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and the average customer churn rate.
- Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions in a given period. This is a critical metric for SaaS companies, as it directly impacts their revenue and profitability.
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): MRR is the predictable and recurring revenue generated by subscriptions on a monthly basis. It assumes that customers will continue to pay their subscriptions regularly.
- Gross Margin: The percentage of revenue that remains after the direct costs of goods sold (COGS) have been subtracted. This metric is an indicator of the company’s ability to generate profit from its products or services.
- Average Revenue Per User (ARPU): ARPU is the average revenue generated per user or customer. It’s important to estimate how much revenue, on average, each customer contributes to the overall business.
- Expansion Revenue: This represents additional revenue generated from existing customers through upselling or cross-selling. SaaS models often assume a certain level of expansion revenue as the customer base grows.
- Sales and Marketing Expenses: Assumptions about the growth of the customer base often involve projections about sales and marketing expenses. This includes advertising, sales team salaries, and other promotional costs.
- Operating Expenses: The costs of running the business, such as salaries, rent, and utilities. These expenses are typically expressed as a percentage of revenue.
- Cash Flow: Assumptions about the timing of cash inflows and outflows are important for understanding the cash flow dynamics of the business. This includes considerations such as payment terms with customers and vendors.
- Investment: The amount of money that the company is planning to invest in growth, such as new product development or marketing.
- Financing: The sources of funding that the company is planning to use, such as venture capital or debt.
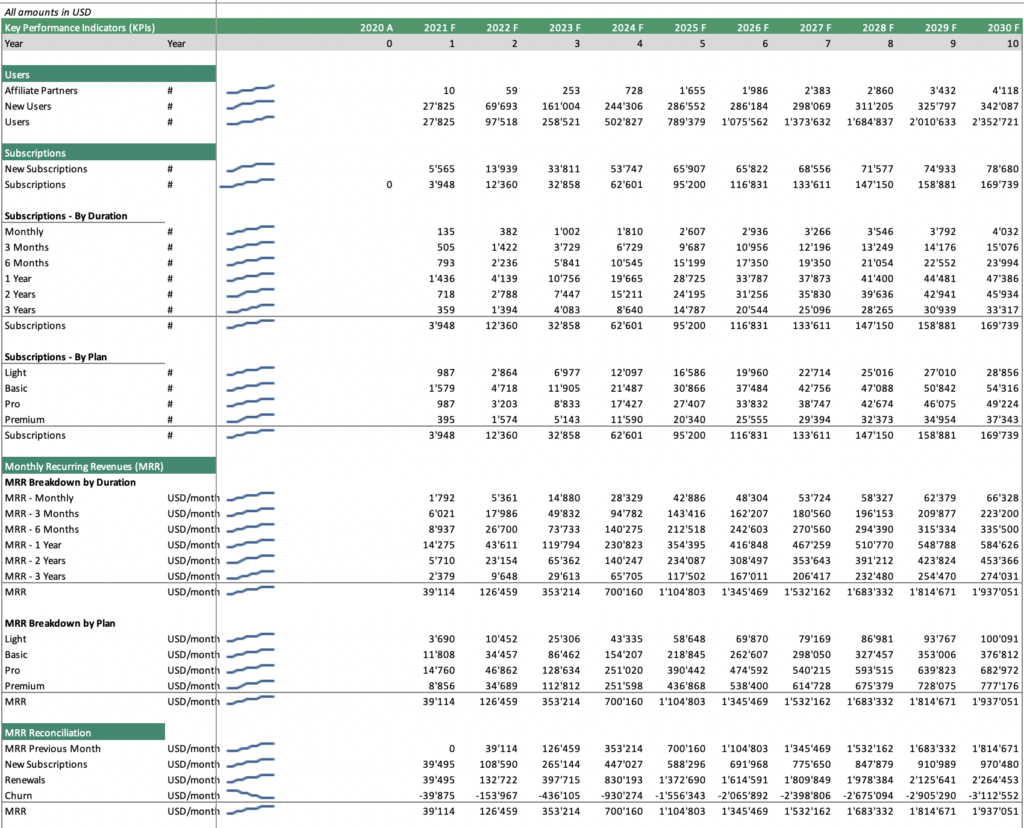
The specific assumptions that are used in a SaaS financial model will vary depending on the company and its industry.
It is important to note that the assumptions in a SaaS financial model are just that – assumptions.
They are based on the best available information, but they are not guarantees of future performance.
Actual results may vary depending on a number of factors, including changes in market conditions, competition, and customer behavior.
SaaS financial model companies should regularly review and update their SaaS financial model to reflect changes in their business and in the market.
This will help them to make more informed decisions about their business strategy and to stay on track to achieve their financial goals.
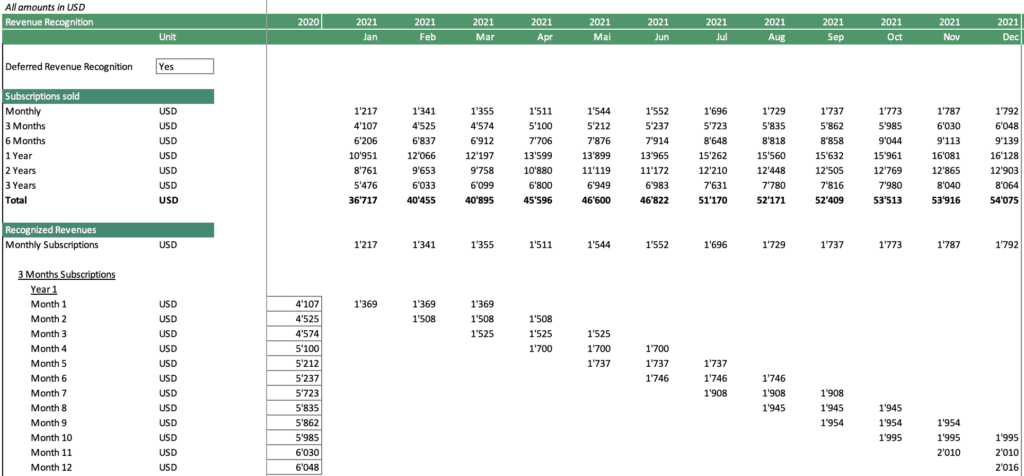

How much does a bookkeeper cost?
we will explore various factors that affect bookkeeper costs and provide insights into average prices to help you make an informed decision. When running a business, keeping track of your financial records is essential for maintaining transparency and making informed decisions. Bookkeeping, the process of recording financial transactions, plays a crucial role in managing the financial health of a company. However, many business owners wonder about the cost of hiring a bookkeeper.

What is bookkeeping?
Bookkeeping involves recording, organizing, and maintaining the financial transactions of a business. It includes tasks such as recording sales and expenses, managing payroll, reconciling bank statements, and preparing financial statements. Accurate bookkeeping ensures compliance with tax regulations, facilitates budgeting, and provides insights into the financial performance of a company.
What is the importance of bookkeeping?
Proper bookkeeping is vital for both small and large businesses. It provides a clear picture of a company’s financial health, helps in identifying areas for improvement, and enables timely decision-making. Bookkeeping also simplifies tax filing and ensures compliance with legal requirements.
What factors affect the bookkeeper cost services?
Several factors influence the cost of hiring a bookkeeper. Understanding these factors will help you estimate the expenses involved and find a bookkeeper that suits your budget and requirements.

Experience and Expertise
The experience and expertise of a bookkeeper significantly impact the cost. Bookkeepers with extensive experience and advanced certifications might charge higher rates due to their specialized skills and knowledge. However, their expertise can bring added value to your business by providing accurate financial insights and helping you navigate complex financial matters.
Geographic Location
The geographic location of your business can affect bookkeeper costs. In areas with a higher cost of living, bookkeepers might charge higher rates to cover their expenses. It’s important to consider the local market rates while budgeting for bookkeeping services.
Type of Business
The size and complexity of your business influence bookkeeper costs. If your business has unique accounting requirements or operates in a specialized industry, you might require a bookkeeper with specific expertise. These specialized bookkeepers may charge higher fees due to the additional knowledge and skills they bring to the table.
Hourly Rates vs. Flat Fees
bookkeeper cost either an hourly rate or a flat fee for their services. The charging method depends on various factors, such as the complexity of the work and the agreement between the bookkeeper and the client.
Hourly rates are based on the time spent on bookkeeping tasks. They can vary depending on the bookkeeper’s experience, geographic location, and the nature of the work involved. On the other hand, some bookkeepers offer flat fees for specific bookkeeping services or a monthly fee that covers a predetermined set of tasks.
Both charging methods have their pros and cons. Hourly rates provide flexibility, especially if you have fluctuating bookkeeping needs. Flat fees, on the other hand, offer predictability and can be advantageous if you have a clear understanding of your ongoing bookkeeping requirements.
Average Bookkeeper Costs
The costs of hiring a bookkeeper can vary depending on the size and complexity of your business. Here are the average bookkeeping costs based on the business size:
Small Business bookkeeper cost
For small businesses with limited transactions, bookkeeper cost typically range from $100 to $500 per month. The fees may include basic bookkeeping tasks such as recording transactions, reconciling bank statements, and preparing financial statements.

Medium-Sized Business bookkeeper cost
Medium-sized businesses with more transactions and complex financial needs may expect to pay between $500 and $2,000 per month for bookkeeping services. These costs cover tasks such as managing accounts payable and receivable, payroll processing, and generating financial reports.
Large Business bookkeeper cost
Large businesses with high transaction volumes and intricate financial operations can expect to pay $2,000 or more per month for bookkeeping services. The fees for large businesses include comprehensive financial management, financial analysis, and advanced reporting.
Additional Bookkeeping Expenses
In addition to the bookkeeper cost there may be additional expenses related to bookkeeping services. These can include software subscriptions, third-party integrations, and other tools necessary for efficient bookkeeping. It’s essential to consider these additional costs while budgeting for bookkeeping services.
How to Find a Bookkeeper?
Finding a reliable and skilled bookkeeper is crucial for your business’s financial well-being. Here are some tips to help you find a suitable bookkeeper:
Seek recommendations from other business owners or professionals in your industry.
Use online platforms and directories that connect businesses with bookkeepers.
Consider the bookkeeper’s experience, certifications, and industry knowledge.
Review testimonials or ask for references from previous clients.
Conduct interviews to assess their compatibility with your business and their understanding of your industry.
Tips for Reducing bookkeeper cost
While bookkeeping is a necessary investment, there are ways to manage and reduce costs. Here are some tips to help you minimize bookkeeping expenses:
Maintain organized records to streamline the bookkeeping process.
Utilize bookkeeping software to automate repetitive tasks and improve efficiency.
Regularly reconcile bank statements to identify errors or discrepancies promptly.
Provide accurate and complete information to your bookkeeper to avoid any rework or delays.
Review your bookkeeping needs periodically to ensure you are not overpaying for unnecessary services.
How much should I pay a bookkeeper per hour?
The hourly rate you should pay a bookkeeper depends on several factors, including their experience, location, and the complexity of the work involved. On average, bookkeepers’ hourly rates can range from $20 to $100 or more. For bookkeepers with less experience or in lower-cost areas, you may find hourly rates closer to the lower end of the range. On the other hand, highly experienced bookkeepers or those in high-cost areas may charge higher rates.
It’s important to consider the value and expertise that a bookkeeper brings to your business. While you may be tempted to opt for the lowest hourly rate, it’s essential to strike a balance between cost and quality. Hiring a skilled bookkeeper who can provide accurate financial records, valuable insights, and assist with complex financial matters can greatly benefit your business in the long run.
How much does a bookkeeper cost per month?
The monthly cost of hiring a bookkeeper for a small business can vary depending on several factors, including the complexity of your business’s financial transactions and the scope of services required. Here are some average estimates: For small businesses with basic bookkeeping needs and a low volume of transactions, the monthly cost can range from $100 to $500.
Small businesses with moderate transaction volumes and additional bookkeeping requirements, such as payroll processing or financial statement preparation, can expect to pay between $500 and $1,500 per month. If your small business has a high volume of transactions, complex financial operations, or specialized industry requirements, the monthly cost for bookkeeping services can exceed $1,500.
It’s important to note that these figures are general estimates, and actual costs can vary based on factors such as the bookkeeper’s experience, geographic location, and the specific needs of your business.

Small business bookkeeper cost per week?
The weekly cost of hiring a bookkeeper for a small business depends on various factors, including the number of hours worked per week and the bookkeeper’s hourly rate. Here’s a general guideline:
Determine the number of hours you require the bookkeeper to work per week. Let’s assume it’s 10 hours.
Research the average hourly rate for bookkeepers in your area. Let’s say the average rate is $40 per hour.
Multiply the number of hours (10) by the hourly rate ($40): 10 hours x $40 = $400
Based on this calculation, the estimated weekly cost for a small business bookkeeper would be $400.
Keep in mind that this is a rough estimate, and actual rates may vary depending on factors such as the bookkeeper’s experience, your geographic location, and the complexity of the bookkeeping tasks involved.
Small business bookkeeper cost per year?
To determine the annual cost of hiring a bookkeeper for a small business, you need to consider factors such as the number of hours worked per week, the bookkeeper’s hourly rate, and any additional services required. Here’s a general approach:
Calculate the weekly cost based on the number of hours worked per week and the bookkeeper’s hourly rate. For example, if the bookkeeper works 10 hours per week at an hourly rate of $40, the weekly cost would be $400 (10 hours x $40).
Multiply the weekly cost by the number of weeks in a year. Assuming a standard 52-week year, the calculation would be $400 x 52 = $20,800.
Based on this calculation, the estimated annual cost for a small business bookkeeper would be $20,800.

How to Find Clients As a Financial Advisor?
As a financial advisor, finding clients is essential for growing your practice and achieving success in the industry. In today’s competitive landscape, it’s crucial to employ effective strategies to attract and retain clients. This article will guide you through various methods and techniques to help you find and connect with potential clients.

What are the duties and responsibilities of a financial advisor?
To effectively find clients, it’s crucial to understand the role of a financial advisor. This section will provide an overview of the responsibilities and services offered by financial advisors, emphasizing the value they bring to clients’ financial well-being.
Providing Financial Guidance and Advice
Assessing Clients’ Financial Goals
Creating Personalized Financial Plans
Managing Investments and Assets
Analyzing Risk Tolerance
Diversifying Investment Portfolios
How do I find a target audience?
Identifying your target audience is essential for tailoring your marketing efforts and finding clients who will benefit most from your services. In this section, we will discuss the importance of defining your target audience and how to identify them effectively.
How to build a successful online presence?
In today’s digital age, having a strong online presence is crucial for attracting potential clients. This section will explore various strategies to build and optimize your online presence, including developing a professional website, utilizing search engine optimization (SEO) techniques, and creating engaging content.
What is a customer referral network?
Networking and referrals are powerful tools for finding clients as a financial advisor. This section will provide tips on building and nurturing professional relationships, leveraging existing networks, and encouraging referrals from satisfied clients and business partners.
How to leverage social media to grow your business?
Leveraging social media can be a powerful strategy to grow a company’s online presence, reach a wider audience, and build brand awareness. Here are some steps you can take to effectively leverage social media for company growth:
Set clear goals: Determine what you want to achieve through social media. It could be increasing website traffic, generating leads, building brand awareness, or engaging with customers. Clear goals will help you focus your efforts and measure success.
Understand your target audience: Identify your target audience’s demographics, interests, and online behavior. This information will guide your content strategy and help you tailor your messages to resonate with your audience.
Choose the right platforms: Select social media platforms that align with your target audience and business objectives. Popular platforms include Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and YouTube. Each platform has its own strengths and user base, so choose the ones that best suit your company’s goals.
Develop a content strategy: Create a content plan that aligns with your goals and resonates with your audience. Your content should be valuable, informative, and engaging. Mix different types of content such as articles, videos, infographics, images, and user-generated content to keep your feed interesting.
Consistency and frequency: Regularly post content to maintain a consistent presence on social media. Develop a posting schedule that suits each platform, taking into account the optimal posting times for your target audience. Aim for a balance between quality and frequency.
Engage with your audience: Actively engage with your followers by responding to comments, messages, and mentions. Encourage discussions, ask questions, and respond to feedback. Building meaningful connections with your audience helps foster loyalty and encourages word-of-mouth marketing.
Utilize visual content: Visual content tends to perform better on social media. Incorporate eye-catching images, videos, and graphics into your posts to increase engagement and shareability. Experiment with different formats and styles to discover what resonates with your audience.
Utilize hashtags and keywords: Research and use relevant hashtags and keywords in your posts to increase discoverability. Hashtags can help your content reach a wider audience and improve visibility.
Collaborate with influencers: Identify influencers or industry experts who align with your brand and target audience. Collaborating with influencers can help amplify your reach and credibility. Consider partnerships, sponsored content, or influencer takeovers to leverage their existing following.
Monitor and analyze performance: Regularly monitor your social media metrics using analytics tools provided by each platform or third-party tools. Track engagement, reach, click-through rates, conversions, and other relevant metrics. Use this data to refine your strategy and optimize future campaigns.

What is the best way to develop a content marketing strategy?
Content marketing is a strategic approach that focuses on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a target audience. Here are some effective content marketing strategies to consider:
Define your target audience: Understand your audience’s demographics, interests, pain points, and preferences. This will help you create content that resonates with them and addresses their specific needs.
Set clear goals: Determine what you want to achieve with your content marketing efforts. Common goals include brand awareness, lead generation, customer engagement, thought leadership, and driving sales. Clear goals will guide your content creation and help measure success.
Develop a content strategy: Create a plan that outlines the types of content you will produce, the topics you will cover, and the channels you will use to distribute your content. Consider using a mix of formats, such as blog posts, videos, infographics, podcasts, and social media posts, to cater to different audience preferences.
Create high-quality, valuable content: Focus on creating content that provides value to your target audience. This could be educational, informative, entertaining, or inspiring content. Ensure your content is well-researched, well-written, and addresses your audience’s pain points or interests.
Optimize content for SEO: Implement search engine optimization (SEO) techniques to make your content more discoverable by search engines. Use relevant keywords, optimize meta tags, headers, and URLs, and ensure your content is well-structured. This will improve your search engine rankings and increase organic traffic.
Leverage different content distribution channels: Identify the channels where your target audience is most active and distribute your content accordingly. This can include your website or blog, social media platforms, email newsletters, industry publications, guest blogging, and more. Adapt your content to suit each channel and engage with your audience.
Encourage audience engagement: Prompt your audience to engage with your content by including clear calls-to-action (CTAs) that encourage comments, shares, likes, or subscriptions. Respond to comments and messages promptly, and foster discussions to build a community around your content.
Repurpose and promote content: Repurpose your existing content into different formats to reach a wider audience. For example, turn a blog post into a video or create an infographic summarizing key points. Also, actively promote your content through social media, email marketing, influencer collaborations, and partnerships to increase its reach.
Measure and analyze performance: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the effectiveness of your content marketing efforts. Monitor metrics such as website traffic, engagement rates, conversion rates, social media reach, and lead generation. Use this data to refine your strategy, identify successful tactics, and optimize future content.
Stay updated and adapt: Keep up with industry trends, changes in audience preferences, and emerging technologies. Experiment with new content formats, platforms, and distribution channels to stay relevant and maintain a competitive edge.

What are the benefits of attending industry events?
Attending industry events can offer a range of benefits for individuals and businesses. Here are some key advantages of attending industry events:
Networking opportunities: Industry events bring together professionals, experts, and thought leaders from the same field or industry. Attending these events provides valuable networking opportunities to meet and connect with like-minded individuals, potential clients, partners, suppliers, and industry influencers. Building relationships through networking can lead to collaborations, business opportunities, and access to new resources.
Knowledge and education: Industry events often feature keynote speakers, panel discussions, workshops, and presentations by experts in the field. These sessions offer insights into the latest trends, innovations, best practices, and challenges within the industry. Attending these events can enhance your knowledge, keep you up-to-date with industry developments, and provide valuable learning opportunities.
Access to industry insights: Industry events often provide a platform for industry leaders to share their experiences, case studies, and success stories. By attending these events, you gain access to firsthand insights and insider information that can help you gain a competitive edge, improve your business strategies, and make informed decisions.
Brand exposure and visibility: Attending industry events offers opportunities to increase your brand’s visibility and raise awareness among a relevant audience. By participating in conferences, trade shows, or exhibitions, you can showcase your products, services, or expertise to potential customers, partners, and investors. This exposure can lead to increased brand recognition, credibility, and potential business leads.
Professional development and career advancement: Industry events can contribute to your professional development and career growth. The knowledge gained, connections made, and insights acquired at these events can expand your skill set, enhance your industry knowledge, and help you stay competitive in the job market. Additionally, attending events can demonstrate your commitment to professional growth and open doors to new career opportunities.
Market research and competitive analysis: Industry events provide an opportunity to gather valuable market insights and conduct competitive analysis. By observing competitors, listening to industry discussions, and exploring new products or services showcased at the event, you can gain a better understanding of the market landscape, identify emerging trends, and assess your competitive position.
Inspiration and motivation: Industry events often feature success stories, motivational speakers, and thought-provoking discussions. These can inspire and motivate attendees by showcasing what is possible within the industry and providing fresh perspectives. Attending events can reignite your passion for your work, spark creativity, and inspire you to take action.
Peer validation and industry recognition: Being present at industry events demonstrates your commitment to your field and positions you as an active participant within the industry. It can enhance your professional reputation, gain recognition from peers and industry stakeholders, and contribute to your personal and professional brand.

How do you collaborate with your team more effectively?
Collaborating with professionals is an excellent way to enhance your skills, learn from experts, and achieve mutual goals. Whether you’re working on a project, seeking mentorship, or building professional relationships, here are some steps to effectively collaborate with professionals:
Identify your objectives: Determine the purpose and goals of your collaboration. Clarify what you hope to achieve by working with professionals and how it aligns with your own aspirations.
Research and identify professionals: Conduct thorough research to identify professionals in your field of interest or those who possess the expertise you require. Look for individuals who have a track record of success and can contribute meaningfully to your collaboration.
Establish a connection: Once you’ve identified potential professionals, reach out to them to establish a connection. This could be done through email, social media platforms, or networking events. Craft a well-written and personalized message introducing yourself, explaining your objectives, and expressing your interest in collaborating with them.
Demonstrate your value: Professionals are more likely to collaborate if they see value in the partnership. Highlight your skills, experiences, and achievements that can contribute to the collaboration. Clearly articulate what you bring to the table and how your involvement can benefit both parties.
Offer mutual benefits: Collaboration should be a mutually beneficial endeavor. Clearly communicate how the professional can benefit from the collaboration. This could include sharing your network, resources, and expertise, or assisting with their projects. Show that you’re committed to a win-win situation.
Communicate effectively: Good communication is crucial for successful collaboration. Clearly express your expectations, responsibilities, and timelines. Be responsive to their messages and requests, and keep them updated on your progress. Regularly communicate and address any issues or concerns that arise during the collaboration.
Respect their expertise and opinions: Remember that professionals have valuable knowledge and experience. Respect their expertise and be open to their ideas and suggestions. Engage in meaningful discussions and be willing to learn from their insights. Collaboration should be a two-way street.
Set clear goals and deadlines: Establish clear goals and set realistic deadlines for collaboration. This helps ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards a common objective. Regularly assess progress and make adjustments as necessary to stay on track.
Foster a positive working environment: Create a positive and supportive working environment. Encourage open communication, provide constructive feedback, and appreciate the contributions of each team member. Celebrate milestones and achievements along the way to maintain motivation and morale.
Reflect and learn: After the collaboration concludes, take the time to reflect on the experience. Assess what went well, what could have been improved, and the lessons learned. Use this knowledge to enhance future collaborations and build stronger professional relationships.
What is exceptional customer service?
Delivering exceptional client service is crucial for client retention and generating referrals. This section will explore strategies for providing excellent client service, including active listening, effective communication, and personalized attention.
What are the best practices for using testimonials and case studies as referral content?
Testimonials and case studies are powerful tools for building trust, establishing credibility, and attracting new clients or customers. When using them as referral content, it’s essential to follow some best practices to maximize their impact. Here are some guidelines to consider:
Choose compelling and relevant testimonials: Select testimonials that highlight specific benefits or positive experiences your clients or customers have had with your product, service, or expertise. Focus on
Use specific and measurable results: Testimonials and case studies that include quantifiable results are more impactful. Whenever possible, highlight specific metrics, such as increased revenue, cost savings, improved efficiency, or customer satisfaction ratings. Tangible results provide evidence of your effectiveness.
Feature credible and recognizable sources: If possible, include testimonials from well-known or respected individuals or companies within your industry. Their endorsement can significantly enhance your credibility and attract attention from potential clients or customers.
Incorporate multimedia elements: Utilize various formats to present testimonials and case studies. Along with written testimonials, consider using audio or video testimonials to add a personal touch. For case studies, include visuals, charts, or graphs to illustrate key points or data.
Display testimonials prominently: Showcase testimonials and case studies prominently on your website, marketing materials, and social media platforms. Make them easily accessible and visible to your target audience. Consider featuring rotating or random testimonials to showcase a variety of positive experiences.
Segment testimonials by use case or industry: If applicable, categorize testimonials and case studies based on different use cases or industries. This allows potential clients or customers to find specific examples that closely match their own situation, making the content more relevant and relatable.
Keep testimonials and case studies up to date: Regularly review and update your testimonials and case studies to ensure they remain current and relevant. Outdated content may diminish its impact and credibility.
Encourage genuine testimonials: Foster a positive customer or client experience to increase the likelihood of receiving authentic and positive testimonials. Provide excellent customer service, solicit feedback, and engage with your clients or customers to build strong relationships.
What is a sample letter to offer services?
An offering services letter is a written communication that a company or individual uses to propose or introduce their services to potential clients or customers. It serves as a formal way to showcase the services offered, their benefits, and how they can meet the needs of the recipient.
Here are some key elements typically included in an offering services letter:
Sender’s information: Begin the letter by providing your company’s or individual’s name, address, contact information, and any relevant credentials or qualifications.
Date and recipient’s information: Include the current date and the name, title, and contact details of the person or organization you are addressing the letter to.
Introduction and purpose: Start with a concise and engaging introduction that captures the reader’s attention. Clearly state the purpose of the letter, which is to offer your services and explain why you believe they would benefit the recipient.
Description of services: Provide a detailed description of the services you offer. Highlight their features, advantages, and unique selling points that differentiate you from competitors. Be specific about the scope of your services and how they address the recipient’s needs or challenges.
Benefits and value proposition: Emphasize the benefits the recipient will gain from utilizing your services. Explain how your expertise, experience, or specific skills can provide value, solve problems, or improve their business operations.
Testimonials or case studies: If available, include testimonials or case studies from satisfied clients or customers to reinforce your claims and build credibility. Briefly describe successful projects or positive outcomes achieved through your services.
Pricing and terms: Provide clear and transparent information about pricing, payment terms, and any other relevant terms and conditions. If applicable, offer different service packages or options to accommodate the recipient’s needs and budget.
Call to action: Encourage the recipient to take the next step by including a strong and compelling call to action. This could be inviting them to schedule a consultation, request a proposal, or contact you for further information.
Contact information: Reiterate your contact details, including phone numbers, email addresses, and website links, making it easy for the recipient to reach out to you with any inquiries or to proceed with engaging your services.
Closing: Conclude the letter with a courteous and professional closing, such as “Sincerely” or “Best regards,” followed by your name, title, and signature (if sending a physical letter).
Attachments: If applicable, mention any additional documents or materials attached to the letter, such as brochures, service catalogs, or a portfolio of past work.
What are the benefits of Continuing Professional Development?
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) refers to the ongoing process of acquiring and enhancing knowledge, skills, and competencies to maintain and improve professional capabilities throughout one’s career. It involves actively engaging in learning activities, training programs, workshops, conferences, and other developmental opportunities to stay up-to-date with industry trends, best practices, and advancements in one’s field. The primary purpose of CPD is to ensure that professionals continue to develop and adapt their knowledge and skills to meet the changing demands of their profession. It enables individuals to enhance their expertise, remain competitive, and deliver high-quality services to clients, customers, or organizations.
Here are some key aspects and benefits of Continuing Professional Development:
Lifelong learning: CPD encourages professionals to adopt a mindset of lifelong learning, recognizing that knowledge and skills need to be continually updated and expanded to stay relevant in today’s dynamic and evolving work environments.
Knowledge expansion: CPD provides opportunities to broaden and deepen one’s understanding of their field, industry trends, emerging technologies, research findings, and best practices. It helps professionals stay current with the latest developments and advancements.
Skill development: CPD focuses on developing and refining specific skills and competencies necessary for professional growth. This may include technical skills, communication skills, leadership skills, project management skills, or any other relevant skills required in the profession.
Career advancement: Engaging in CPD activities demonstrates a commitment to professional growth and can enhance career prospects. Employers and clients often value professionals who actively invest in their development and can demonstrate up-to-date knowledge and expertise.
Networking and collaboration: CPD opportunities, such as conferences, workshops, and industry events, facilitate networking and collaboration with peers, experts, and industry leaders. Building professional relationships can lead to valuable connections, shared knowledge, and potential career opportunities.
Professional recognition: Some professions or industries require professionals to accumulate a certain number of CPD hours or credits to maintain their professional licenses or certifications. Participating in CPD activities ensures compliance with regulatory or licensing requirements.
Personal satisfaction: CPD allows professionals to pursue their interests, passions, and areas of specialization within their field. It can lead to personal fulfillment, increased job satisfaction, and a sense of professional achievement.
Continuous improvement: CPD fosters a mindset of continuous improvement, encouraging professionals to critically reflect on their practice, identify areas for growth, and actively seek opportunities to enhance their performance and deliver better outcomes.
How to build trust and credibility as a leader?
Building trust and credibility as a leader is essential for fostering strong relationships, inspiring others, and achieving organizational success. Here are some strategies to help you build trust and credibility:
Lead by example: Demonstrate integrity and ethical behavior in all aspects of your work. Consistently uphold your values and principles, and align your actions with your words. Be honest, transparent, and reliable in your interactions with others.
Communicate effectively: Establish open and honest communication channels with your team members. Clearly and consistently communicate your expectations, goals, and objectives. Listen actively to their ideas, concerns, and feedback. Provide regular updates and ensure that information flows freely within the organization.
Empower and delegate: Trust your team members and empower them to take ownership of their work. Delegate responsibilities and provide them with the necessary resources, support, and autonomy to accomplish their tasks. Encourage their professional growth and development.
Build relationships: Invest time and effort in building positive relationships with your team members. Show genuine interest in their well-being, goals, and aspirations. Be approachable, supportive, and empathetic. Foster a culture of collaboration, respect, and inclusivity.
Be accountable: Take responsibility for your actions and decisions. Admit mistakes and learn from them. Hold yourself and others accountable for meeting goals and delivering results. Take ownership of failures and share credit for successes.
Seek input and involve others: Encourage participation and input from your team members. Value their opinions and perspectives. Involve them in decision-making processes whenever appropriate. This inclusiveness creates a sense of ownership and commitment.
Demonstrate competence: Continuously develop your knowledge, skills, and expertise in your field. Stay informed about industry trends, best practices, and emerging technologies. Share your expertise with others and actively contribute to the professional growth of your team members.
Maintain confidentiality: Respect and protect sensitive information shared with you. Honor confidentiality commitments and handle confidential information with utmost care. This demonstrates your trustworthiness and reliability.
Be consistent: Consistency in your behavior, decision-making, and communication builds trust. Avoid favoritism or playing favorites within your team. Treat all team members fairly and equally, based on merit and performance.
Learn and grow: Be open to feedback and self-reflection. Continuously seek opportunities for self-improvement and growth. Actively solicit feedback from your team members, superiors, and peers. Use constructive feedback to enhance your leadership skills and address any areas of improvement.
Deliver on promises: Follow through on your commitments and promises. Be reliable and deliver results. This builds trust and confidence in your ability to lead and execute.
How long does it take to find clients as a financial advisor?
Finding clients can vary depending on various factors such as your target audience, marketing efforts, and networking skills. It can take several months to build a client base, but consistent effort and effective strategies can expedite the process.
Should financial advisors specialize in a specific area?
Specializing in a specific niche or industry can help you stand out from the competition and attract clients who require expertise in that particular area. However, it’s not mandatory, and generalist financial advisors can also find success by offering a wide range of services.
How important is networking for finding clients?
Networking plays a significant role in finding clients as a financial advisor. Building and maintaining professional relationships can lead to referrals, partnerships, and opportunities for business growth. It’s crucial to actively engage in networking activities to expand your client base.
What are the key qualities of a successful financial advisor?
Successful financial advisors possess strong interpersonal skills, in-depth knowledge of financial markets, the ability to communicate complex concepts clearly, and a dedication to ongoing professional development. Building trust, providing exceptional client service, and demonstrating integrity are also essential qualities.
How can I showcase my expertise as a financial advisor?
You can showcase your expertise by creating educational content, such as blog posts, videos, and webinars. Participating in industry events as a speaker or panelist, publishing articles in reputable publications, and leveraging social media platforms can also help establish your thought leadership and attract clients.
How does QuickBooks inventory management work?
QuickBooks is a versatile accounting software that goes beyond managing your financial transactions. QuickBooks inventory management works by tracking the flow of goods into, out of, and within a business. It helps businesses to:
- Track inventory levels
- Set reorder points
- Generate inventory reports
- Make better decisions about inventory
To use QuickBooks for inventory management, businesses need to:
- Set up inventory tracking in their account settings. This can be done by going to Settings > Products and Services and turning on Track quantity and price/rate.
- Add their inventory items to QuickBooks. This can be done by going to Products and Services and clicking New. Businesses should enter the name, description, and other details for each inventory item.
- Set reorder points for their inventory items. This can be done by going to Products and Services and clicking Edit for the inventory item they want to update. Under Inventory Information, businesses should enter the Reorder point.
- Track their inventory levels by entering sales and purchase transactions. This can be done by going to Sales > Create Sales Receipt or Expenses > Create Bill. Businesses should enter the quantity of each inventory item that is sold or purchased.
- Generate inventory reports to track their inventory activity and make better decisions about inventory. This can be done by going to Reports > Inventory. Businesses can choose from a variety of inventory reports, such as the Inventory Valuation Report, Inventory Stock Status Report, and Inventory Summary Report.
QuickBooks inventory management works by automatically updating inventory levels as sales and purchase transactions are entered. This helps businesses to ensure that their inventory levels are accurate and that they have enough stock on hand to meet customer demand.
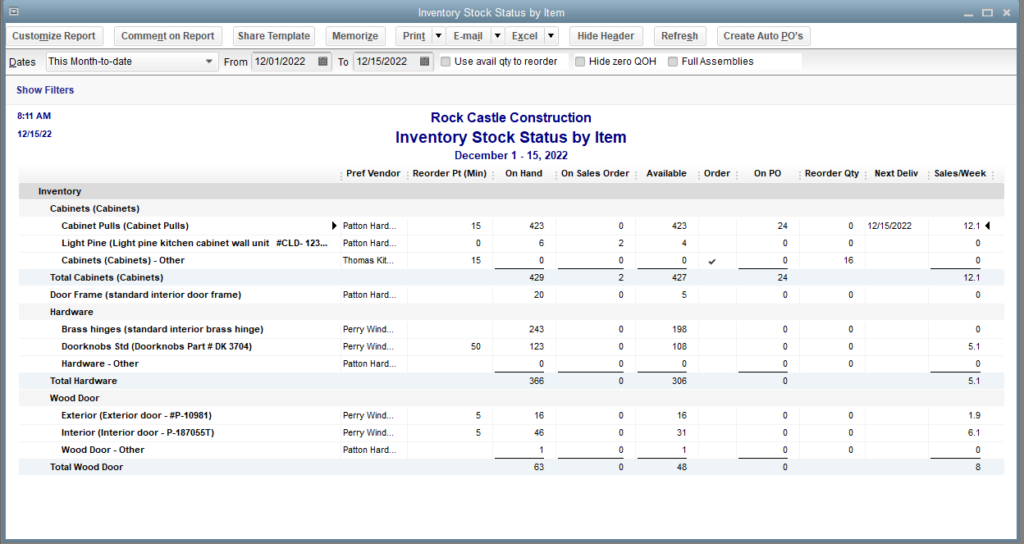
What are the benefits of using QuickBooks for inventory management?
There are many benefits to using QuickBooks for inventory management, including:
- Accuracy: QuickBooks automatically updates your inventory levels as you enter sales and purchase transactions, which helps to ensure that your inventory levels are accurate.
- Efficiency: QuickBooks can save you time and effort by automating many of the tasks involved in inventory management, such as tracking inventory levels, generating reports, and setting reorder points.
- Scalability: QuickBooks can scale to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes. Whether you are a small business with just a few inventory items or a large business with thousands of inventory items, QuickBooks can help you manage your inventory efficiently.
How do I get started with QuickBooks inventory management?
To get started with QuickBooks inventory management, you will need to:
- Set up inventory tracking in your account settings.
- Add your inventory items to QuickBooks.
- Set reorder points for your inventory items.
- Start tracking your inventory levels by entering sales and purchase transactions.
- Generate inventory reports to track your inventory activity and make better decisions about inventory.
Some common mistakes to avoid with QuickBooks inventory management
- Not setting up inventory tracking in your account settings.
- Not adding all of your inventory items to QuickBooks.
- Not setting reorder points for your inventory items.
- Not entering sales and purchase transactions regularly.
- Not generating inventory reports regularly.
Can QuickBooks handle large inventories?
Yes, QuickBooks can manage inventories of varying sizes, making it suitable for both small businesses and larger enterprises.
How often should I update my inventory in QuickBooks?
Regular updates are crucial. Ideally, you should update your inventory every time there is a stock movement, such as a sale, return, or new purchase.
Can I integrate QuickBooks with my online store?
Yes, QuickBooks can be integrated with the most popular e-commerce platforms, streamlining your online sales and inventory management.
What reports can I generate with QuickBooks Inventory Management?
You can generate various reports, including inventory valuation, sales by product or service, and more to gain insights into your business.
Is QuickBooks Inventory Management suitable for businesses with multiple locations?
Absolutely. QuickBooks allows businesses with multiple locations to efficiently manage their inventory across all sites, improving overall coordination and efficiency.
Conclusion
QuickBooks inventory management is a powerful tool that can help businesses of all sizes to track inventory levels, generate reports, and make better decisions about inventory. By following the tips in this article, businesses can avoid common mistakes and get the most out of QuickBooks inventory management.
Why is financial modeling important for startups?
Why is Financial Modeling Important for Startups?
Financial modeling is a crucial element in the journey of financial modeling important for startups. It provides a structured framework for assessing, analyzing, and making informed financial decisions. In this article, we’ll explore the significance of financial modeling for startups and understand why it’s considered an indispensable tool for success.
Introduction
Financial modeling involves creating a comprehensive representation of a company’s financial performance. It encompasses various aspects, including income statements, balance sheets, cash flow projections, and more. financial modeling is important for startups to use these models to simulate their financial future, making it easier to plan and strategize effectively.
Role of Startups
Startups are in a unique position, often working with limited resources and high uncertainty. Financial modeling helps startups navigate these challenges by providing a structured approach to managing their finances.

The Significance of Financial Planning
Effective financial planning is the cornerstone of a successful financial modeling important for startups. Financial models allow entrepreneurs to set realistic goals and allocate resources efficiently. This, in turn, ensures the company’s longevity and growth.
Accuracy in Decision-Making
Financial modeling is important for startups that often face critical decisions regarding investments, expansion, and product development. Financial modeling enables them to make these decisions with confidence, backed by data-driven insights.
Attracting Investors
Investors are more likely to support financial modeling important for startups that can demonstrate a clear and organized financial plan. A well-structured financial model can instill trust and attract potential investors.
Securing Loans and Funding
financial modeling important for startups often requires capital to fuel their growth. Financial models provide a compelling case for lenders and investors, making it easier to secure loans and funding.
Strategic Resource Allocation
Efficient resource allocation is vital for financial modeling important for startups. Financial modeling helps in identifying areas that need investment and those that can be trimmed, optimizing resource utilization.
Risk Mitigation
financial modeling is important for startups that face a higher degree of risk. Financial models allow for scenario analysis, helping to prepare for unexpected challenges and mitigate potential risks.
Business Growth and Scaling
Financial modeling is important for startups that intend to scale and need to understand how their financials will evolve. Financial modeling provides insights into the financial requirements of growth.
Assessing Viability and Sustainability
Financial modeling important for startup ideas financially viable in the long run? Financial models answer this question, helping entrepreneurs assess the sustainability of their business model.
Building Credibility
Startups need to build credibility with stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and partners. Accurate financial modeling enhances a startup’s reputation and reliability.
Benchmarking and Performance Tracking
Financial models act as benchmarks for performance. Startups can compare actual financial results with their projections, making it easier to identify areas that require improvement.
Adaptability and Flexibility
financial modeling is important for startups that often need to pivot or adapt to changing market conditions. Financial models can be adjusted to reflect these changes, ensuring the business remains agile.
Compliance and Regulation
financial modeling is important for startups that need to adhere to financial regulations and tax requirements. Financial models help in ensuring compliance and avoiding legal issues.
The Key to Startup Success
In conclusion, financial modeling is important for startups and is the key to financial modeling important for startups’ success. It empowers entrepreneurs with the tools and insights needed to navigate the complexities of business in its initial stages. By providing accurate financial projections and a roadmap for resource allocation, financial modeling is important for startups can confidently pursue their goals and aspirations.
What software can I use for financial modeling as a startup?
There are several software options available, including Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and specialized financial modeling tools like QuickBooks and Quicken.
How frequently should I update my financial model as a startup?
It’s advisable to update your financial model regularly, especially when significant changes occur in your business, such as a new round of funding, a major pivot, or substantial growth.
Can financial modeling help me secure venture capital funding?
Yes, a well-constructed financial model can significantly increase your chances of attracting venture capital funding. It demonstrates your business acumen and commitment to financial planning.
Are there professional services that can assist startups with financial modeling?
Yes, many financial consultants and advisory firms specialize in helping financial modeling important for startups with financial modeling, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
How do I learn to create effective financial models for my startup?
You can find various online courses and resources that provide guidance on creating effective financial models. Additionally, consider hiring a financial expert or consultant to assist you in the process.
What is a Property Management Company and How Does It Make Money?
What is a Property Management Company and How Does It Make Money?
In the world of real estate, property management companies play a pivotal role in the efficient management of properties. Whether you’re a property owner looking to free up your time or a tenant seeking a well-maintained place to live, understanding the functions and revenue streams of property management companies is essential. In this article, we’ll explore what property management companies are, the services they provide, and how they generate income.
What is a Property Management Company?
A property management company is a professional firm or entity that specializes in the management of real estate properties on behalf of property owners. These properties can include residential, commercial, or industrial real estate. Property management companies act as intermediaries between property owners and tenants, handling a range of responsibilities related to property maintenance, tenant interactions, and financial management.

Services Offered by Property Management Companies
Property Marketing
Property management companies are responsible for marketing vacant properties. They use their expertise to list properties on various platforms, showcase them to potential tenants, and ensure a quick and efficient rental process.
Tenant Screening
Tenant screening is a crucial service offered by property management companies. They thoroughly vet prospective tenants, conducting background checks, credit evaluations, and reference verifications to ensure that reliable and responsible tenants occupy the properties.
Rent Collection
Property management companies take care of rent collection on behalf of property owners. They establish rent due dates, send out reminders, and handle the collection of rent payments, ensuring consistent cash flow for property owners.

Maintenance and Repairs
Maintenance and repairs are a significant aspect of property management. These companies oversee property upkeep, addressing maintenance issues promptly and organizing repairs as needed. This proactive approach helps in preserving the property’s value.
Financial Reporting
Property management companies maintain detailed financial records and provide property owners with regular reports on income, expenses, and financial performance. This transparency is invaluable to property owners for tracking their investments.
How Property Management Companies Make Money
Property management companies generate revenue through various means. Here are the primary ways they make money:
Management Fees
The most common source of income for property management companies is management fees. Property owners typically pay a percentage of the property’s rental income as a fee for the services provided. The fee varies but typically ranges from 5% to 12% of the monthly rent.
Leasing Fees
When a property management company secures a new tenant for a property, they may charge a leasing fee. This fee is typically equivalent to one month’s rent and covers the cost of advertising, tenant screening, and lease preparation.
Maintenance and Repair Markup
Property management companies may also make money by marking up the cost of maintenance and repair services. This markup is usually a percentage of the total expense and contributes to the company’s revenue.
Ancillary Services
Some property management companies offer additional services, such as landscaping, cleaning, or security, for an extra fee. These ancillary services add another stream of income to their business.
Benefits of Hiring a Property Management Company
Property owners benefit from hiring a property management company in several ways. These advantages include saving time, minimizing vacancies, ensuring rent collection, and maintaining well-kept properties. Additionally, professional management can often lead to higher rental rates and better tenant retention.

Challenges Faced by Property Management Companies
While property management companies offer valuable services, they face several challenges. These include dealing with difficult tenants, managing property maintenance, and staying updated on local regulations and laws.
Tips for Choosing the Right Property Management Company
When selecting a property management company, it’s crucial to consider factors like experience, reputation, and the range of services they offer. Conducting thorough research and seeking referrals can help property owners make an informed choice.
The Future of Property Management
The property management industry is continually evolving, with advancements in technology and changes in tenant preferences. Embracing digital tools for property management and staying attuned to market trends is essential for staying competitive in the industry.
Conclusion
Property management companies play a vital role in the real estate ecosystem. They offer a wide range of services, from property marketing to financial reporting, making the lives of property owners easier. By understanding how these companies generate revenue and the benefits they provide, property owners can make informed decisions about entrusting their properties to these professionals.
How much do property management companies typically charge for their services?
Property management companies usually charge a management fee that ranges from 5% to 12% of the monthly rent. Leasing fees, maintenance markups, and ancillary services may also contribute to their revenue.
What are the benefits of hiring a property management company?
Hiring a property management company saves time, ensures efficient rent collection, and leads to well-maintained properties. It can also result in higher rental rates and better tenant retention.
What are the challenges faced by property management companies?
Property management companies face challenges such as dealing with difficult tenants, managing property maintenance, and staying updated on local regulations and laws.
How can property owners choose the right property management company?
To choose the right property management company, property owners should consider factors like experience, reputation, services offered, and referrals from others in the industry.
How is the property management industry evolving?
The property management industry is evolving through the adoption of digital tools and technology. Staying updated with market trends and tenant preferences is essential for remaining competitive in the industry.
What kind of property manager makes the most money?
Property managers who oversee high-end luxury properties or large commercial real estate portfolios tend to make the most money.
5 Best Accounting Software for Amazon Sellers
To simplify these tasks and ensure compliance with tax regulations, Amazon sellers turn to specialized accounting software. Running a successful Amazon business requires meticulous financial management. This entails tracking sales, expenses, taxes, and profits accurately. In this article, we will introduce you to the top five accounting software solutions tailored to the unique needs of Amazon sellers.

Why Amazon Sellers Need Specialized Accounting Software
Accounting for an Amazon business can quickly become complex due to the high volume of transactions and the need to comply with Amazon’s policies. Here’s why specialized accounting software is essential:
Accurate Sales Tracking: Amazon accounting software can accurately record sales, including fees, refunds, and other variables, providing you with a clear picture of your revenue.
Expense Management: It helps you keep track of expenses such as shipping, advertising, and storage fees, allowing you to calculate your true profit margins.
Tax Compliance: Specialized software ensures you’re compliant with tax regulations, making tax season less stressful.
QuickBooks Online
Features and Benefits
Seamless Integration: QuickBooks Online seamlessly integrates with Amazon, allowing for automatic data syncing.
Comprehensive Reporting: It offers detailed financial reports, making it easier to analyze your Amazon business’s performance.
Scalability: QuickBooks can accommodate businesses of all sizes, from startups to established enterprises.
Pricing
QuickBooks Online offers various pricing plans to suit different needs, starting at $25 per month.
Xero
Features and Benefits
Inventory Tracking: Xero enables you to monitor your Amazon inventory and manage stock levels effectively.
Multi-Currency Support: Ideal for international Amazon sellers, Xero supports multiple currencies.
User-Friendly Interface: Its user-friendly dashboard makes it easy to navigate and use.
Pricing
Xero offers pricing plans starting at $20 per month, making it an affordable option for small businesses.
A2X
Features and Benefits
Accurate Payouts: A2X automates the reconciliation of Amazon settlements, ensuring accuracy in your financial records.
Audit Trail: It provides a clear audit trail, making it easier to track financial changes over time.
Amazon Fee Separation: A2X separates Amazon fees from your revenue, simplifying your financial reports.
Pricing
A2X’s pricing varies based on your transaction volume, with plans starting at $19 per month.
Sage 50cloud
Features and Benefits
In-Depth Inventory Management: Sage 50cloud offers robust inventory management features, vital for Amazon sellers with extensive product lines.
Advanced Reporting: It provides advanced reporting options for in-depth financial analysis.
User Permissions: You can set user permissions to control access to sensitive financial data.
Pricing
Sage 50cloud’s pricing starts at $50 per month, making it suitable for businesses that require advanced inventory management.
Wave Financial
Features and Benefits
Free Accounting Software: Wave Financial is a free accounting software option, making it budget-friendly for startups.
Invoicing: It offers invoicing capabilities, allowing you to create and send invoices directly to Amazon customers.
Bank Integration: Wave Financial can sync with your bank accounts, simplifying reconciliation.
Pricing
Wave Financial’s core accounting features are free, making it an excellent choice for budget-conscious Amazon sellers.
Comparison Chart
Before making a decision, let’s compare the key features and pricing of these accounting software options for Amazon sellers:
| Software | Integration with Amazon | Pricing |
| QuickBooks Online | Yes | Starting at $25/month |
| Xero | Yes | Starting at $20/month |
| A2X | Yes | Starting at $19/month |
| Sage 50cloud | Yes | Starting at $50/month |
| Wave Financial | Limited | Core features are free |
How to Choose the Right Accounting Software
Selecting the right accounting software for your Amazon business depends on your specific needs, budget, and business size. Consider factors like integration capabilities, inventory management, and pricing before making a decision.
Conclusion
Efficient financial management is a cornerstone of a successful Amazon business. By investing in specialized accounting software, you can streamline your operations, make informed decisions, and stay compliant with tax regulations. Whether you choose QuickBooks Online, Xero, A2X, Sage 50cloud, or Wave Financial, you’re one step closer to financial success in the world of Amazon selling.
Is specialized accounting software necessary for Amazon sellers?
Yes, specialized software helps you manage your finances accurately and stay compliant with Amazon’s policies and tax regulations.
Can I use the free version of Wave Financial for my Amazon business?
Yes, you can use Wave Financial’s core accounting features for free, making it a budget-friendly option.
Which accounting software is best for small Amazon businesses?
Xero and Wave Financial are budget-friendly options suitable for small Amazon businesses.
Do these accounting software options offer customer support?
Yes, all of the mentioned software options offer customer support to assist users.
Is there a trial period for these accounting software solutions?
Some of them may offer trial periods, so it’s recommended to check their respective websites for current offers.
E-commerce Accounting: What to Know About the Income (P&L) Statement
The Income (P&L) Statement is a critical financial tool that provides a snapshot of your business’s financial health. E-commerce businesses operate in a dynamic and competitive landscape. To thrive, you need to stay on top of your financial performance. Let’s delve deeper into what it is and why it matters for your e-commerce venture.
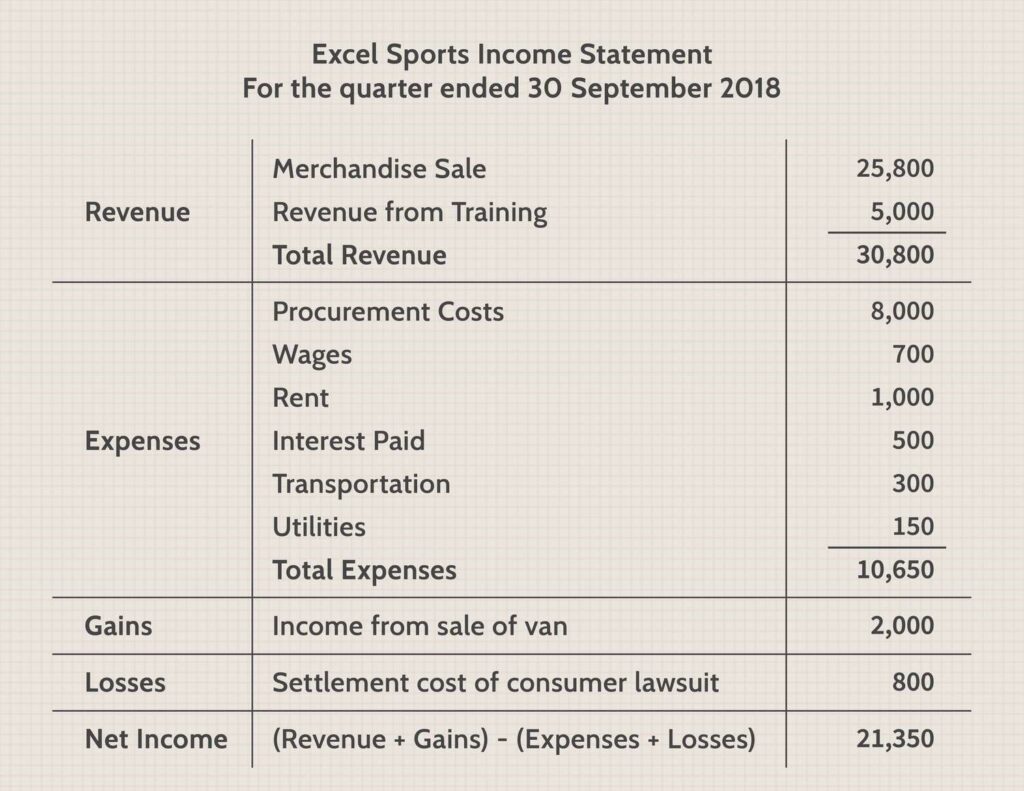
What’s on the income statement (profit and loss)?
The Income Statement, also known as the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, is a financial report that summarizes your business’s revenues, costs, and expenses during a specific period. It is typically prepared on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, allowing you to track your financial performance over time.
Profit and Loss (P&L) typically includes the following components:
Revenue: This represents the total income generated from sales, services, or other sources.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): These are the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods or services that were sold.
Gross Profit: Calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue, it reflects the profitability of core business operations.
Operating Expenses: These encompass all other costs related to running the business, such as marketing, rent, utilities, and employee salaries.
Net Profit (or Loss): The final figure on the income statement, is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit and represents the ultimate measure of profitability.
Common mistakes made in the e-commerce Income (P&L) Statement
Creating an accurate e-commerce income statement is essential for making informed financial decisions. However, there are several common mistakes that businesses often make when preparing their income statements:
Failure to Account for All Expenses: Some e-commerce businesses may overlook certain operating expenses or underestimate their costs, leading to an inaccurate representation of their financial health.
Ignoring Depreciation: Depreciation of assets like equipment or software should be included in the income statement to reflect the true cost of using these assets over time.
Inconsistent Revenue Recognition: Businesses may not consistently recognize revenue, particularly when dealing with subscription-based models or long-term contracts, which can distort financial results.
Improper Inventory Valuation: E-commerce businesses need to accurately value their inventory, as using the wrong valuation method can lead to incorrect cost of goods sold (COGS) figures and, consequently, inaccurate gross profit calculations.
Not Adjusting for Seasonal Fluctuations: Many e-commerce businesses experience seasonality in their sales, but failing to adjust the income statement for these fluctuations can result in misleading financial data.
Miscalculating Gross Profit Margin: Incorrectly calculating the gross profit margin can misrepresent the efficiency of your core operations. It’s important to use the right formula to calculate this critical metric.
Neglecting Non-Recurring Items: Sometimes, one-time expenses or extraordinary gains are not properly distinguished in the income statement, which can skew the financial analysis.
Not Comparing to Previous Periods: Failing to compare current income statements to those of previous periods makes it difficult to track trends and assess the business’s financial progress.
Not Considering Tax Implications: Taxes are a significant expense for businesses. Not accounting for them accurately can lead to financial surprises and potentially impact cash flow.
Relying Solely on Accounting Software: While accounting software is valuable, it’s essential to have a deep understanding of financial principles and manually review and verify the numbers generated by the software.
Overlooking Non-Financial Metrics: While the income statement focuses on financial aspects, e-commerce businesses should also consider non-financial metrics like customer acquisition cost (CAC) and customer lifetime value (CLV) to gain a more holistic view of their performance.
To avoid these common mistakes, e-commerce businesses should invest in robust accounting practices, regularly review their income statements, seek professional assistance when necessary, and stay up-to-date with changes in accounting standards and tax regulations.
Why should you keep track of your Income (P&L) Statement?
Keeping track of your income statement is crucial for several compelling reasons:
Financial Health Assessment: Your income statement provides a snapshot of your business’s financial health. By regularly reviewing it, you can assess whether your business is profitable or facing financial challenges. It offers insights into how well your company is performing financially.
Profitability Monitoring: The income statement calculates your net profit, which is the amount left after deducting all expenses from your revenue. Monitoring net profit over time helps you gauge the success of your business and make necessary adjustments to enhance profitability.
Expense Management: It breaks down your expenses, allowing you to identify where your money is going. This insight is crucial for controlling costs and optimizing spending, ensuring that your business operates efficiently.
Decision-Making: An accurate Income (P&L) Statement is a valuable tool for making informed business decisions. Whether it’s setting prices, expanding operations, or adjusting your budget, having access to your financial data is essential for strategic planning.
Investor and Lender Confidence: If you seek external funding or investments, potential investors or lenders will scrutinize your income statement. A healthy income statement can instill confidence in stakeholders, making it easier to secure financing or attract investors.
Tax Compliance: Accurate Income (P&L) Statements are essential for tax compliance. They provide the necessary financial data for calculating and paying taxes, helping you avoid legal issues and penalties.
Performance Tracking: By comparing Income (P&L) Statements from different periods, you can track the performance and progress of your business. This historical data helps you identify trends, strengths, and weaknesses.
Operational Efficiency: Analyzing the income statement allows you to assess the efficiency of your operations. You can identify areas where you can cut costs, reallocate resources, or optimize processes to improve your bottom line.
Planning and Budgeting: Income (P&L) Statements are valuable for creating realistic budgets and financial forecasts. They serve as a foundation for setting financial goals and tracking progress toward achieving them.
Investor Relations: If your business is publicly traded, investors rely on income statements to evaluate your company’s financial performance. A well-maintained income statement can influence investor confidence and stock prices.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Depending on your jurisdiction and industry, legal and regulatory requirements may exist to maintain and report Income (P&L) Statements. Non-compliance can result in legal penalties.
How to analyze your e-commerce business’s income statement
Analyzing your e-commerce business’s income statement is crucial for gaining insights into its financial performance and making informed decisions. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to effectively analyze your income statement:
Review the Time Period: Start by identifying the time period covered by the Income (P&L) Statement. Ensure you’re comparing it to the appropriate historical data or industry benchmarks.
Check for Accuracy: Verify that all the numbers on the Income (P&L) Statement are accurate and properly categorized. Look for any discrepancies or errors in calculations.
Understand Revenue Sources: Examine the revenue section to understand where your income is coming from. Identify the primary sources of revenue, such as product sales, subscriptions, or services.
Analyze Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Evaluate the COGS section to determine the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods or services sold. Ensure that inventory valuation methods are consistent and accurate.
Calculate Gross Profit: Subtract COGS from revenue to calculate the gross profit. Assess whether your gross profit margin is in line with industry standards or your own historical performance.
Review Operating Expenses: Analyze the operating expenses section. Identify which expenses are essential for running your e-commerce business and look for any unusual or unexpected costs.
Calculate Net Profit: Subtract the total operating expenses from the gross profit to calculate the net profit (or loss). This figure represents the overall profitability of your e-commerce business.
Assess Net Profit Margin: Calculate the net profit margin by dividing net profit by total revenue and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. A higher net profit margin indicates better profitability.
Compare to Previous Periods: Compare the current income statement to previous periods, such as the previous month, quarter, or year. Look for trends and changes in revenue, expenses, and profitability.
Analyze Expense Ratios: Calculate expense ratios by dividing individual operating expenses by total revenue. This helps identify which expenses have the most significant impact on your profitability.
Identify Seasonal Trends: If your business experiences seasonal fluctuations, assess how these affect your income statement. Consider how you can adjust your operations and budget accordingly.
Benchmark Against Industry Averages: Compare your Income (P&L) Statement to industry benchmarks to see how your business stacks up against competitors. Identify areas where you may need to improve.
Assess Cost Control: Look for opportunities to control costs and improve efficiency. Consider whether certain operating expenses can be reduced without compromising quality or customer satisfaction.
Evaluate Pricing Strategies: If your gross profit margin is lower than desired, analyze your pricing strategies. Determine if price adjustments are necessary to improve profitability.
Set Financial Goals: Use the insights gained from your analysis to set financial goals for your e-commerce business. Create actionable plans to achieve these goals.
Consult with Experts: If you’re unsure about any aspect of your income statement or need assistance with financial analysis, consider consulting with accountants or financial advisors who specialize in e-commerce businesses.
Regularly Monitor and Update: Financial analysis is an ongoing process. Regularly monitor your income statement and update your analysis as new data becomes available. Adjust your strategies based on the insights you gain.
Breaking down your income statement
Breaking down your income statement involves a detailed examination of each component and line item to gain a comprehensive understanding of your business’s financial performance. Here’s a breakdown of the typical sections and key elements found in an income statement:
Revenue (Sales):
This is the starting point of your income statement.
It includes all the income generated from sales, services, or other revenue streams.
Segment revenue sources (e.g., product sales, subscriptions, service fees) for deeper insights.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS):
These are the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods or services that you sell.
It includes expenses like raw materials, manufacturing costs, and shipping fees.
Gross Profit:
Calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue.
Represents the profitability of your core business operations.
Operating Expenses:
This section encompasses all other costs related to running your business.
Common operating expenses include marketing, rent, utilities, employee salaries, and office supplies.
Operating expenses are typically categorized into selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A).
Operating Income (or Loss):
Calculated by subtracting total operating expenses from gross profit.
It reflects the profitability of your business before considering other income or expenses.
Other Income and Expenses:
This section includes non-operating items like interest income, interest expenses, and gains or losses from investments.
Non-recurring or extraordinary items may also be reported here.
Net Profit (or Loss):
Calculated by subtracting total other income and expenses from operating income.
Represents the ultimate measure of your business’s profitability.
A positive net profit indicates a profit, while a negative value suggests a loss.
Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT):
Also known as operating profit, EBIT represents the profit generated by your core operations before considering interest and taxes.
Calculated by subtracting interest and taxes from operating income.
Interest Expenses and Income:
Interest expenses reflect the cost of borrowing, such as loans or credit lines.
Interest income includes earnings from investments or savings accounts.
Income Before Taxes (EBT):
Calculated by subtracting interest expenses and income from EBIT.
Represents the profit or loss before accounting for taxes.
Income Taxes:
This section shows the taxes owed by your business based on its taxable income.
Tax rates and tax regulations can significantly impact this figure.
Net Income (or Loss) After Taxes:
The final line item on your Income (P&L) Statement is calculated by subtracting income taxes from EBT.
It’s the actual profit or loss your business reports for tax purposes.
Analyzing each of these components in detail helps you gain insights into your revenue sources, the cost structure of your business, your profitability, and your financial performance. By breaking down your income statement, you can make informed decisions, track trends over time, and identify areas for improvement in your business operations.
Gross profit and gross profit margin
Gross profit and gross profit margin are important financial metrics that provide insights into a company’s profitability and the efficiency of its core operations. Here’s what each term means:
Gross Profit:
Gross profit is the amount of money a company earns from its core business activities after deducting the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods or services it sells.
To calculate gross profit, use the following formula: Gross Profit = Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
For example, if a company generates $100,000 in revenue from selling products and incurs $60,000 in direct production costs, the gross profit is $40,000.
Gross Profit Margin:
Gross profit margin is expressed as a percentage and represents the portion of revenue that remains after covering the cost of goods sold.
To calculate gross profit margin, use the following formula: Gross Profit Margin = (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100%
Using the example above, if the company’s revenue is $100,000 and the gross profit is $40,000, the gross profit margin would be (40,000 / 100,000) x 100% = 40%.
Gross profit margin is a critical metric because it measures the efficiency of a company’s core operations in generating profit. A higher gross profit margin indicates that a company is more efficient in producing or sourcing its products or services.
A gross profit margin of 40% means that for every dollar in revenue, the company retains 40 cents after covering the direct production costs.
Gross profit and gross profit margin are particularly important for businesses with goods-based revenue models, such as e-commerce companies, manufacturers, and retailers. These metrics help assess the profitability of the products or services a company offers and provide insights into pricing strategies, cost control, and overall financial health.
A rising gross profit margin over time suggests improved efficiency and pricing power, while a declining margin may indicate increased production costs or pricing pressures. It’s essential for businesses to monitor and analyze these metrics to make informed decisions and optimize profitability.
Comparison with percentages
Comparing financial metrics using percentages can provide valuable insights into a company’s performance and help with benchmarking against industry standards or historical data. Let’s explore how percentages can be used to compare financial metrics, focusing on gross profit and gross profit margin:
1. Gross Profit Comparison with Percentages:
Suppose you want to compare the gross profit of two companies, Company A and Company B, over a certain period. Here’s how you can do it with percentages:
Company A: Gross Profit = $200,000
Company B: Gross Profit = $250,000
Now, calculate the percentage difference:
Percentage Difference = [(Company B Gross Profit – Company A Gross Profit) / Company A Gross Profit] x 100%
Percentage Difference = [($250,000 – $200,000) / $200,000] x 100% Percentage Difference = ($50,000 / $200,000) x 100% Percentage Difference = 25%
In this comparison, Company B’s gross profit is 25% higher than Company A’s. This percentage comparison highlights the difference in the absolute values of gross profit between the two companies.
2. Gross Profit Margin Comparison with Percentages:
Let’s compare the gross profit margin of Company X and Company Y:
Company X: Gross Profit = $80,000, Revenue = $200,000
Company Y: Gross Profit = $70,000, Revenue = $150,000
Calculate the gross profit margins for both companies and the percentage difference:
Company X Gross Profit Margin = ($80,000 / $200,000) x 100% = 40%
Company Y Gross Profit Margin = ($70,000 / $150,000) x 100% = 46.67%
Percentage Difference = [(Company Y Gross Profit Margin – Company X Gross Profit Margin) / Company X Gross Profit Margin] x 100%
Percentage Difference = [(46.67% – 40%) / 40%] x 100% Percentage Difference = (6.67% / 40%) x 100% Percentage Difference = 16.67%
In this comparison, Company Y has a gross profit margin that is approximately 16.67% higher than Company X’s. This percentage comparison indicates that Company Y is retaining a larger portion of its revenue as gross profit.
Comparing financial metrics with percentages allows for a more meaningful and standardized evaluation, especially when dealing with companies of different sizes or when assessing changes in performance over time. It provides a relative perspective that can aid in decision-making and strategic planning.
Why is the Income Statement Important for E-commerce?
Tracking Revenue and Expenses
For e-commerce businesses, tracking revenue and expenses is essential. Your income statement provides a clear breakdown of all income sources, including sales, subscriptions, and other revenue streams. On the flip side, it outlines various expenses such as marketing, shipping, and operating costs. This insight helps you identify areas where you can optimize your spending and increase profitability.
Assessing Profitability
Profitability is the lifeblood of any business. The Income (P&L) Statement calculates your net profit, which is the amount left after deducting all expenses from your revenue. Monitoring your net profit over time allows you to gauge the health of your e-commerce venture and make necessary adjustments to enhance profitability.
Components of an Income (P&L) Statement
The components of an income statement are vital for comprehending your business’s financial performance.
Revenue
Revenue, also known as sales or turnover, represents the total income generated from your e-commerce operations. It’s the starting point of your income statement.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS includes the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods or services that you sell. In e-commerce, this encompasses expenses like inventory costs and shipping fees.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the COGS from your total revenue. It reflects the profitability of your core business operations.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses encompass all other costs related to running your e-commerce business, such as marketing, rent, utilities, and employee salaries.
Net Profit
Net profit is the ultimate measure of your business’s profitability. It is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit.
Calculating Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin is a crucial metric for e-commerce businesses. It measures the profitability of your core operations as a percentage of your revenue. A higher gross profit margin indicates better efficiency in producing or sourcing your products.
Analyzing Operating Expenses
Effectively managing your operating expenses is key to improving your e-commerce business’s bottom line. Regularly reviewing your Income (P&L) Statement can help you identify areas where you can cut costs or allocate resources more efficiently.
Net Profit
Net profit is what’s left in your coffers after all expenses have been accounted for. It’s the true measure of your business’s success, and keeping a close eye on it is essential for long-term sustainability.
Common E-commerce Income Statement Challenges
E-commerce businesses often face unique challenges when preparing an Income (P&L) Statement.
Seasonal Fluctuations
Many e-commerce businesses experience seasonal fluctuations in sales. Your Income (P&L) Statement should reflect these fluctuations accurately to help you plan for lean periods.
Inventory Valuation
Properly valuing your inventory is crucial. Using the wrong valuation method can distort your Income (P&L) Statement, leading to inaccurate financial decisions.
Using the Income (P&L) Statement for Business Decision-Making
Your Income (P&L) Statement is not just a financial report; it’s a powerful tool for making informed business decisions.
Pricing Strategies
By analyzing your Income (P&L) Statement, you can adjust your pricing strategies to maximize profit without compromising competitiveness.
Cost Control
Identifying areas of overspending in your operating expenses can lead to cost-saving measures that directly impact your bottom line.
Tools for Creating and Analyzing Income (P&L) Statement
There are various accounting software tools available that can simplify the process of creating and analyzing income statements for your e-commerce business.
Best Practices for E-commerce Income (P&L) Statement
To make the most of your Income (P&L) Statement, consider implementing these best practices:
Keep accurate records of all transactions.
Regularly reconcile your financial data.
Seek professional accounting assistance if needed.
How often should I review my income statement for my e-commerce business?
It’s advisable to review your Income (P&L) Statement monthly to stay on top of your financial performance.
What is a good gross profit margin for an e-commerce business?
A healthy gross profit margin for e-commerce typically falls between 40% to 60%, but this can vary by industry.
How can I deal with seasonal fluctuations in my income statement?
To manage seasonal fluctuations, create a budget that accounts for lean periods and consider adjusting marketing strategies accordingly.
Can I prepare an income statement manually, or do I need accounting software?
While you can prepare an Income (P&L) Statement manually, accounting software can streamline the process and reduce the chances of errors.
Where can I find professional help for understanding and analyzing my income statement?
You can seek assistance from certified accountants or financial advisors who specialize in e-commerce businesses. They can provide expert guidance tailored to your specific needs.
What is E-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting?
E-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting refers to the specialized financial processes and procedures that e-commerce businesses employ to manage their finances. It involves tracking revenue, expenses, inventory, and other financial aspects specific to online retail. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar businesses, e-commerce ventures have distinctive accounting needs due to their online nature.
Difference Between eCommerce Bookkeeping and Accounting
E-commerce bookkeeping and accounting are both crucial financial processes for e-commerce businesses, but they serve different purposes and have distinct roles within the overall financial management of the business. Here are the key differences between e-commerce bookkeeping and accounting:
Scope and Purpose:
E-commerce Bookkeeping: Bookkeeping is the process of recording and categorizing all financial transactions in a systematic and organized manner. It involves tasks like recording sales, expenses, and purchases and maintaining detailed records of financial activities. The primary purpose of bookkeeping is to maintain accurate and up-to-date financial records for the business.
E-commerce Accounting: Accounting, on the other hand, is a broader and more analytical process that goes beyond bookkeeping. Accounting involves interpreting, summarizing, and analyzing financial data to provide insights into the financial health and performance of the e-commerce business. Accounting also includes tasks like financial reporting, budgeting, forecasting, and making financial decisions based on the data.
Recording Transactions:
E-commerce Bookkeeping: Bookkeepers focus on the daily or regular recording of financial transactions. They ensure that every transaction, such as sales, expenses, and inventory changes, is accurately recorded in the books of accounts. Bookkeepers typically use accounting software for this purpose.
E-commerce Accounting: Accountants use the data entered by bookkeepers to prepare financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. They analyze these statements to gain insights into the financial performance of the e-commerce business and make strategic financial decisions.
Compliance and Taxes:
E-commerce Bookkeeping: Bookkeepers help maintain accurate financial records to ensure compliance with tax regulations. They often work closely with tax professionals to prepare financial information for tax returns.
E-commerce Accounting: Accountants play a crucial role in tax planning and strategy. They analyze the financial data to optimize tax liability and ensure the business is taking advantage of available tax deductions and credits.
Frequency:
E-commerce Bookkeeping: Bookkeeping is an ongoing, day-to-day process. It involves recording transactions as they occur and maintaining up-to-date financial records.
E-commerce Accounting: Accounting processes may occur on a less frequent basis, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, to prepare financial statements and assess the overall financial health of the business.
Analysis and Decision-Making:
E-commerce Bookkeeping: Bookkeeping primarily deals with data entry and record-keeping. It does not involve in-depth analysis of financial data or strategic decision-making.
E-commerce Accounting: Accounting involves financial analysis, performance evaluation, and strategic planning based on financial data. Accountants provide insights and recommendations for improving the financial health and profitability of the e-commerce business.

What Are the Two Types of Accounting for eCommerce Businesses?
There are two main types of accounting for eCommerce businesses
Cash Basis Accounting
Accrual Method
Cash Basis Accounting
Cash basis accounting is a simpler method often used by small businesses and individuals, and it records financial transactions when actual cash is received or paid. Here are the key features and characteristics of cash basis accounting:
Recognition of Revenue and Expenses:
Revenue Recognition:
Under cash-based accounting, revenue is recognized when cash is received from customers or clients. This means that sales are recorded only when the payment is received, regardless of when the products or services were delivered.
Expense Recognition:
Expenses are recognized when cash is paid. This means that expenses are recorded when bills are settled and payments are made, rather than when the expenses are incurred.
Simplicity:
Cash basis accounting is straightforward and easy to understand, making it a suitable choice for small businesses with simple financial transactions.
Cash Flow Focus:
This method provides a clear view of the actual cash flow of a business since it records transactions when cash changes hands.
Limited Financial Reporting:
Cash basis accounting may not provide a complete picture of a business’s financial performance and position because it doesn’t account for accounts receivable, accounts payable, or other accruals. It can lead to distortions in financial statements, especially for businesses with large credit sales and purchases.
Tax Reporting:
Some small businesses use cash-based accounting for tax purposes because it aligns with the timing of cash flows. However, tax authorities in some jurisdictions may require businesses to use accrual-based accounting if they exceed certain revenue thresholds.
No Matching Principle:
Cash basis accounting does not adhere to the accounting principle of matching revenues with expenses, which is one of the key principles of accrual basis accounting. This means that it may not provide an accurate reflection of a business’s profitability.
Limited Use for Large or Complex Businesses:
Cash basis accounting is generally not suitable for large or complex businesses with significant credit transactions, inventories, or long-term contracts. Accrual basis accounting is more appropriate in such cases.
Regulatory and Reporting Limitations:
Some regulatory bodies and lenders may require businesses to use accrual-based accounting for financial reporting, especially if they need a more comprehensive view of the company’s financial health.
Accrual Method
The accrual method recognizes revenue and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is received or paid. Here are the key features and characteristics of the accrual method of accounting:
Recognition of Revenue and Expenses:
Revenue Recognition:
Under the accrual method, revenue is recognized when it is earned, which typically occurs when goods are delivered or services are provided, even if the payment has not yet been received. This means that sales are recorded when they are made, not necessarily when cash is received.
Expense Recognition:
Expenses are recognized when they are incurred, regardless of when the payment is made. This includes expenses such as salaries, rent, utilities, and the cost of goods sold.
Matching Principle:
The accrual method adheres to the accounting principle of matching expenses with revenues. This means that expenses are recognized in the same accounting period as the related revenue, helping to provide a more accurate picture of a business’s profitability.
Complexity:
The accrual method is more complex than the cash-based method because it requires tracking accounts receivable (unreceived income) and accounts payable (unpaid expenses). This method is often used by larger businesses or those with more complex financial transactions.
Financial Reporting:
Accrual accounting provides a more comprehensive view of a business’s financial performance and position. It produces financial statements that include a balance sheet, income statement (profit and loss statement), and cash flow statement. These statements offer a more accurate representation of a company’s financial health.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements:
Some businesses are required by regulatory bodies, such as the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) in the United States or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) in many other countries, to use the accrual method for financial reporting.
Smoothed Revenue and Expense Recognition:
The accrual method can smooth out revenue and expense recognition over time, making it easier to evaluate financial performance and trends.
Cash Flow vs. Profitability:
The accrual method can result in differences between a company’s cash flow and its reported profitability. This is because revenue and expenses are recognized based on accruals, not actual cash movements.
Deferred Revenue and Prepaid Expenses:
Under the accrual method, businesses may record deferred revenue (unearned income) and prepaid expenses (expenses paid in advance) to reflect the timing of when economic benefits are realized.
Why Are Bookkeeping and Accounting Important for eCommerce?
E-commerce accounting plays a pivotal role in the success and sustainability of online businesses. Here are some reasons why it’s crucial:
Accurate Financial Reporting
E-commerce businesses must maintain precise financial records to comply with tax regulations and assess their financial health. Accurate reporting ensures transparency and helps in making informed business decisions.
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is vital for e-commerce companies. Accounting helps track inventory levels, prevent overstocking or understocking, and optimize product listings.
Tax Compliance
E-commerce businesses often deal with complex tax issues, such as sales tax across multiple states or countries. Proper accounting ensures compliance with tax laws and minimizes the risk of penalties.
Financial Analysis
Analyzing financial data helps e-commerce entrepreneurs identify trends, assess profitability, and strategize for growth.
What Does Effective eCommerce Bookkeeping and Accounting Look Like?
Effective e-commerce accounting is crucial for the financial health and success of an online business. It involves a set of practices and processes that help accurately track, manage, and analyze financial transactions related to e-commerce operations. Here’s what effective e-commerce accounting looks like:
Accurate Record-Keeping:
Accurate and detailed record-keeping is the foundation of effective e-commerce accounting. This includes recording all financial transactions, such as sales, expenses, refunds, and inventory changes, in a timely manner.
Accounting Software:
Utilizing specialized accounting software designed for e-commerce can streamline the accounting process. E-commerce accounting software often integrates with online sales platforms, payment gateways, and inventory management systems, allowing for automated data entry and real-time updates.
Separate Business and Personal Finances:
E-commerce business owners should maintain a clear separation between their personal and business finances. This involves having separate bank accounts, credit cards, and financial records for the business.
Inventory Management:
Effective inventory management is critical for e-commerce businesses, especially those selling physical products. Proper tracking of inventory levels, costs, and valuation methods (e.g., FIFO or LIFO) ensures accurate financial reporting and helps prevent overstocking or stockouts.
Expense Tracking:
Track all e-commerce-related expenses, including shipping costs, advertising expenses, website maintenance, hosting fees, and payment processing fees. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the true cost of sales.
Sales Tax Compliance:
E-commerce businesses must adhere to sales tax regulations in the jurisdictions where they operate. Effective e-commerce accounting includes proper collection and remittance of sales taxes and accurate reporting to tax authorities.
Financial Statements:
Regularly generate and review financial statements, including income statements (profit and loss), balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These statements provide insights into the financial health and performance of the business.
Reconciliation:
Regularly reconcile financial accounts, such as bank accounts, credit card statements, and merchant accounts, to ensure that recorded transactions match actual financial activity.
Budgeting and Forecasting:
Create budgets and financial forecasts to plan for future expenses, revenue targets, and cash flow needs. Comparing actual results to budgeted figures helps identify areas that need attention.
Cash Flow Management:
Monitor cash flow closely to ensure there is enough liquidity to cover expenses, especially during periods of growth or seasonal fluctuations in sales.
Tax Planning:
Engage in tax planning strategies to optimize tax liabilities, take advantage of deductions and credits, and ensure compliance with tax regulations. This may include working with tax professionals.
Auditing and Internal Controls:
Implement internal controls to safeguard against fraud and errors. Periodic financial audits or reviews can help identify and rectify issues in the accounting process.
Data Security:
Protect sensitive financial data by implementing robust cybersecurity measures. Security breaches can have severe financial and legal consequences.
Adaptability and Scaling:
Effective e-commerce accounting systems should be adaptable and scalable to accommodate growth and changes in the business. This includes adjusting processes, software, and personnel as needed.
Consultation with Professionals:
Consider consulting with accounting professionals or hiring an experienced e-commerce accountant or CPA to ensure compliance with accounting standards and best practices.
Accounting Reports Are the Root of Great Decision-Making
Accounting reports serve as the foundation for informed and effective decision-making in businesses. They provide essential financial data and insights that help business owners, managers, and stakeholders make sound decisions regarding operations, investments, and strategic planning. In essence, accounting reports offer the necessary information to assess the financial health and performance of a business, which is critical for making informed choices that can impact its future success.
What Is eCommerce Accounting and Why Is It Important?
E-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting is the specialized accounting process for online businesses that involves tracking, recording, and managing financial transactions related to online sales, expenses, and other financial activities. It’s important because it ensures accurate financial records, and compliance with tax regulations, and provides insights into the profitability and financial health of the e-commerce business. Effective e-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting is crucial for making informed decisions, managing cash flow, and achieving long-term success in the digital marketplace.

Key Components of E-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting
Now that we understand the importance of e-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting let’s delve into its key components:
Revenue Tracking
E-commerce businesses must accurately track their sales revenue, including online sales, returns, and discounts. A robust accounting system ensures all income sources are accounted for.
Expense Management
This involves monitoring and categorizing expenses, such as advertising costs, website maintenance, shipping fees, and employee salaries. Tracking expenses helps in budgeting and cost control.
Inventory Accounting
Inventory accounting methods like FIFO (First-In, First-Out) or LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) are crucial for e-commerce businesses. They determine how inventory costs affect profitability and tax liability.
Sales Tax Management
Managing sales tax can be complex for e-commerce companies operating in multiple jurisdictions. E-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting software can automate this process and ensure compliance.
Financial Reporting
Generating financial statements, such as profit and loss statements and balance sheets, provides a clear picture of the business’s financial health.
E-commerce Accounting Software
To streamline e-commerce accounting, many businesses opt for specialized accounting software. These tools are designed to handle the unique needs of online retailers. Popular e-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting software options include QuickBooks Commerce, Xero, and Zoho Books.
Challenges in E-commerce Accounting
While e-commerce accounting offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges. Some common challenges include:
Integration with E-commerce Platforms
Ensuring seamless integration between accounting software and e-commerce platforms is essential for accurate data transfer.
Currency Conversion
E-commerce businesses selling internationally must deal with multiple currencies, making currency conversion and exchange rate management critical.
Data Security
E-commerce companies handle sensitive customer information, so robust cybersecurity measures are crucial to protect financial data.
Rapid Growth
As e-commerce businesses grow, their accounting needs become more complex. Scalable Bookkeeping and Accounting solutions are necessary to keep up with expansion.
Conclusion
In the world of e-commerce, effective Bookkeeping and Accounting is not just a choice but a necessity. It ensures financial stability, compliance with tax laws, and the ability to make informed business decisions. By understanding the unique challenges and employing the right accounting tools and practices, e-commerce entrepreneurs can thrive in this competitive online landscape.
Is e-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting different from traditional accounting?
Yes, e-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting have unique aspects, such as sales tax management and inventory accounting, which are specific to online businesses.
What e-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting software do you recommend for small businesses?
For small e-commerce businesses, QuickBooks Commerce and Xero are popular choices due to their user-friendly interfaces and scalability.
How can I ensure the security of my e-commerce financial data?
Implement robust cybersecurity measures, use secure payment gateways, and regularly update your e-commerce platform and Bookkeeping and Accounting software.
What are some common mistakes in e-commerce Bookkeeping and Accounting?
Common mistakes include inaccurate revenue tracking, failure to reconcile accounts, and not properly accounting for inventory.
Is it necessary to hire an accountant for e-commerce businesses?
While some e-commerce entrepreneurs handle accounting themselves, hiring a professional accountant or using specialized software can help ensure accuracy and compliance as your business grows.
2 Alternatives for GoDaddy Bookkeeping for Etsy, eBay, and Amazon Sellers
In the ever-expanding world of e-commerce, managing your finances efficiently is crucial for the success of your online business. GoDaddy Bookkeeping has been a popular choice among Etsy, eBay, and Amazon sellers for streamlining their financial processes. However, if you’re looking for alternatives that offer similar features and benefits, you’re in the right place. In this article, we will explore two excellent alternatives to GoDaddy Bookkeeping that cater to the specific needs of online sellers.

QuickBooks GoDaddy Online
Simplifying Financial Management
For many small business owners, GoDaddy QuickBooks Online has been a trusted companion for years. It offers a comprehensive suite of tools that can be tailored to fit the unique needs of Etsy, eBay, and Amazon sellers.
Seamlessly Sync with Marketplaces
One of the standout features of QuickBooks Online is its ability to seamlessly sync with popular online marketplaces like GoDaddy Etsy, eBay, and Amazon. This means that all your sales, fees, and expenses are automatically imported into the system, saving you precious time and minimizing the risk of data entry errors.
Robust Reporting and Analytics
QuickBooks Online provides detailed financial reports and analytics that allow you to gain insights into your business’s performance. You can track your sales trends, monitor expenses, and even prepare for tax season with ease.
User-Friendly Interface
The user-friendly interface of QuickBooks Online GoDaddy makes it accessible even for those without a strong financial background. Navigating through income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements becomes a breeze.
Scalability
As your online business grows, QuickBooks Online grows with you. You can easily upgrade to more advanced plans that offer additional features, making it suitable for both startups and established enterprises.
Wave Financial
Budget-Friendly Solution
If you’re just starting out as a GoDaddy Etsy, eBay, or Amazon seller and want a budget-friendly accounting solution, Wave Financial might be the perfect fit. It’s a free accounting software that offers essential features without the cost.
Invoice and Receipt Scanning
Wave Financial simplifies invoicing and expense tracking by allowing you to scan receipts and generate professional invoices right from the platform. This is particularly handy for small business owners who are always on the go.
Bank Reconciliation
Keeping your financial records accurate is crucial. Wave Financial helps you reconcile your bank accounts effortlessly, ensuring that your books are always up-to-date.
Collaboration
If you have a team working on your e-commerce business, Wave Financial allows multiple users to collaborate on the platform. This ensures that everyone is on the same page when it comes to financial matters.
Tax Services
Preparing for tax season can be a daunting task, but Wave Financial offers tax services to simplify the process. You can generate tax reports and even connect with tax professionals for assistance.
Conclusion
Managing the finances of your GoDaddy, Etsy, eBay, or Amazon business is a critical aspect of your success. While GoDaddy Bookkeeping has been a reliable choice for many, QuickBooks Online and Wave Financial offer compelling alternatives with unique features tailored to the needs of e-commerce sellers.
Whether you prioritize seamless synchronization with marketplaces, budget-friendly solutions, or in-depth financial insights, there’s an alternative that suits your preferences. Consider your business’s specific requirements and choose the accounting software that best aligns with your goals.
Are QuickBooks Online GoDaddy and Wave Financial suitable for small businesses?
Yes, both QuickBooks Online GoDaddy and Wave Financial are suitable for small businesses, including Etsy, eBay, and Amazon sellers. They offer scalable solutions that can grow with your business.
Can I use QuickBooks Online and Wave Financial on mobile devices?
Yes, both QuickBooks Online and Wave Financial offer mobile apps, allowing you to manage your finances on the go.
Do these alternatives offer customer support?
Yes, both QuickBooks Online and Wave Financial provide customer support to assist you with any questions or issues you may encounter while using their platforms.
Are there any hidden fees with QuickBooks Online and Wave Financial?
QuickBooks Online and Wave Financial are transparent about their pricing. While Wave Financial offers a free plan, QuickBooks Online has various pricing tiers, so you can choose the one that suits your budget and needs.
Can I import my existing financial data into QuickBooks Online or Wave Financial?
Yes, both platforms offer tools to help you import your existing financial data, making the transition to a new accounting system smooth and hassle-free.
How to start a bookkeeping business?
How to Start a Bookkeeping Business Step-by-Step
Starting your own bookkeeping business can be a rewarding venture. Not only is there a growing demand for bookkeeping services, but it also allows you the flexibility of being your own boss. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the essential steps to kickstart your bookkeeping business successfully.

What are the basic steps of a bookkeeping business?
Before diving into the bookkeeping business, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of bookkeeping principles. If you’re not already trained in bookkeeping, consider taking courses or obtaining relevant certifications to boost your credibility.
What is the next step in your skills assessment?
Evaluate your skills and qualifications honestly. Are you proficient in accounting software? Do you have attention to detail? Knowing your strengths and weaknesses will help you determine your niche in the bookkeeping business.
What is target market research & why is it important?
Research your local market to identify potential clients and competitors. Determine your target audience, whether it’s small businesses, startups, or individuals.
How do I find a target audience?
Finding a target audience following these steps:
Market Research: Study your industry and competition to identify potential customers.
Customer Profiling: Create detailed personas of your ideal customers, considering demographics, interests, and behavior.
Surveys and Feedback: Gather input from existing customers to refine your target audience understanding.
Social Media Insights: Use analytics tools to analyze your social media following and engagement to pinpoint your audience.
Test and Refine: Experiment with different approaches and refine your target audience as you gain insights.

What are the legal requirements when starting a business?
Create a business plan outlining your goals, services, and financial projections. Register your business and comply with legal requirements, including licenses and permits.
How do you set up an office?
Set up a dedicated workspace in your home or consider renting an office. Ensure it is well-organized and equipped with the necessary tools.
Investing in Necessary Tools and Software
Invest in accounting software and tools to streamline your work. Popular choices include QuickBooks, Xero, or FreshBooks.
What price should be set under marginal cost pricing?
Determine your pricing strategy. Will you charge hourly or offer package deals? Consider competitive rates while ensuring you cover your costs and make a profit.
What are the most effective branding strategies?
Create a strong brand identity, including a logo and business cards. Develop a marketing strategy that includes online and offline promotion.
How can I improve my social media presence?
In today’s digital age, having a website and active social media profiles is essential. It helps potential clients find and connect with you.
What is customer acquisition & retention?
Network with local businesses and attend industry events. Offer excellent service to retain clients and gain referrals.
How do I Manage my finances?
Practice what you preach – maintain impeccable financial records for your business. This not only keeps you organized but also sets an example for your clients.
What is professional growth in the context of workplace learning?
Stay updated with industry trends and regulations. Consider joining professional associations and attending workshops.
What is business networking?
Build relationships with other professionals in related fields like accounting, tax, and business consulting. Collaboration can lead to new opportunities.
How do you handle a challenge?
Expect challenges along the way. Competition is fierce, but staying focused on your goals and continuously improving your skills will set you apart.
What Are Professional and Specialized Services?
Consider specializing in a niche. While general bookkeeping is always in demand, focusing on a specific industry or type of client can give you a competitive edge. For example, you could specialize in healthcare, e-commerce, or freelancers. Specialization allows you to tailor your services and marketing efforts more effectively.
How to build trust and credibility as a leader?
Trust is crucial in the bookkeeping business. Clients are entrusting you with their financial data, so you must build credibility. Maintain confidentiality, adhere to ethical standards, and consider obtaining professional certifications like Certified Public Bookkeeper (CPB) or Certified Bookkeeper (CB).
How does tax compliance work?
Bookkeepers often play a vital role in helping clients with tax preparation and compliance. Stay updated on tax laws and regulations relevant to your clients. Offering tax planning services can be a significant value-add.
How do I scale my business?
As your business grows, you may want to hire additional staff or subcontract work. Ensure that your team is well-trained and aligned with your business’s values and quality standards. Scaling can lead to increased revenue and client capacity.
Client Relationship Management
Building strong relationships with your clients is key to long-term success. Listen to their needs, communicate regularly, and provide valuable insights. Happy clients are more likely to stay with you and refer others.
What is Cybersecurity and Data Protection?
Given the sensitive financial data you handle, prioritize cybersecurity. Invest in robust data protection measures, use secure software, and educate yourself on common cybersecurity threats. Clients need to trust that their information is safe with you.
Handling Seasonal Workloads
bookkeeping business often involves seasonal peaks, such as during tax season. Plan ahead for increased workloads by hiring temporary help or implementing efficient workflow management systems.
Evaluating Your Progress
Regularly assess your business’s performance. Track key metrics like client retention, revenue growth, and profitability. Use this data to make informed decisions about your business strategy.
Community Involvement
Engage with your local community. Sponsor local events, give workshops, or volunteer your bookkeeping services for non-profits. Community involvement can raise your profile and attract local clients.
Embracing Technology
Stay updated with the latest accounting and bookkeeping software. Automation can save you time and reduce errors. Additionally, cloud-based solutions allow you to work remotely and collaborate with clients seamlessly.
Adapting to Changes
The financial industry is continuously evolving, with new technologies and regulations emerging. Stay flexible and be willing to adapt to these changes to remain competitive and relevant.
What qualifications do I need to start a bookkeeping business?
To start a bookkeeping business, it’s essential to have a strong understanding of accounting principles. Obtaining relevant certifications or training is highly recommended.
How do I determine my pricing as a bookkeeper?
Your pricing should consider factors like your location, the complexity of services offered, and market rates. Research local competitors and set competitive yet profitable rates.
Do I need a physical office to run a bookkeeping business?
While a physical office is not mandatory, having a dedicated workspace is advisable for organization and professionalism. Many bookkeepers operate from home offices.
What software is best for bookkeeping businesses?
Popular bookkeeping software options include QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks. The choice depends on your specific needs and preferences.
How can I market my bookkeeping services effectively?
Effective marketing strategies include building a strong online presence, networking with local businesses, and offering exceptional service to generate word-of-mouth referrals.
How do I learn basic bookkeeping concepts?
How to Learn Basic Bookkeeping Concepts?
When it comes to managing your finances, whether for personal use or in the context of a small business, understanding basic bookkeeping concepts is paramount. Bookkeeping serves as the foundation of financial management, enabling you to keep track of income, expenses, and overall financial health. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the fundamentals of bookkeeping, making it accessible to beginners and providing valuable insights for those looking to refine their skills.
What is Bookkeeping?
Bookkeeping is the process of systematically recording, organizing, and maintaining financial transactions. It forms the basis of accounting and ensures that all financial data is accurate and up-to-date.
Importance of Bookkeeping
Learn why bookkeeping is essential for individuals and businesses. We’ll explore how it helps in budgeting, tax compliance, and decision-making.
Basic Bookkeeping Principles
In this section, we will delve into the core principles of bookkeeping, including the accrual and cash basis methods, double-entry accounting, and the accounting equation.
Setting Up Your Books
Discover the practical steps to set up a bookkeeping system. We’ll cover choosing the right software or ledger, creating accounts, and organizing financial documents.
Recording Transactions
Learn how to record various types of financial transactions, from income and expenses to assets and liabilities. We’ll provide real-world examples to illustrate the process.
Chart of Accounts
Understand the importance of a chart of accounts and how to create one tailored to your specific needs. This tool helps you categorize and track financial activities efficiently.
Debits and Credits
Demystify the concept of debits and credits, a fundamental aspect of double-entry accounting. We’ll explain how they affect your financial records.
Financial Statements
Explore the creation of key financial statements: the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Learn how they provide insights into your financial health.
Reconciliation
Discover the importance of reconciling your bank statements with your bookkeeping records. We’ll walk you through the process to ensure accuracy.
Budgeting and Forecasting
See how bookkeeping plays a crucial role in creating budgets and forecasts. Effective financial planning is vital for success.
Taxation
Gain insights into how bookkeeping helps you prepare for tax season. Learn about deductions, credits, and the importance of accurate records.
Software and Tools
Explore the various bookkeeping software options available, from simple spreadsheets to advanced accounting software. We’ll help you choose the right one for your needs.
Common Bookkeeping Mistakes
Avoid pitfalls by learning about common bookkeeping errors and how to prevent them. Accuracy is key in maintaining your financial records.
Continuous Learning
Bookkeeping is a skill that evolves. Discover resources and strategies for ongoing learning and staying updated with industry trends.
What are creative bookkeeping techniques?
You’ve grasped the fundamentals, let’s explore some advanced bookkeeping techniques:
Accrual vs. Cash Basis Accounting
We touched upon these two accounting methods. As you become more proficient, you may need to decide which method best suits your needs. Accrual accounting records transactions when they occur, while cash-based accounting records them when cash changes hands. The choice depends on your business type and financial goals.
Depreciation
Understanding depreciation is crucial, especially for businesses with significant assets like machinery or vehicles. Depreciation accounts for the gradual reduction in the value of assets over time. Learning how to calculate and record depreciation expenses accurately is essential for financial accuracy.
Inventory Management
If you run a business that involves selling products, managing your inventory is vital. Effective inventory tracking ensures you have enough stock to meet demand without overstocking, which can tie up capital.
Payroll Accounting
If you have employees, you’ll need to master payroll accounting. This includes accurately recording salary and wage expenses, payroll taxes, and benefits. Payroll accounting also involves compliance with labor laws and tax regulations.
Bank Reconciliation
While we discussed reconciling your books in Chapter 9, advanced bookkeepers often deal with more complex financial transactions. These may include multiple bank accounts, investments, and loans. Being proficient in reconciling such accounts is crucial to maintaining financial accuracy.
What is the difference between bookkeeping and accounting?
Bookkeeping involves recording financial transactions, while accounting involves interpreting, analyzing, and summarizing those transactions to make informed financial decisions.
Do I need to hire a professional bookkeeper?
It depends on the complexity of your financial situation. Many individuals and small businesses successfully manage their bookkeeping, especially with the help of user-friendly software.
Is bookkeeping software necessary, or can I use a spreadsheet?
While spreadsheets can be used for basic bookkeeping, specialized software can streamline the process and provide more robust financial insights.
How often should I reconcile my books?
Reconciliation should ideally be done monthly to catch discrepancies early and maintain accurate financial records.
Can I outsource bookkeeping for my small business?
Yes, many firms offer bookkeeping services for businesses of all sizes. It can be a cost-effective solution that allows you to focus on growing your business.
Can I switch from cash basis to accrual accounting (or vice versa)?
Yes, you can switch accounting methods, but it may have tax implications. Consult with a tax professional or accountant before making the switch.
What is the role of bookkeeping in audits?
Accurate bookkeeping is crucial during an audit. It provides a clear trail of financial transactions and helps demonstrate compliance with tax and accounting regulations.
Are there any free bookkeeping courses available?
Yes, many online platforms offer free or low-cost bookkeeping courses. Look for reputable sources like universities or well-known financial institutions.
How can I use bookkeeping to make better financial decisions?
Bookkeeping provides the data you need to make informed decisions. Regularly review your financial statements to spot trends, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic choices.
Can bookkeeping be automated?
Yes, there are numerous bookkeeping software options that offer automation for routine tasks. However, a human touch is often needed for complex transactions and decision-making.
What is financial advisory?

What is financial advisory?
Financial advisory refers to the practice of providing expert advice and guidance to individuals, businesses, and organizations regarding their financial decisions. It encompasses a wide range of services aimed at helping clients make informed choices and achieve their financial goals.
Importance of Financial Advisory
In today’s complex and ever-changing financial landscape, having access to professional financial advice is crucial. Financial advisory services play a vital role in helping individuals and businesses navigate the complexities of investments, taxes, estate planning, retirement, and more. By working with a knowledgeable financial advisor, clients can gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and optimize their financial resources for long-term success.
What are the duties and responsibilities of a financial advisor?
Financial advisors play a crucial role in guiding individuals, businesses, and organizations in their financial decision-making. Their duties and responsibilities encompass a wide range of tasks aimed at helping clients achieve their financial goals.
Financial Assessment: A financial advisor begins by conducting a comprehensive assessment of a client’s financial situation. This includes analyzing their income, expenses, assets, liabilities, investments, and financial goals. By understanding the client’s current financial standing, the advisor can provide tailored recommendations and strategies.
Goal Setting: Once the financial assessment is complete, the financial advisor works closely with the client to define their short-term and long-term financial goals. These goals may include saving for retirement, buying a home, funding education, starting a business, or achieving financial independence. The advisor helps clarify objectives and establishes realistic benchmarks for progress.
Financial Planning: Based on the client’s financial assessment and goals, the financial advisor develops a comprehensive financial plan. This plan outlines specific strategies and recommendations to help the client achieve their objectives. It may include investment strategies, tax planning, retirement planning, risk management, estate planning, and other relevant components.
Investment Management: One key responsibility of a financial advisor is managing and optimizing a client’s investment portfolio. This involves conducting research, analyzing market trends, assessing risk tolerance, and recommending appropriate investment options. The advisor monitors the portfolio’s performance, makes adjustments as necessary, and ensures it aligns with the client’s objectives and risk profile.
Risk Management: Financial advisors help clients identify and manage financial risks. They assess the client’s risk tolerance and recommend suitable risk management strategies, such as insurance coverage or diversification of investments. The advisor guides clients on protecting their assets, managing debt, and mitigating potential financial setbacks.
Retirement Planning: Planning for retirement is a critical aspect of financial advisory services. Financial advisors help clients estimate their retirement needs, develop savings strategies, and create retirement income plans. They provide guidance on retirement accounts, pension plans, Social Security, and other retirement-related considerations to ensure clients are well-prepared for their post-work years.
Tax Planning: Financial advisors assist clients in optimizing their tax strategies. They stay updated on tax laws, deductions, credits, and exemptions to help clients minimize their tax liabilities while remaining compliant. The advisor provides guidance on tax-efficient investment options, retirement account contributions, charitable giving, and other strategies to maximize tax advantages.
Estate Planning: Financial advisors work with clients to develop estate plans that ensure the smooth transfer of assets to intended beneficiaries. They assist in creating wills, establishing trusts, and implementing strategies to minimize estate taxes. The advisor considers the client’s wishes, family dynamics, and long-term financial goals when crafting an effective estate plan.
Ongoing Monitoring and Reviews: Financial advisors regularly review and monitor their client’s financial plans and portfolios. They track progress toward goals, assess the performance of investments, and make adjustments as necessary. The advisor keeps clients informed about their financial status, providing periodic reports and conducting meetings to discuss any changes or updates.
Client Education and Communication: Financial advisors play a vital role in educating and empowering clients to make informed financial decisions. They explain complex financial concepts, investment strategies, and industry trends in a clear and accessible manner. The advisor communicates regularly with clients, providing guidance, answering questions, and ensuring clients have a comprehensive understanding of their financial situation.
What are the Qualifications and Certifications of a Financial Advisor?
When seeking a financial advisor, it is crucial to consider their qualifications and certifications. Look for professionals who hold relevant certifications such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP), Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), or Certified Public Accountant (CPA). These designations indicate that the advisor has undergone rigorous training, possesses the necessary knowledge and expertise, and adheres to ethical standards.
What are the benefits of having a financial advisor?
Engaging a financial advisor offers numerous benefits. Firstly, they bring expertise and experience to the table, providing clients with a comprehensive understanding of various financial aspects. Advisors can help identify blind spots and potential risks while uncovering opportunities for growth and wealth accumulation. Moreover, they provide objective advice, free from emotional biases that often hinder sound decision-making. Financial advisors also save clients valuable time by handling complex financial tasks, allowing them to focus on other aspects of their lives or businesses.
Do I really need a financial adviser?
Financial advisory services cover a broad spectrum. Some advisors specialize in investment management, helping clients build portfolios and make strategic investment decisions. Others focus on retirement planning, ensuring clients have a solid financial foundation for their post-work years. Estate planning advisors assist clients in creating plans for the distribution of assets after their demise. Additionally, tax advisors help individuals and businesses optimize their tax strategies, while insurance advisors provide guidance on risk management and protection.
What Does a Financial Advisor Do?
The financial advisory process typically involves several steps. Firstly, the advisor and client establish a relationship and define the client’s financial goals and objectives. The advisor then collects relevant financial information, assesses the client’s risk tolerance, and analyzes their current financial situation. Based on this analysis, the advisor develops a customized financial plan that outlines strategies and recommendations for achieving the client’s goals. Once the plan is implemented, the advisor monitors its progress, making adjustments as necessary.
How To Choose A Financial Advisor?
Choosing the right financial advisor is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your financial well-being. With numerous options available, it’s essential to consider several key factors when selecting a financial advisor who aligns with your needs and goals. Here are some important steps to help you make an informed choice:
1. Determine Your Needs: Start by identifying your specific financial needs and goals. Are you looking for assistance with retirement planning, investment management, tax planning, estate planning, or a comprehensive financial plan? Understanding your requirements will help you narrow down your search and find an advisor with expertise in the areas that matter most to you.
2. Research Credentials and Qualifications: Look for financial advisors who hold relevant professional certifications and qualifications. Common certifications include Certified Financial Planner (CFP), Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), or Personal Financial Specialist (PFS). These designations indicate that the advisor has met rigorous educational and ethical standards.
3. Check for Experience and Expertise: Consider the advisor’s experience in the financial industry and their specific area of expertise. Look for advisors who have worked with clients similar to you in terms of financial goals, assets, and life stage. A seasoned advisor with a deep understanding of your needs is more likely to provide tailored advice and strategies.
4. Seek Recommendations: Ask for recommendations from trusted sources such as friends, family, or colleagues who have had positive experiences with financial advisors. Personal referrals can provide valuable insights and help you identify advisors with a track record of delivering quality service and achieving client satisfaction.
5. Research Reputation and Reviews: Conduct online research to learn more about the advisor’s reputation and client reviews. Visit their website, check for testimonials, and search for any news articles or disciplinary actions related to the advisor. Reviewing unbiased feedback from previous or current clients can provide valuable insights into the advisor’s professionalism and performance.
6. Evaluate Fee Structure: Understand how the financial advisor charges for their services. Some advisors charge a percentage of assets under management (AUM), while others may charge an hourly fee or a fixed fee for specific services. Compare fee structures and ensure they align with your budget and preferences.
7. Consider Fiduciary Duty: It is advisable to work with a financial advisor who operates under a fiduciary standard. Fiduciary advisors are legally obligated to act in your best interest and prioritize your needs above their own. This ensures that they provide objective advice and recommendations that are solely focused on your financial well-being.
8. Request a Consultation: Schedule initial consultations with a shortlist of financial advisors to gauge their communication style, approach, and compatibility. During these meetings, ask questions about their experience, services, investment philosophy, and how they tailor their advice to clients’ goals. Pay attention to how well the advisor listens, communicates, and addresses your concerns.
9. Consider Communication and Accessibility: Ensure that the financial advisor you choose maintains open and clear communication channels. They should be accessible and responsive to your inquiries and provide regular updates on your financial plan and investments. Clear communication and a strong working relationship are essential for a successful advisory partnership.
10. Trust Your Instincts: Ultimately, trust your instincts when selecting a financial advisor. Consider how comfortable you feel with the advisor, their level of transparency, and their ability to explain complex concepts in a way that you understand. Building trust and rapport is vital for a long-term advisory relationship.
By following these steps and conducting thorough due diligence, you can increase your chances of finding a reputable financial advisor who is well-suited to your needs.
What is financial advisor misconduct?
There are various misconceptions surrounding financial advisory that need to be addressed. One common misconception is that financial advisory is only for the wealthy. In reality, financial advisory services are beneficial for individuals at various income levels, as they provide guidance on managing finances, saving, and investing. Another misconception is that financial advisors are primarily focused on selling financial products. While some advisors may sell products, reputable professionals prioritize their client’s best interests and provide holistic advice that extends beyond product recommendations.
What is a Case Study: Real-life Examples of Successful Financial Advisory?
Real-life case studies can demonstrate the tangible benefits of financial advisory. For example, a couple struggling with debt and financial mismanagement may seek the guidance of a financial advisor. Through proper budgeting, debt management strategies, and long-term planning, the advisor helps the couple regain control over their finances and achieve stability. Another case study could involve a business owner who consults with a financial advisor to optimize their company’s cash flow, expand operations, and plan for succession.
Tips for Maximizing the Value of Financial Advisory
To maximize the value of financial advisory, clients can follow certain tips and best practices. Firstly, it is crucial to communicate openly and honestly with the advisor, providing all relevant financial information and expressing clear goals and expectations. Regularly reviewing and updating the financial plan, especially during significant life events, ensures its relevance and effectiveness. So, clients should actively engage in the advisory process, asking questions, seeking clarification, and actively participating in decision-making.
What are the pros and cons of being a financial advisor?
While financial advisory offers numerous benefits, it is essential to acknowledge its inherent risks and limitations. Financial markets are unpredictable, and investment returns are subject to various factors beyond the advisor’s control. Advisors can provide recommendations based on historical data and analysis, but future outcomes are never guaranteed. It is also important to recognize that financial advisory fees can vary, and some advisors may have conflicts of interest. Clients should carefully evaluate the terms of engagement and seek transparency from their advisors.
Do financial advisors need to be ready for the future?
The field of financial advisory continues to evolve with advancements in technology and changing client expectations. Robo-advisors, for example, leverage artificial intelligence and algorithms to provide automated investment advice and portfolio management. Virtual advisory platforms are also gaining popularity, allowing clients to access advisory services remotely. As the financial industry becomes increasingly digitized, financial advisors must adapt to new technologies and offer personalized, tech-driven solutions to remain competitive.
Do I really need a financial adviser?
Navigating the complexities of personal finance can be challenging, and you may find yourself wondering if you really need a financial adviser. While it is possible to manage your finances independently, there are several compelling reasons why working with a financial adviser can be highly beneficial. Let’s explore some key considerations to help you make an informed decision.
1. Expertise and Experience: Financial advisers possess specialized knowledge and expertise in various areas of finance. They stay up-to-date with market trends, tax laws, investment strategies, and other financial aspects. By leveraging their experience and insights, they can provide valuable guidance tailored to your unique financial situation.
2. Objective Advice: Emotions can often cloud our judgment when it comes to financial decision-making. A financial adviser provides an objective viewpoint and can help you make rational choices based on your goals and risk tolerance. They can guide you through tough decisions and keep you focused on your long-term financial objectives.
3. Personalized Financial Plan: A financial adviser will work closely with you to understand your financial goals, aspirations, and concerns. They will assess your current financial situation and develop a personalized financial plan that aligns with your objectives. This plan will serve as a roadmap to guide your financial decisions and ensure you stay on track.
4. Comprehensive Financial Management: Managing finances goes beyond just investments. A financial adviser can assist you with various aspects of your financial life, including budgeting, tax planning, retirement planning, estate planning, insurance coverage, and more. They take a holistic approach, considering all relevant factors to help you achieve financial well-being.
5. Time and Convenience: Handling your finances can be time-consuming, especially if you have complex financial needs or a busy schedule. Engaging a financial adviser allows you to delegate financial tasks to a professional, freeing up your time to focus on other priorities. They will handle the research, analysis, paperwork, and ongoing monitoring, providing you with convenience and peace of mind.
6. Accountability and Discipline: A financial adviser acts as a trusted accountability partner. They will help you stay disciplined and committed to your financial plan, providing encouragement and guidance along the way. This accountability can be invaluable, especially during challenging times or when faced with tempting financial opportunities.
7. Maximizing Opportunities and Minimizing Risks: Financial advisers can identify potential opportunities for growth and wealth accumulation while mitigating risks. They conduct thorough research, assess investment options, and develop strategies to optimize your financial resources. By tapping into their expertise, you can make more informed decisions and potentially enhance your financial outcomes.
How much does financial advisory typically cost?
The cost of financial advisory services varies depending on factors such as the complexity of the client’s financial situation, the scope of services provided, and the advisor’s fee structure. Advisors may charge a percentage of assets under management, an hourly fee, or a fixed fee for specific services. It is important to discuss and clarify the fee structure with the advisor before engaging in their services.
Can I benefit from financial advisory if I have limited financial resources?
Yes, financial advisory can be beneficial regardless of the size of your financial resources. Advisors can provide guidance on budgeting, saving, debt management, and other financial aspects that can help individuals make the most of their current resources and plan for future growth.
How often should I meet with my financial advisor?
The frequency of meetings with your financial advisor depends on your specific needs and circumstances. Initially, meetings may be more frequent to establish a financial plan and set goals. Subsequently, regular reviews and updates can be conducted annually or semi-annually, or as significant life events occur that may require adjustments to the plan.
Are financial advisors required to act in my best interest?
Financial advisors who are registered as fiduciaries are legally obligated to act in the best interests of their clients. They must prioritize their client’s needs and goals above any potential conflicts of interest. It is advisable to work with advisors who operate under a fiduciary standard to ensure they are working in your best interest.
How can I find a reputable financial advisor?
Finding a reputable financial advisor involves conducting thorough research and due diligence. Seek recommendations from trusted sources, such as friends, family, or other professionals in the financial industry. Verify the advisor’s credentials, certifications, and disciplinary history, if any. Additionally, consider scheduling initial consultations with multiple advisors to evaluate their expertise, communication style, and compatibility with your financial goals.

What is property management accounting?
Property management accounting is a specialized field that focuses on the financial management of real estate assets. It encompasses a range of activities related to tracking, analyzing, and reporting financial data associated with properties. The primary goal of property management accounting is to ensure that property owners, managers, and stakeholders have accurate and timely financial information to make informed decisions and optimize the performance of their real estate investments.
What are the most important property management accounting principles?
To effectively manage property finances, several key principles guide property management accounting:
Accuracy and Integrity of Financial Data
Accurate and reliable financial data is essential in property management accounting. It involves maintaining precise records of income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. By ensuring the integrity of financial information, property management accountants can provide a clear picture of the property’s financial health and facilitate informed decision-making.
Compliance with Regulations and Standards
Property management accounting must adhere to relevant regulations and accounting standards. This includes complying with local, state, and federal tax laws, as well as adhering to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or international financial reporting standards (IFRS). Compliance helps prevent legal issues and ensures transparency in financial reporting.
Cost Management and Efficiency
Property management accountants focus on optimizing costs and improving efficiency in property operations. They analyze expenses, identify cost-saving opportunities, negotiate contracts, and monitor budgetary allocations. Effective cost management enhances profitability and increases the value of the property.
Why are financial reports so important?
Accurate financial reporting is crucial in property management accounting for several reasons:
Informed Decision-Making
Accurate financial reports provide property owners and managers with valuable insights into the property’s financial performance. This information enables them to make informed decisions regarding rental rates, property improvements, cost reductions, and investment strategies.
Transparency and Accountability
Transparent financial reporting fosters trust and accountability among property owners, investors, and stakeholders. It allows them to assess the property’s financial health, evaluate the effectiveness of management practices, and ensure compliance with financial obligations.
Tax Compliance and Planning
Proper financial reporting ensures compliance with tax regulations and facilitates effective tax planning. Property management accountants can track deductible expenses, depreciation, and other tax-related items accurately, minimizing tax liabilities and maximizing tax benefits for property owners.
Investor Confidence
Accurate financial reporting enhances investor confidence in real estate assets. Potential investors rely on financial statements and reports to assess the profitability and viability of investment opportunities. Reliable financial information helps attract investors and secure financing for property acquisitions and developments.
Components of Property Management Accounting
Property management accounting comprises various components that contribute to effective financial management. Let’s explore some key components:
Rental Income Tracking
Tracking rental income is a fundamental aspect of property management accounting. It involves recording and monitoring rental payments, ensuring timely collections, and reconciling any discrepancies. Accurate rental income tracking helps property managers assess cash flow, evaluate rental performance, and identify any rental arrears or potential issues.
Expense Management
Managing expenses is crucial for maintaining profitability in property management. Property management accountants track and categorize various expenses, including property maintenance, repairs, insurance, utilities, and property taxes. By closely monitoring expenses, they can identify cost-saving opportunities and implement strategies to optimize spending.
Budgeting and Forecasting
Property management accounting involves creating budgets and financial forecasts to guide decision-making. Accountants work closely with property managers to develop realistic budgets that align with the property’s financial goals. Regular monitoring of actual performance against budgeted amounts allows for early detection of deviations and prompt corrective actions.
Cash Flow Analysis
Cash flow analysis is essential to ensure the property’s financial stability and liquidity. Property management accountants track cash inflows and outflows, project future cash flows, and assess the property’s ability to meet financial obligations. Effective cash flow management helps property owners avoid cash shortages and maintain a healthy financial position.
Lease and Tenant Management
Property management accounting involves managing leases and tenant-related financial transactions. This includes recording lease agreements, tracking rental terms, calculating rent escalations, and managing security deposits. Accurate lease and tenant management contribute to efficient rent collection, lease renewals, and tenant relations.
Tax Compliance
Property management accountants play a vital role in ensuring tax compliance for property owners. They keep abreast of tax regulations, prepare necessary tax documentation, and submit accurate tax returns. By managing tax compliance effectively, property management accountants help property owners avoid penalties and maximize tax benefits.
What are the benefits of property management?
Implementing property management accounting systems offers several benefits:
Streamlined Financial Processes
Property management accounting systems automate financial processes, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency. These systems facilitate seamless data entry, integration with other property management software, and the generation of accurate financial reports.
Enhanced Decision-Making
Access to real-time financial information enables property owners and managers to make data-driven decisions. Property management accounting systems provide comprehensive reports, dashboards, and analytics that help evaluate performance, identify trends, and make informed choices to maximize profitability.
Improved Tenant Relations
Effective property management accounting contributes to positive tenant relations. Clear and accurate financial communication, such as itemized rent statements and transparent expense tracking, fosters trust and strengthens tenant relationships.
Risk Mitigation
Proper financial record-keeping and compliance with regulations help mitigate risks associated with property management. Property management accounting systems enable proper documentation, tracking of legal obligations, and adherence to accounting standards, reducing the likelihood of legal disputes and financial irregularities.
What is the best property management accounting software?
Several property management accounting software solutions are available in the market. These software options offer features such as rent tracking, expense management, financial reporting, and integration with other property management tools. Some popular software choices include:
QuickBooks- Rent Manager
AppFolio Property Manager
Yardi Voyager
Buildium
Propertyware
RealPage
When selecting a property management accounting software, it is important to consider the specific needs of your property portfolio, budget constraints, user-friendliness, and customer support offered by the software provider.
What are the best property management accounting tools?
When choosing a property management accounting solution, consider the following factors:
Scalability and Flexibility
Select a software solution that can accommodate the size and complexity of your property portfolio. Ensure that the software allows for scalability and flexibility as your business grows.
Integration Capabilities
Consider whether the accounting software can integrate with other property management tools you use, such as maintenance management systems or tenant screening platforms. Integration capabilities streamline processes and enhance efficiency.
User-Friendliness and Training
Opt for software that is intuitive and user-friendly, reducing the learning curve for your team. Additionally, inquire about training and support options provided by the software vendor to ensure smooth implementation and ongoing assistance.
Security and Data Privacy
Data security is paramount in property management accounting. Evaluate the software’s security measures, including data encryption, user access controls, and compliance with data protection regulations.
Property management accounting best practices
To optimize property management accounting practices, consider the following best practices:
Regular Reconciliation
Perform regular reconciliations of financial records to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies promptly. Reconcile bank statements, rental income, and expense records to maintain the integrity of financial data.
Document Management
Maintain proper documentation of all financial transactions, including invoices, receipts, lease agreements, and vendor contracts. Organized and easily accessible documentation facilitates audits, compliance, and dispute resolution.
Ongoing Education and Professional Development
Stay updated with changes in accounting regulations and industry best practices. Invest in ongoing education and training for property management accountants to enhance their skills and knowledge.
Utilize Technology Solutions
Leverage technology solutions, such as cloud-based accounting software and automation tools, to streamline processes, reduce manual errors, and improve efficiency.
The Role of Property Management Accountants
Property management accountants play a crucial role in managing the financial aspects of real estate assets. Their responsibilities include:
Tracking rental income and expenses
Preparing financial statements and reports
Analyzing financial data to assess property performance
Managing budgets and cash flow
Ensuring compliance with tax regulations
Providing financial insights and recommendations to property owners and managers
Property management accountants work closely with property managers, stakeholders, and external parties such as auditors and tax advisors to maintain accurate financial records and drive profitability.
Challenges in Property Management Accounting
Property management accounting faces several challenges, including:
Complexities in Revenue Recognition
Different types of revenue sources in property management, such as rent, utilities, and ancillary services, can pose challenges in revenue recognition. Property management accountants must accurately allocate revenue from various sources and ensure compliance with accounting standards.
Expense Tracking and Allocation
Tracking and allocating expenses across multiple properties can be complex, particularly for property portfolios with diverse assets. Property management accountants must develop efficient systems to track and allocate expenses accurately.
Evolving Regulatory Environment
Changes in tax regulations and accounting standards require property management accountants to stay updated and adapt their practices accordingly. Compliance with evolving regulations can be challenging, particularly for properties located in different jurisdictions.
Future Trends in Property Management Accounting
The field of property management accounting is evolving to keep pace with technological advancements and industry trends. Some future trends to watch out for include:
Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Automation and AI technologies are increasingly being integrated into property management accounting processes. These technologies streamline repetitive tasks, enhance data accuracy, and provide real-time insights for decision-making.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based property management accounting solutions offer greater flexibility, accessibility, and collaboration. They allow property managers and accountants to access financial data from anywhere, improving efficiency and facilitating remote work.
Data Analytics and Predictive Insights
Data analytics tools enable property management accountants to extract meaningful insights from large volumes of financial data. Predictive analytics can help forecast rental trends, identify potential risks, and optimize property performance.
Sustainability Reporting
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in the real estate industry, property management accounting will include sustainability reporting. Accountants will track and report on energy consumption, carbon emissions, and other sustainability metrics.
Accounting for property management companies
Property management accounting involves tracking rental income, managing expenses, and maintaining financial records for multiple properties. It includes tasks such as rent collection, lease and tenant management, budgeting, cash flow analysis, and tax compliance.
By implementing sound accounting practices, property management companies can optimize their financial performance, streamline processes, and maintain transparency with property owners and stakeholders. Accurate accounting enables property managers to assess profitability, monitor cash flow, make informed investment decisions, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
What is property management fee?
A property management fee refers to the compensation charged by property management companies for their services in managing and overseeing properties on behalf of property owners. This fee is typically a percentage of the monthly rental income or a flat fee agreed upon between the property owner and the management company.
The property management fee covers a range of services, including tenant screening, lease administration, rent collection, property maintenance and repairs, financial reporting, and handling tenant inquiries and complaints. The fee is justified by the expertise, time, and resources invested by the property management company to ensure the smooth operation and optimal performance of the property.
Property owners benefit from the convenience and peace of mind that comes with entrusting the day-to-day management responsibilities to professionals, allowing them to focus on other aspects of their investment portfolio.
What is property management agreement?
A property management agreement is a legally binding contract between a property owner or investor and a property management company. This agreement outlines the terms and conditions under which the management company will provide services to the property owner.
It typically includes details such as the duration of the agreement, the scope of services to be provided, the responsibilities and obligations of both parties and the financial arrangements, including the property management fee. The agreement may cover various aspects, including tenant screening and placement, rent collection, property maintenance and repairs, lease administration, financial reporting, and legal compliance.
It serves as a blueprint for the working relationship between the property owner and the management company, ensuring clear expectations and a mutual understanding of the roles and responsibilities. A well-drafted property management agreement helps protect the interests of both parties and establishes a framework for effective property management.
Property management accounting best practices
Property management accounting best practices are essential for maintaining accurate financial records and optimizing the financial management of properties. Some key best practices include regular reconciliations to ensure the accuracy of financial data, proper documentation of transactions to facilitate audits and compliance, ongoing education and professional development for property management accountants to stay updated with industry regulations, and the utilization of technology solutions such as cloud-based accounting software and automation tools to streamline processes and reduce manual errors.
Property management accounting certification
Obtaining a property management accounting certification is a valuable credential for professionals working in the field of property management accounting. This certification demonstrates a high level of expertise and knowledge in financial management specific to the real estate industry.
There are several certification programs available that focus on property management accounting, such as the Certified Property Manager (CPM) designation offered by the Institute of Real Estate Management (IREM). These certifications typically require meeting specific education and experience requirements, passing examinations, and adhering to a code of ethics.
By earning a property management accounting certification, professionals can enhance their credibility, expand their career opportunities, and gain a deeper understanding of best practices and industry regulations. Employers and clients often value individuals with certifications as they indicate a commitment to professionalism and a comprehensive understanding of property management accounting principles.
Property management accounting salary
Property management accounting salaries can vary depending on factors such as location, experience, qualifications, and the size and complexity of the property portfolio being managed. In general, property management accountants can expect to earn a competitive salary that reflects their specialized skills and responsibilities.
According to available data, the average annual salary for property management accountants ranges from around $45,000 to $75,000, with the potential for higher earnings based on factors like seniority and industry demand. Professionals with advanced certifications or those working in larger property management firms or high-value real estate markets may command higher salaries. It’s worth noting that salaries can also include additional benefits such as healthcare, retirement plans, and performance bonuses.
Property management accounting journal entries
Property management accounting journal entries are a crucial aspect of maintaining accurate financial records for properties. These entries are used to record various transactions and events related to property management, such as rental income, expenses, repairs, and depreciation. Journal entries follow the double-entry accounting system, which means each entry has a corresponding debit and credit entry.
For example, when recording rental income, the debit entry is made to the cash or accounts receivable account, while the credit entry is made to the rental income account. Similarly, when recording expenses like maintenance or property taxes, the debit entry is made to the respective expense account, and the credit entry is made to the cash or accounts payable account.
Properly documenting these journal entries ensures accurate financial reporting, enables analysis of property performance, and aids in tax compliance. Property management accountants must be knowledgeable about accounting principles and regulations to accurately record these journal entries and maintain the integrity of financial records.
Property management accounting for dummies
Property management accounting can seem daunting at first, but with a simplified approach, even beginners can understand the basics. Property management accounting involves tracking and managing financial transactions related to properties. It includes tasks such as recording rental income, tracking expenses, maintaining financial records, and preparing financial reports.
For those new to property management accounting, it’s important to grasp key concepts such as debits and credits, the double-entry accounting system, and the use of various accounts such as cash, rental income, and expense accounts. It’s also essential to understand the importance of accurate record-keeping, as it enables property managers to analyze property performance, make informed decisions, and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
While property management accounting may involve some complexities, breaking down the concepts and seeking resources and guidance can help beginners navigate this aspect of property management effectively.
Property management accounting policies
Property management accounting policies are a set of guidelines and procedures that govern the financial practices and reporting standards within a property management organization. These policies ensure consistency, accuracy, and transparency in managing the financial aspects of properties. Some common property management accounting policies include guidelines for rent collection, expense tracking and categorization, budgeting and forecasting, vendor payments, and financial reporting.
These policies outline the specific steps to be followed for recording transactions, maintaining proper documentation, and adhering to regulatory requirements. They also address internal controls to prevent fraud or errors, such as the segregation of duties and approval processes. Property management accounting policies provide a framework for property managers and accountants to follow, ensuring that financial practices are conducted in a standardized and compliant manner.
Why is property management accounting important?
Property management accounting is important because it provides property owners and managers with accurate financial information to make informed decisions, ensures compliance with regulations, and enhances profitability.
What are some popular property management accounting software options?
Popular property management accounting software options include QuickBooks, Rent Manager, AppFolio Property Manager, Yardi Voyager, Buildium, Propertyware, and RealPage.
What are the key components of property management accounting?
The key components of property management accounting include rental income tracking, expense management, budgeting and forecasting, cash flow analysis, lease and tenant management, and tax compliance.
How does property management accounting benefit property owners?
Property management accounting benefits property owners by providing them with accurate financial reports for informed decision-making, enhancing tenant relations, ensuring compliance with tax regulations, and attracting investors.
What are some future trends in property management accounting?
Future trends in property management accounting include automation and AI integration, cloud-based solutions, data analytics and predictive insights, and sustainability reporting. These trends aim to improve efficiency, provide real-time insights, and address sustainability concerns in property management accounting.
How do I find a good Small Business Accountant?
Managing the financial aspects of a small business can be challenging, especially for entrepreneurs who may not have a background in accounting. Hiring a good small business accountant can be a game-changer, as they can help you navigate through complex financial matters, optimize tax strategies, and ensure your business’s financial health. In this article, we will explore the process of finding a reliable and proficient small business accountant that suits your specific needs.
Do Banks Hire Accountants?
Yes, banks do hire accountants, and they play a crucial role in the financial operations of banking institutions. Here’s how accountants are typically employed in banks:
Financial Reporting: Accountants in banks are responsible for preparing financial statements and reports in accordance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. This includes balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, which provide an accurate picture of the bank’s financial health.
Audit and Compliance: Accountants ensure that the bank’s financial practices comply with industry regulations and government laws. They often work closely with auditors to facilitate external audits and internal compliance checks.
Risk Assessment: Accountants analyze financial data to identify potential risks and opportunities. They help the bank assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and evaluate the performance of various financial products and services.
Tax Planning and Reporting: Banks have complex tax obligations, and accountants are essential in managing these responsibilities. They ensure the bank complies with tax laws and take advantage of available tax incentives.
Financial Analysis: Accountants in banks conduct financial analysis to assess profitability, cost efficiency, and overall financial performance. They provide valuable insights to help the bank make informed decisions.
Budgeting and Forecasting: Accountants assist in creating budgets and financial forecasts. They work with bank management to allocate resources effectively and plan for future financial needs.
Fraud Detection and Prevention: Accountants play a role in detecting and preventing fraudulent activities within the bank. They analyze transactions and account for unusual patterns that may indicate fraud.
Customer Service: Some banks employ accountants in customer-facing roles, such as financial advisors or loan officers, where their expertise helps clients make informed financial decisions.
Treasury and Cash Management: Accountants in banks manage the institution’s cash flow, ensuring there’s enough liquidity to meet day-to-day operational needs while optimizing the use of available funds.
Investment Management: In larger banks, accountants may be involved in managing the bank’s investments, ensuring that surplus funds are invested wisely to generate returns while managing associated risks.
Importance of a Small Business Accountant
Before diving into the search for a small business accountant, it’s essential to recognize the crucial role they play in your company’s success. Accountants bring their expertise in financial management, tax regulations, and compliance to the table, which can save you time, money, and potential legal troubles. Their guidance and advice can lead to better financial decisions, helping your business thrive.
How do I start a small business accounting system?
The first step in finding the right accountant is to assess your small business’s accounting needs. Consider the size of your business, the volume of financial transactions, and the complexity of your finances. Determine whether you require basic bookkeeping services, tax planning, financial analysis, or all of these and more.
Qualities to Look for in a Small Business Accountant
To ensure a successful partnership, look for specific qualities in a small business accountant. Seek out individuals who are not only qualified and experienced but also possess excellent communication skills, reliability, and a deep understanding of your industry. A good accountant should be someone you can trust with sensitive financial information.
Researching Potential Accountants
Begin your search by researching potential accountants in your local area or online. Check their websites, read reviews, and explore their services to gain insight into their expertise and approach. Narrow down your list to those who appear to align well with your business’s requirements.
Asking for Referrals and Recommendations
Word-of-mouth referrals are valuable in the search for a good accountant. Reach out to fellow business owners, friends, or colleagues who have had positive experiences with accountants and request their recommendations. Personal referrals often provide a level of trust that other forms of research may not offer.
Conducting Interviews
Once you have a shortlist of potential accountants, schedule interviews to get to know them better. During the interviews, discuss your business’s needs and listen to how they propose to address them. Pay attention to their communication style and how well they understand your concerns.
Evaluating Communication Skills
Effective communication between you and your accountant is crucial. Assess how well the accountant listens to your questions and concerns and how clearly they explain financial matters to you. A good small business accountant should be able to break down complex concepts into understandable terms.
Checking Credentials and Certifications
Before making a decision, verify the accountant’s credentials and certifications. Ensure they have the necessary qualifications and are a member of professional accounting bodies. This step will give you confidence in their abilities and ethical standards.
Considering Industry Experience
Industry-specific experience can be an advantage when selecting an accountant. An accountant familiar with your industry will have a better understanding of its financial dynamics, regulations, and challenges, enabling them to offer more tailored solutions.
Analyzing Pricing and Fees
Discuss the accountant’s pricing structure and fees during the interview process. Look for transparency and make sure their pricing aligns with the services they provide. Avoid surprises and hidden costs by getting a clear understanding of their fee structure.
Assessing Accounting Software Knowledge
In today’s digital age, proficiency in accounting software is essential. Inquire about the accountant’s knowledge and experience with accounting software that your business uses or intends to adopt. Familiarity with such tools can streamline financial management processes.
Evaluating Customer Reviews and Testimonials
While you may have already read some reviews during the research phase, it’s essential to delve deeper into customer reviews and testimonials. Look for patterns in feedback to understand how the accountant has consistently served their clients.
Accountant’s Approach to Taxation
Taxation is a critical aspect of small business finance. Discuss the accountant’s approach to taxation, including their strategies for tax planning and compliance. A proactive approach to taxes can help you optimize your tax liability and avoid potential issues.
Making the Final Decision
After careful consideration, it’s time to make your decision. Choose the small business accountant who not only possesses the necessary qualifications and experience but also feels like the best fit for your business. Trust your instincts and move forward confidently.
How We Can Help
As an eCommerce business owner, your time is precious. If you find yourself too busy or too overwhelmed to keep track of your bookkeeping, Financial Foxe can help. Together with Yasir at Summit eCommerce, we can help you hire the right person to manage your bookkeeping so that you can get back to what matters most: growing your business. Whatsapp +923024100558.
Do I really need a small business accountant?
Yes, a small business accountant can provide valuable financial insights and help ensure compliance, ultimately benefiting your business’s growth and success.
How much should I expect to pay for small business accounting services?
The cost of small business accounting services can vary depending on your business’s size, complexity, and scope of services required. It’s essential to discuss pricing with potential accountants.
What qualifications should I look for in a small business accountant?
Look for accountants with relevant qualifications, certifications, and memberships in professional accounting organizations.
Can a small business accountant help with tax planning?
Yes, a good small business accountant can assist with tax planning to optimize your tax liability and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
How often should I communicate with my small business accountant?
Regular communication with your accountant is crucial, especially during critical financial periods and when making significant business decisions.

What are the Features of Xero Accounting Software?
Xero accounting software has become increasingly popular among businesses due to its user-friendly interface and comprehensive range of features. Designed to streamline financial management processes, Xero offers a robust platform that allows businesses to efficiently handle their accounting needs. Xero accounting software is a cloud-based platform that offers a wide range of features to simplify financial management for businesses. It provides a user-friendly interface and powerful tools that enable businesses to efficiently handle their accounting processes.
What is the best cloud platform service?
One of the standout Xero features is its cloud-based platform. This means that users can access their financial data from anywhere, at any time, as long as they have an internet connection. The cloud-based nature of Xero allows for real-time collaboration with team members and provides the flexibility needed for businesses that operate in multiple locations.
What is a Bank Reconciliation
Xero simplifies bank reconciliation by automatically importing and categorizing bank transactions. This feature saves businesses valuable time that would otherwise be spent on manual data entry. With bank reconciliation in Xero, businesses can easily match transactions, identify discrepancies, and ensure accurate financial records.
Invoicing and Accounts Receivable
Creating and managing invoices is a breeze with Xero’s invoicing and accounts receivable feature. Users can customize professional-looking invoices, send them to clients, and track payment statuses. Xero also offers automated invoice reminders, making it easier for businesses to get paid on time and improve cash flow.
Where can I track my expenses?
Xero provides a convenient way to track expenses and manage accounts payable. Users can capture receipts digitally, categorize expenses, and reconcile them with bank transactions. The software also allows businesses to schedule and make payments, ensuring timely settlement of bills and reducing the risk of missed payments.
What is Financial Reporting and Analysis
Xero offers robust financial reporting and analysis tools that provide businesses with insights into their financial performance. Users can generate various reports, such as profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These reports help businesses make informed decisions, identify trends, and monitor their financial health.
What is the goal of inventory management?
For businesses that deal with inventory, Xero provides inventory management capabilities. Users can track stock levels, manage purchase orders, and receive notifications when inventory needs to be replenished. This feature ensures businesses have better control over their inventory and helps prevent stockouts or overstocking.
Payroll Management
Xero’s payroll management feature simplifies the process of paying employees. Users can calculate wages, manage employee details, and generate pay stubs. The software also handles tax calculations and submissions, ensuring businesses remain compliant with payroll regulations.
What is integration as a capability?
Xero seamlessly integrates with a wide range of third-party applications, such as payment gateways, CRM systems, and e-commerce platforms. This integration capability allows businesses to streamline their operations by connecting different software tools and automating workflows.
What is Data Security
Data security is a top priority for Xero. The software utilizes advanced encryption and security protocols to safeguard financial information. Regular data backups and secure servers ensure that businesses’ data is protected from loss or unauthorized access.
How do you meet the mobile accessibility needs of your audience?
With the Xero mobile app, users can manage their finances on the go. The mobile app provides access to key features, such as invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting. This mobility enables business owners and managers to stay connected and make informed decisions wherever they are.
How do you integrate a third-party API?
Xero’s marketplace offers a vast selection of third-party apps that can extend the functionality of the software. Users can integrate apps for specific business needs, such as project management, time tracking, or inventory control. This flexibility allows businesses to tailor Xero to their unique requirements.
What does customer support mean?
Xero provides excellent customer support through various channels, including live chat, email, and a comprehensive knowledge base. Users can get assistance with software-related issues or seek guidance on accounting practices. The responsive support team ensures that businesses can resolve any queries or concerns promptly.
How do I choose the right price?
Xero offers different pricing plans to cater to businesses of all sizes. The plans vary in terms of features and the number of users. This flexibility allows businesses to choose a plan that aligns with their needs and budget.
Is Xero suitable for small businesses?
Xero is suitable for businesses of all sizes, including small businesses. Its flexible pricing options and scalable features make it a popular choice for startups and growing enterprises.
Can I access Xero on my mobile device?
Yes, Xero has a mobile app available for both iOS and Android devices. The mobile app allows users to manage their finances on the go.
Can Xero integrate with other software applications?
Yes, Xero offers integration capabilities with a wide range of third-party applications. This allows businesses to streamline their workflows and connect different software tools.
How secure is my data in Xero?
Xero takes data security seriously and employs industry-standard measures to protect your financial information. This includes encryption, regular data backups, and secure servers.
Does Xero offer customer support?
Yes, Xero provides customer support through various channels, including live chat, email, and a comprehensive knowledge base. Their support team is responsive and ready to assist with any inquiries or issues.

What is a Chart of Accounts for E-commerce Sellers?
When it comes to managing finances for your e-commerce business, having a clear and organized system is crucial. One essential tool for maintaining financial records is a chart of accounts. In this article, we will explore what a chart of accounts is, why it is important for e-commerce sellers, and how to create one that suits your business needs.
What is a Chart of Accounts?
A chart of accounts is a systematic listing of all the financial accounts used by a business. It provides a comprehensive overview of the company’s financial transactions and helps organize and categorize them into different account types. Each account in the chart of accounts is assigned a unique number or code, making it easier to track and analyze financial information.
Chart of accounts for e-commerce business?
In the realm of e-commerce, a chart of accounts is the financial compass that guides businesses through the complex landscape of online retail. It’s the backbone of financial management, providing a systematic structure to categorize and track all monetary transactions. This essential tool not only ensures that revenues and expenses are recorded accurately but also offers invaluable insights into the financial health of an e-commerce venture.
From managing inventory and shipping costs to analyzing the effectiveness of advertising campaigns, a well-organized chart of accounts is the linchpin that empowers e-commerce entrepreneurs to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and navigate the often turbulent waters of online business with confidence.
Sample chart of accounts for e-commerce business
Here’s a sample chart of accounts with account codes for an e-commerce business. Keep in mind that the specific account codes may vary depending on your accounting software and preferences, but this should give you a good starting point.
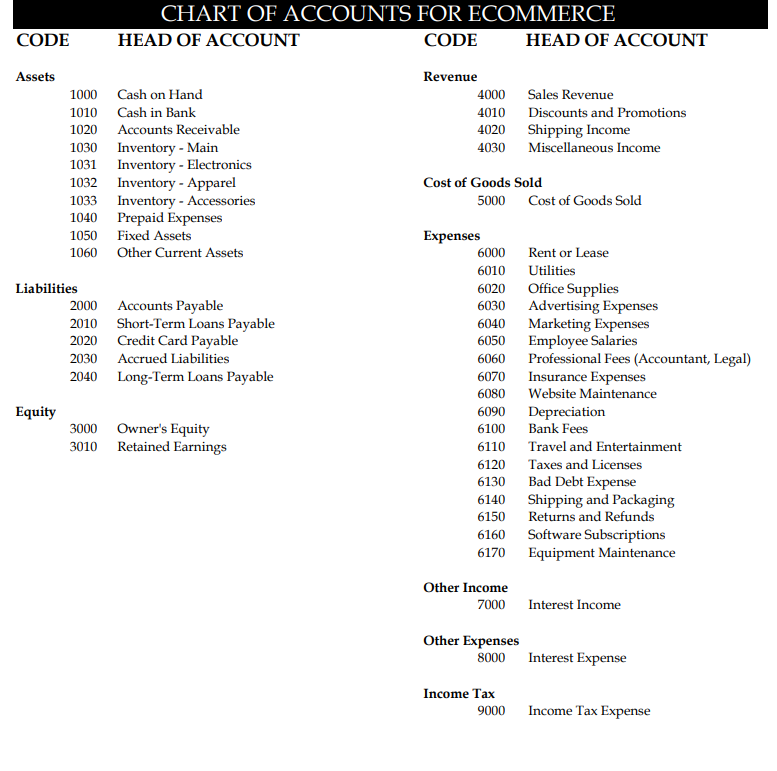
The Importance of a Chart of Accounts for E-commerce Sellers
A well-designed chart of accounts is essential for e-commerce sellers for several reasons:
Accurate Financial Reporting: By categorizing transactions into specific accounts, a chart of accounts ensures that financial reports accurately reflect the financial health of the business. It allows sellers to track revenue, expenses, and other important metrics.
Effective Decision Making: With a properly structured chart of accounts, e-commerce sellers can easily access and analyze financial data. This information is crucial for making informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, inventory management, marketing campaigns, and more.
Tax Compliance: A chart of accounts helps e-commerce sellers keep track of taxable income, deductible expenses, and other financial information required for tax reporting. It simplifies the tax filing process and reduces the risk of errors or omissions.
Chart of accounts for e-commerce company
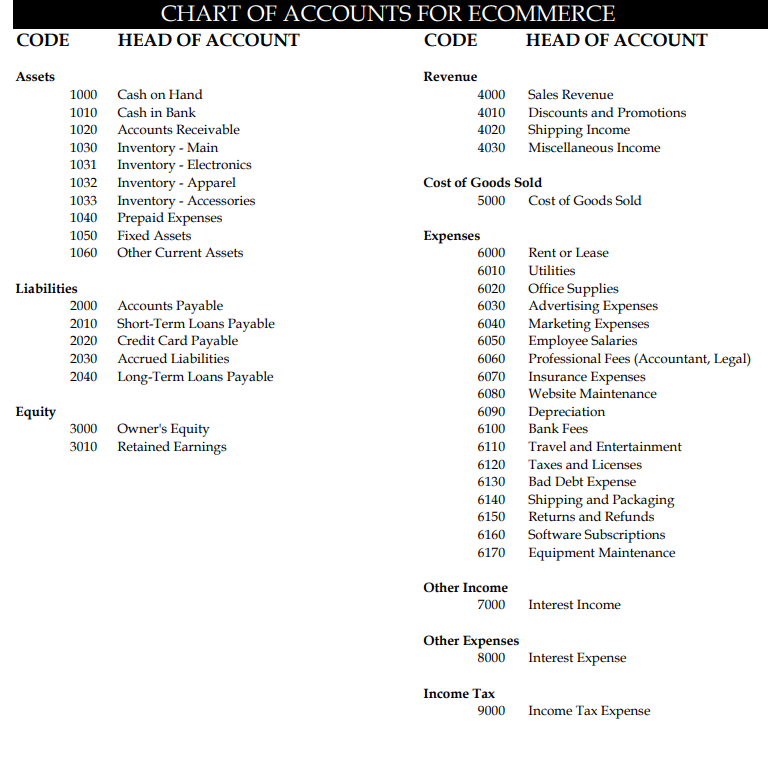
Key Elements of a Chart of Accounts
A chart of accounts typically consists of five main elements:
Assets
Assets represent the resources owned by a business. For e-commerce sellers, assets can include inventory, cash, accounts receivable, and fixed assets like equipment or property. Each asset account should be labeled and assigned a unique account number for easy identification.
Liabilities
Liabilities are the debts and obligations owed by a business. This can include accounts payable, loans, credit card balances, and other outstanding liabilities. Properly tracking liabilities helps e-commerce sellers understand their financial obligations and plan for repayment.
Equity
Equity represents the owner’s or shareholders’ interest in the business. It includes initial investments, retained earnings, and any additional capital contributions. Equity accounts help measure the overall value of the e-commerce business.
Revenue
Revenue accounts track the income generated from the sale of products or services. For e-commerce sellers, revenue accounts can include sales revenue, shipping income, or revenue from other sources like advertising or affiliate programs. Accurately categorizing revenue allows sellers to analyze sales performance and identify areas for improvement.
Expenses
Expense accounts track the costs incurred in running an e-commerce business. This includes expenses such as the cost of goods sold, marketing expenses, shipping costs, utilities, employee salaries, and other operational expenses. Properly categorizing expenses helps sellers monitor spending and identify areas where costs can be reduced.
How to set up a chart of accounts for Your E-commerce Business?
When designing a chart of accounts for your e-commerce business, it is important to consider the specific needs and characteristics of your operation. Here are some steps to help you create an effective chart of accounts:
Identify Account Categories: Determine the main account categories relevant to your business, such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses. This will serve as the foundation for your chart of accounts.
Create Account Codes: Assign unique codes or numbers to each account to facilitate easy organization and identification.
Consider Sub-Accounts: If your e-commerce business has complex operations or multiple product lines, consider using sub-accounts to provide more detailed tracking and analysis. Sub-accounts can be used to break down revenue or expenses by specific product categories, sales channels, or geographical regions.
Consult Accounting Professionals: If you’re uncertain about the best way to structure your chart of accounts, it’s advisable to seek guidance from accounting professionals who specialize in e-commerce businesses. They can provide valuable insights and ensure compliance with accounting standards.
How many categories are in a chart of accounts?
A chart of accounts typically consists of five main categories or account types. These categories are used to organize and classify financial transactions in an accounting system. The five main categories are:
- Assets: This category includes all the resources and items of value that a business owns. It’s typically divided into current assets (those expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year) and non-current assets (those with a longer lifespan).
- Liabilities: Liabilities represent the debts and obligations that a business owes to external parties. Like assets, liabilities are also often divided into current liabilities (due within one year) and non-current liabilities (due beyond one year).
- Equity: Equity, also known as owner’s equity or shareholders’ equity, represents the ownership interest in the business. It’s the residual interest in the assets after deducting liabilities. Equity accounts include common stock, retained earnings, and additional paid-in capital.
- Revenue: Revenue accounts track the income generated by the business from its primary operations. These accounts include sales revenue, service revenue, interest income, and any other income earned by the company.
- Expenses: Expense accounts represent the costs incurred by the business in order to generate revenue. These accounts include items such as salaries and wages, rent, utilities, office supplies, and other operating expenses.
Can a business use a class to track account balances?
Yes, a business can use classes or cost centers to track account balances within its accounting system. This is a common practice in accounting and financial management, especially for businesses that want to analyze and report financial data for different segments or divisions of the company.
How it works:
Classes or Cost Centers: Classes, sometimes called cost centers or departments, are used to categorize transactions within an organization. For example, a business might have separate classes for different product lines, geographical locations, projects, or divisions. Each class represents a distinct category or segment of the business.
Tracking Transactions: When recording financial transactions, businesses can assign a class to each transaction. This class designation allows them to associate the transaction with a specific category or segment of the business. For example, if a company has two product lines, it can assign a class to each sale to indicate which product line generated the revenue.
Reporting and Analysis: By using classes, a business can generate financial reports that provide insights into the performance and financial health of different segments or categories. This can be valuable for assessing the profitability of specific product lines, measuring the success of projects, or evaluating the financial performance of different branches or divisions.
Budgeting and Planning: Classes are also helpful for budgeting and planning. Businesses can create separate budgets for each class or cost center, allowing them to set specific financial goals and allocate resources accordingly.
Tax and Compliance Reporting: In some cases, businesses may use classes for tax and compliance purposes. For example, they might need to track revenue and expenses separately for different tax jurisdictions or legal entities.
Using classes to track account balances can provide a more granular view of a business’s financial data and help management make informed decisions about resource allocation, strategy, and performance improvement.
How do I start using Patriot’s accounting software?
To streamline your financial management processes, consider integrating your chart of accounts with accounting software designed for e-commerce businesses. These software solutions often come with built-in templates and tools that facilitate the creation and maintenance of a chart of accounts. By automating data entry and report generation, accounting software can save time and reduce the risk of manual errors in financial record-keeping.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating Your Chart of Accounts
As your e-commerce business evolves and grows, it is essential to periodically review and update your chart of accounts. Regularly assess whether the existing accounts are still relevant, make adjustments to accommodate new revenue streams or expenses, and ensure that your chart of accounts aligns with your business goals and reporting requirements.
Can I use a standard chart of accounts for my e-commerce business?
While there are general guidelines for structuring a chart of accounts, it’s recommended to tailor it to your specific e-commerce business needs. This ensures that your accounts accurately reflect your operations and facilitate meaningful financial analysis.
How often should I review and update my chart of accounts?
It’s advisable to review your chart of accounts annually or whenever significant changes occur in your e-commerce business. Regularly updating your accounts ensures that they remain relevant and provide accurate financial insights.
Do I need accounting software to maintain a chart of accounts?
While not mandatory, accounting software can greatly simplify the process of maintaining and managing your chart of accounts. It automates data entry, generates financial reports, and provides real-time insights into your business’s financial performance.
Can I add new accounts to my chart of accounts as my business grows?
Yes, you can add new accounts to your chart of accounts as your e-commerce business expands. It’s important to maintain consistency in account naming and numbering to ensure clarity and avoid confusion.
How can a well-designed chart of accounts benefit my e-commerce business?
A well-designed chart of accounts provides a clear and organized system for tracking financial transactions, facilitating accurate financial reporting, informed decision-making, and tax compliance. It allows you to analyze revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity, gaining valuable insights into your business’s financial health and performance.

E-commerce chart of accounts
E-commerce Chart of Accounts
Running a successful e-commerce business requires meticulous financial management. Having a clear understanding of your revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities is essential for making informed business decisions. A well-designed chart of accounts serves as the foundation for organizing and categorizing financial transactions in a systematic manner.
What is a Chart of Accounts?
A chart of accounts is a structured list of all the financial accounts used by a business. It provides a standardized framework for categorizing and recording various types of transactions. Each account is assigned a unique code or number that helps in identifying and organizing the data effectively.
Importance of a Chart of Accounts in E-commerce
In the context of e-commerce, where numerous transactions take place daily, a chart of accounts plays a vital role. It enables you to track revenue sources, monitor expenses, manage inventory, and analyze the overall financial health of your business. By having a well-defined chart of accounts, you can gain valuable insights into your business’s performance and make data-driven decisions.
Creating an Ecommerce Chart of Accounts
Defining the Main Categories
When setting up your e-commerce chart of accounts, it is important to establish the main categories that will encompass your financial transactions. Some common categories include revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Each category will have multiple subcategories to provide more detailed information.
Subcategories and Account Codes
Revenue Accounts
Revenue accounts capture the income generated from sales or services. Common revenue subcategories for e-commerce businesses may include:
Product Sales
Service Sales
Shipping Revenue
Discounts and Coupons
Expense Accounts
Expense accounts record the costs incurred in running your e-commerce business. Examples of expense subcategories are:
Advertising and Marketing
Inventory Costs
Shipping and Fulfillment
Website Maintenance
Asset Accounts
Asset accounts represent the resources owned by your e-commerce business. Common asset subcategories may include:
Cash and Bank Accounts
Inventory Assets
Accounts Receivable
Fixed Assets (e.g., equipment, vehicles)
Liability Accounts
Liability accounts track the debts and obligations of your e-commerce business. Some liability subcategories are:
Accounts Payable
Loans and Credit Lines
Sales Tax Payable
Refunds and Returns
Organizing the Chart of Accounts
To ensure clarity and ease of use, it is essential to organize your chart of accounts in a logical manner. Consider using a numbering system that follows a hierarchical structure, such as the four-digit account code. This structure allows for expansion and simplifies the identification of accounts.
Best Practices for Managing Your Chart of Accounts
To maximize the effectiveness of your e-commerce chart of accounts, follow these best practices:
Consistency and Standardization
Maintain consistency in naming conventions and account codes across all categories and subcategories. This consistency enhances clarity and simplifies data analysis.
Flexibility for Growth and Expansion
Design your chart of accounts with future growth in mind. Incorporate accounts and subcategories that accommodate potential business expansions, product lines, or new revenue streams.
Regular Review and Adjustment
Periodically review your chart of accounts to ensure it remains aligned with your evolving business needs. Make necessary adjustments to reflect any changes in your operations, revenue streams, or financial goals.
Integrating Your Chart of Accounts with E-commerce Platforms
Integrating your chart of accounts with your e-commerce platforms can streamline your financial management processes. Consider the following integration points:
Syncing Sales Data
Automatically sync sales data from your e-commerce platform to the corresponding revenue accounts in your chart of accounts. This integration eliminates manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors.
Automating Expense Tracking
Integrate your expense tracking system with your chart of accounts. This automation ensures that expenses are accurately recorded and allocated to the appropriate expense accounts.
Streamlining Inventory Management
Connect your inventory management software to your chart of accounts to maintain accurate records of inventory costs, valuation, and adjustments.
Reporting and Analysis with Your Chart of Accounts
An effectively implemented chart of accounts enables you to generate insightful reports and perform meaningful analyses. Here are some key aspects to consider:
Generating Financial Statements
With a well-structured chart of accounts, you can easily generate financial statements, such as profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These statements provide an overview of your business’s financial performance.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
By analyzing the data within your chart of accounts, you can identify key performance indicators (KPIs) specific to your e-commerce business. Examples include gross margin, average order value, customer acquisition cost, and inventory turnover rate.
Making Informed Business Decisions
With accurate financial data at your disposal, you can make informed business decisions that drive growth and profitability. The insights derived from your chart of accounts enable you to identify trends, evaluate strategies, and optimize your operations.
What is the purpose of a chart of accounts?
A chart of accounts serves as a structured framework for organizing and categorizing financial transactions within a business. It provides a clear overview of income, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
Can I customize my chart of accounts for my specific e-commerce business?
Yes, you can customize your chart of accounts to align with your unique business needs, revenue streams, and expense categories.
Why is it important to integrate my chart of accounts with my e-commerce platform?
Integration with your e-commerce platform ensures accurate and automated recording of financial data, reducing manual errors and saving time.
How often should I review and update my chart of accounts?
Regular reviews are recommended, especially when there are significant changes in your business operations, revenue sources, or financial goals.
Can I generate financial reports using my chart of accounts?
Yes, a properly structured chart of accounts allows you to generate financial statements, helping you assess your business’s financial health and performance.
What is a rental property income statement?
Investing in rental properties can be a lucrative venture, but it comes with its fair share of financial responsibilities. To succeed as a real estate investor, one must have a clear understanding of their property’s financial performance. This is where a rental property income statement plays a crucial role. In this article, we will delve into the significance of rental property income statements, their components, and how they aid investors in making informed financial decisions.
Definition and Purpose
A rental property income statement is a financial document that outlines the revenue generated and expenses incurred by a rental property during a specific period. Its primary purpose is to provide a comprehensive view of the property’s financial health and profitability. By tracking income and expenses, property owners can evaluate their investment performance and identify areas for improvement.
Statement of rental income
A statement of rental income is a financial document that summarizes the income generated from a rental property during a specific period. Landlords or property owners use this statement to track rental revenue, assess the property’s financial performance, and report their rental income for tax purposes.
Components of a Rental Property Income Statement
The income statement typically consists of two main sections: income and expenses. Under the income section, the document lists all sources of revenue, such as rent payments, pet fees, and laundry income. The expenses section, on the other hand, includes various costs, such as mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, maintenance, and property management fees.
Rental Income: This section lists all the rental payments received from tenants during the specified period. It includes both regular monthly rent and any additional income sources, such as late fees or pet fees.
Other Income: This section covers any other sources of income related to the rental property, like income from laundry facilities, parking fees, or storage units, if applicable.
Vacancy Loss: This part accounts for any potential rental income lost due to vacant units during the period. It may include a calculation based on the number of vacant days or an estimated percentage of vacancies.
Total Gross Income: This is the sum of rental income and other income, minus the vacancy loss. It represents the total income generated from the property before any expenses are deducted.
Deductions and Expenses: Here, various expenses related to the rental property are listed. Common deductions include property management fees, property taxes, insurance premiums, maintenance and repairs, utilities, advertising costs, mortgage interest, and any other relevant expenses.
Net Rental Income: The net rental income is calculated by subtracting the total deductions and expenses from the total gross income. This figure represents the income that the property owner earns from the rental property after accounting for all expenses.
Depreciation: While not an actual cash expense, depreciation can be claimed as a deduction for tax purposes to reflect the wear and tear of the property over time.
Taxable Income: This section shows the net rental income after depreciation deductions and any other allowable deductions. It is the amount that will be subject to taxation.
Importance of Tracking Income and Expenses
Tracking income and expenses is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it allows property owners to calculate their net operating income (NOI), which is a key indicator of a property’s profitability. Secondly, it helps in identifying potential issues, such as high vacancy rates or excessive maintenance costs, which could be impacting the property’s financial performance.
Creating a Rental Property Income Statement
Gathering Income Data
To create an accurate income statement, property owners must gather all income-related data. This includes rent received from tenants, any additional fees or charges, and income from ancillary services or amenities. Maintaining detailed and organized records is crucial during this step.
Tracking Expenses
On the expense side, property owners must diligently record all costs associated with the property. This includes mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance premiums, utilities, repairs, and any other relevant expenses. Categorizing expenses correctly helps in better analysis and decision-making.
Calculating Net Operating Income (NOI)
NOI is a fundamental metric that indicates the property’s ability to generate revenue after deducting operating expenses. It is calculated by subtracting total operating expenses from total income. A positive NOI implies profitability, while a negative NOI signals potential financial challenges.
Analyzing the Rental Property Income Statement
Assessing Profitability
Once the rental property income statement is prepared, the next step is to analyze its profitability. Property owners can determine if their investment is yielding positive returns and if it aligns with their financial goals.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
Regularly reviewing income statements over time helps in identifying trends and patterns. For instance, if the maintenance expenses are consistently rising, it may indicate the need for proactive maintenance or capital improvements.
Making Informed Financial Decisions
A well-maintained income statement empowers property owners to make informed financial decisions. It allows them to identify areas where costs can be reduced, assess the impact of rental rate changes, and allocate resources effectively.
Tax Implications of Rental Property Income Statements
Deductible Expenses
One significant advantage of rental property income statements is that they assist property owners in identifying deductible expenses. These deductions can help in reducing the taxable income, ultimately resulting in lower tax liabilities.
Depreciation Benefits
The income statement also factors in depreciation, which is a non-cash expense that allows property owners to recover the cost of their investment over time. This depreciation expense can further reduce taxable income.
Tax Reporting and Compliance
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date income statements ensures compliance with tax regulations. Property owners can use these statements to report rental income and expenses accurately on their tax returns.
Best Practices for Maintaining Rental Property Income Statements
Consistent Recording of Transactions
Consistency is key when it comes to maintaining income statements. Property owners should record all transactions promptly and accurately to ensure the financial data is reliable.
Utilizing Accounting Software
Using specialized accounting software simplifies the process of creating and managing income statements. These tools offer various features to track income and expenses efficiently.
Seeking Professional Advice
For complex financial matters, it’s advisable to seek advice from qualified accountants or financial advisors. Their expertise can help property owners optimize their income statements and maximize profitability.
What is a self rental property?
A self-rental property, also known as a “self-rental activity,” refers to a situation where a taxpayer rents a property or asset they own to their own business or another business they operate. In this scenario, the property owner (individual or entity) acts as both the landlord and the tenant, effectively paying rent to themselves.
The concept of self-rental is most commonly associated with small business owners or investors who have both business and real estate holdings. For example, a business owner may own a commercial property and then lease that property to their own business to conduct its operations. Similarly, a real estate investor might own residential properties and then rent them out to a property management company they also own.
Self-rental arrangements can be beneficial for various reasons:
Tax Planning: Self-rental allows for potential tax advantages. For example, the rental payments received by the property owner may be considered passive income, which could be offset by passive losses, including depreciation and other allowable deductions.
Asset Protection: By keeping the business and the real estate holdings separate, it may provide an additional layer of liability protection.
Control: As both the landlord and tenant, the property owner retains control over the property and its use.
However, it’s essential to handle self-rental transactions appropriately and in compliance with tax regulations. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) closely scrutinizes self-rental arrangements to prevent abuse of tax laws. The rental rate and terms should be set at fair market value to avoid tax issues related to improper income shifting or tax evasion. Proper record-keeping is crucial to substantiate the rental activity’s legitimacy and to demonstrate that the arrangement is a genuine business transaction. If you are considering a self-rental property arrangement, it’s essential to consult with a qualified tax advisor or financial professional to ensure compliance with all tax regulations and to fully understand the implications of such an arrangement on your tax situation.
What is the difference between NOI and cash flow?
Net Operating Income (NOI) represents the property’s revenue after deducting operating expenses but excluding debt service and income taxes. Cash flow, on the other hand, considers all income and expenses, including debt payments and taxes, and reflects the amount of money left after all obligations are met.
Can I use a rental property income statement for multiple properties?
Yes, you can use a single income statement to track the financial performance of multiple rental properties. However, it’s essential to ensure that the data is well-organized and clearly separated for each property.
Are repairs and maintenance expenses deductible?
Yes, repairs and maintenance expenses are generally deductible as operating expenses on a rental property income statement. However, it’s essential to differentiate between repairs (deductible) and improvements (capital expenses with depreciation benefits).
How often should I update my income statement?
It’s recommended to update your income statement regularly, at least monthly or quarterly. Frequent updates help in staying on top of your property’s financial health and making timely adjustments.
What is the 1% rule in real estate investing?
The 1% rule is a general guideline used by some real estate investors. It suggests that the monthly rental income of a property should be at least 1% of its total acquisition cost. For instance, if you buy a property for $200,000, the monthly rent should be $2,000 or more to meet the 1% rule.
What are illustrative financial statements?
Illustrative Financial Statements
Financial statements are crucial tools that provide insight into a company’s financial performance and position. Among the various types of financial statements, illustrative financial statements play a vital role in helping stakeholders understand complex financial information in a clear and visually appealing manner. In this article, we will explore what illustrative financial statements are, their importance, and how they are used by businesses. Illustrative financial statements are a set of example financial reports presented in a structured and easy-to-understand format. These statements go beyond mere numbers and present financial data with accompanying explanations, notes, and visual aids, such as charts and graphs. They provide a real-life representation of how a company’s financial information is organized, giving readers a practical and tangible perspective.
The Purpose of Illustrative Financial Statements
Clarity and Comprehension
The primary purpose of illustrative financial statements is to enhance clarity and comprehension. Traditional financial statements can be dense and difficult for non-financial professionals to interpret. Illustrative financial statements, on the other hand, use more reader-friendly language and visual elements, enabling better understanding.
Education and Training
Illustrative financial statements are valuable tools for educational and training purposes. Aspiring accountants, finance professionals, and business students often use these statements to learn how to analyze financial data and create their own financial reports.
Decision-Making
Business owners and management teams use illustrative financial statements to aid in their decision-making process. By having a clear view of financial performance, companies can make informed choices regarding investments, expansions, or cost-cutting measures.
Key Components of Illustrative Financial Statements
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder’s equity at a specific point in time. It showcases what the company owns and owes.
Income Statement
The income statement, or profit and loss statement, shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and net income over a specific period. It helps assess the company’s profitability.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement outlines the cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities. It reveals how a company generates and uses its cash.
Notes to the Financial Statements
Accompanying the main financial statements, the notes provide additional information and explanations, giving context to the numbers presented in the statements.
Benefits of Using Illustrative Financial Statements
Enhanced Communication
Illustrative financial statements offer improved communication with various stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and regulators. The visual representations make it easier for these parties to grasp the financial performance of a company.
Transparent Reporting
By including detailed explanations and notes, illustrative financial statements promote transparency and accountability. This openness can enhance investors’ trust and confidence in the company.
Comparison and Analysis
Illustrative financial statements allow for easy comparison and analysis of a company’s financial performance across different periods. This feature is crucial for identifying trends and potential areas of improvement.
How to Create Illustrative Financial Statements
Choose the Appropriate Format
Before creating illustrative financial statements, businesses need to choose the format that best suits their needs. The format should align with the industry standards and the company’s reporting requirements.
Use Consistent Branding
Maintaining consistent branding elements, such as logos and colors, throughout the financial statements helps reinforce the company’s identity.
Utilize Visual Aids
Graphs, charts, and other visual aids enhance the presentation of financial data and make it more accessible to the audience.
Are illustrative financial statements legally binding?
No, illustrative financial statements are not legally binding. They are provided as examples and visual aids to help users understand financial information better. The actual legal and binding financial statements are those prepared in accordance with accounting standards and regulations.
Can I use illustrative financial statements for my small business?
Yes, you can use illustrative financial statements for your small business. They can be a helpful tool to present your financial data in a clear and understandable manner to stakeholders and potential investors.
Do illustrative financial statements comply with accounting standards?
Illustrative financial statements may follow the general structure and principles of accounting standards, but they are not actual financial statements and do not require strict compliance. They are meant for illustrative purposes and do not replace formal financial reporting.
Where can I find templates for illustrative financial statements?
Templates for illustrative financial statements can be found online, on various financial and accounting websites. Many accounting software platforms also offer customizable templates that you can use as a starting point for creating your own illustrative financial statements.
Can I create illustrative financial statements for non-profit organizations?
Yes, you can create illustrative financial statements for non-profit organizations. These statements can be particularly useful in presenting the financial information of non-profits to donors, volunteers, and other stakeholders in a more accessible manner.
How to Find the Right Business for You?
Starting a business can be an exciting venture, but it requires careful planning and consideration to ensure its success. Whether you are a budding entrepreneur or looking to make a career change, finding the right business that aligns with your interests, skills, and financial situation is essential. In this article, we will guide you through the process of finding the perfect business opportunity for you.
Assess Your Interests and Passions
The first step in finding the right business is to assess your interests and passions. Consider what activities and industries excite you the most. Your passion for the business will fuel your motivation and determination to succeed. Make a list of your hobbies, interests, and things you enjoy doing in your free time. This exercise will help you identify potential business ideas that resonate with your heart.
Evaluate Your Skills and Expertise
Apart from your interests, you must evaluate your skills and expertise. Determine what you are good at and what skills you have acquired over the years. Assess your educational background, work experience, and any specialized knowledge you possess. Matching your skills with the business idea will enhance your chances of running a successful venture.
Research Market Opportunities
Once you have identified potential business ideas based on your interests and skills, conduct thorough market research. Analyze current trends, consumer preferences, and market gaps. Look for opportunities where your business can fulfill unmet needs or solve problems. A comprehensive understanding of the market will help you make informed decisions and set realistic goals.
Consider Your Financial Situation
Your financial situation plays a significant role in determining the type of business you can start. Evaluate your savings, investments, and available resources. Consider how much capital you can invest in the business and how much you will need to sustain operations until the business becomes profitable. It is essential to have a clear financial plan to avoid running into financial troubles later on.
Analyze the Competition
Competition is inevitable in any business. Analyze the competitors in your chosen industry and identify their strengths and weaknesses. This analysis will help you understand the market landscape and allow you to position your business uniquely to stand out from the crowd.
Choose a Business Structure
Decide on the legal structure of your business. Common options include sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), and corporation. Each structure has its advantages and disadvantages, so choose the one that aligns with your long-term goals and offers the most protection for your assets.
Seek Professional Advice
Seek advice from professionals like business consultants, accountants, or legal experts. Their expertise can provide valuable insights into the specific industry you are considering and help you avoid potential pitfalls. They can also guide you through the legal and financial aspects of starting a business.
Test Your Idea
Before fully committing to your business idea, test it on a small scale. Launch a pilot project or conduct a soft launch to gauge customer response and gather feedback. Testing your idea will give you a better understanding of its viability and potential areas for improvement.
Develop a Business Plan
A well-structured business plan is essential for any successful business. Outline your business goals, target audience, marketing strategy, financial projections, and operational plan in detail. A business plan will serve as a roadmap for your business’s growth and provide a sense of direction.
Secure Funding
If your business requires additional funding beyond your personal resources, explore funding options like bank loans, venture capital, or crowdfunding. Prepare a compelling pitch to attract potential investors or lenders.
Build Your Team
As your business grows, you may need to build a team to support your operations. Hire employees who share your passion and vision for the business. Building a strong team is crucial for achieving long-term success.
Register Your Business
Register your business with the appropriate government authorities and obtain all necessary licenses and permits. Compliance with legal requirements will ensure that your business operates smoothly and avoids any legal issues.
Set Up Business Operations
Set up the necessary infrastructure, equipment, and processes to start your business operations. Depending on your business type, you may need to secure a physical location, invest in technology, or establish an online presence.
Market Your Business
Marketing plays a vital role in attracting customers and promoting your brand. Develop a marketing strategy that targets your ideal audience and utilizes various marketing channels such as social media, content marketing, and advertising.
How long does it take to find the right business idea?
Finding the perfect business idea can vary from person to person. It may take some time to thoroughly research and evaluate different opportunities. Be patient and focus on finding the best fit for you.
What if my chosen business idea fails to take off?
Business success is not always guaranteed, and failures are part of the entrepreneurial journey. Learn from your experiences, make necessary adjustments, and consider exploring new ideas if needed.
Is it necessary to have prior business experience?
While prior experience can be beneficial, it is not a strict requirement. Many successful entrepreneurs have started businesses in industries where they had no prior experience. Passion, dedication, and a willingness to learn can compensate for a lack of experience
Should I start a business alone or with a partner?
The decision to start alone or with a partner depends on various factors, including your own strengths and weaknesses, the nature of the business, and your compatibility with potential partners. Choose an option that aligns with your goals and provides the necessary support.
Can I change my business idea later on?
Yes, it is possible to pivot or change your business idea if circumstances demand it. Entrepreneurs often adapt to market changes or new opportunities. Stay open to innovation and be willing to make adjustments along the way.
How do I find the right bookkeeper for my business?
Finding the right bookkeeper for your business is a crucial step to ensuring your financial records are accurate and well-managed. Here are some steps to help you find the right bookkeeper:
Identify your needs: Before you start looking for a bookkeeper, determine the specific tasks you want them to handle. Bookkeepers can assist with various financial tasks such as recording transactions, reconciling accounts, managing payroll, and producing financial statements. Knowing your requirements will help you find a bookkeeper with the appropriate skills and experience.
Look for qualifications and experience: A competent bookkeeper should have relevant qualifications and experience in the field. Look for candidates who have a background in accounting, finance, or bookkeeping and have experience working with businesses similar to yours in terms of size and industry.
Seek referrals: Ask other business owners, colleagues, or professionals for recommendations. Personal referrals can be valuable as they come from people who have had direct experience with the bookkeeper’s services.
Check online platforms: Websites like LinkedIn, Indeed, or local business directories can be helpful in finding potential bookkeepers. Look for professionals with positive reviews or testimonials from previous clients.
Interview candidates: Once you have a list of potential bookkeepers, conduct interviews to assess their suitability for your business. Prepare a list of questions to ask, focusing on their qualifications, experience, software skills, and understanding of your industry’s specific financial requirements.
Assess communication skills: Effective communication is crucial in bookkeeping as it involves interpreting financial data and working with other team members. Ensure the bookkeeper can communicate clearly and is attentive to your needs.
Inquire about software proficiency: Modern bookkeeping heavily relies on accounting software. Check if the bookkeeper is proficient in popular accounting software such as QuickBooks, Xero, or any other software you use for your business.
Discuss fees and terms: Bookkeepers may charge hourly rates or flat fees for specific services. Discuss their fees and terms upfront to ensure they fit your budget and align with your financial needs.
Request references: Don’t hesitate to ask for references from previous clients. Contacting these references will give you valuable insights into the bookkeeper’s work ethic and reliability.
Consider certifications: While not mandatory, bookkeepers with certifications such as Certified Bookkeeper (CB) or Certified Public Bookkeeper (CPB) from reputable organizations demonstrate a commitment to their profession.
Evaluate their understanding of tax regulations: A good bookkeeper should have a solid understanding of tax regulations relevant to your business. They can help ensure compliance and may collaborate with your tax accountant during tax season.
Trust your instincts: Ultimately, go with the bookkeeper who not only meets the technical requirements but also feels like a good fit for your business. Trust your instincts after assessing their qualifications, experience, and interpersonal skills.
How We Can Help
As an eCommerce business owner, your time is precious. If you find yourself too busy or too overwhelmed to keep track of your bookkeeping, financial foxe can help. Together with Yasir at Summit eCommerce, we can help you hire the right person to manage your bookkeeping so that you can get back to what matters most: growing your business. Whatsapp +923024100558.
Financial Statement of a Construction Company
A company’s financial statement is like a mirror that reflects its financial health and performance. For construction companies, these statements play a crucial role in providing insights into their operations, profitability, and overall financial standing. In this article, we will delve into the key components of a construction company’s financial statement and understand why it is essential for both internal decision-making and external stakeholders.
The Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a vital financial statement that portrays a construction company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It consists of three primary components:
Assets
Assets encompass everything that a construction company owns and controls, including property, equipment, cash, and accounts receivables. The value of assets represents the company’s potential to generate future economic benefits.
Liabilities
Liabilities encompass the company’s obligations and debts, such as loans, accounts payable, and accrued expenses. These represent the company’s financial obligations that need to be settled in the future.
Shareholders’ Equity
Shareholders’ equity, also known as net worth or shareholders’ funds, reflects the company’s residual interest in its assets after deducting liabilities. It represents the ownership interest of the shareholders.
Analyzing the Income Statement
The income statement provides a summary of a construction company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period, usually a quarter or a year.
Revenue
Revenue in a construction company typically includes income from completed projects, progress billings, and change orders. It is crucial to analyze the sources of revenue to assess the company’s performance in different segments.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
The COGS in a construction company comprises the direct costs associated with the projects, such as labor, materials, subcontractors, and equipment expenses. Effective cost management is essential to maintain profitability.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is calculated by deducting COGS from revenue. It reflects the company’s ability to produce and deliver projects efficiently.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses include all indirect costs related to running the construction business, such as salaries, administrative expenses, marketing, and other overheads.
Operating Income
Operating income is derived by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. It indicates the company’s profitability from its core operations.
Other Income and Expenses
This category includes non-operating items like interest income, interest expenses, and gains or losses from the sale of assets.
Net Income
Net income, also known as the bottom line, is the final profit or loss figure after accounting for all revenues, expenses, and taxes. It indicates the overall financial performance of the construction company.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement provides an overview of how cash flows in and out of the construction company during a specific period. It consists of three sections:
Operating Activities
This section includes the cash flows from the company’s primary activities, such as cash receipts from customers and cash paid to suppliers and employees.
Investing Activities
Investing activities involve cash flows from the purchase or sale of long-term assets, investments, and other financial instruments.
Financing Activities
Financing activities encompass cash flows related to the company’s capital structure, including issuing or repurchasing shares, taking loans, and making debt repayments.
Importance of Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are essential tools for analyzing a construction company’s financial statement. Some crucial ratios include:
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. The current ratio and quick ratio are common liquidity ratios for construction companies.
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios measure a company’s ability to generate profits from its operations. Gross profit margin and net profit margin are significant profitability ratios.
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency ratios evaluate how well a construction company utilizes its assets and resources to generate revenue. Examples include asset turnover and inventory turnover ratios.
Solvency Ratios
Solvency ratios gauge a company’s long-term financial stability by comparing its long-term debts to its assets or equity.
Utilizing Financial Statements for Decision-Making
Financial statements are valuable tools for construction company owners and managers to make informed decisions. They provide insights into financial strengths, weaknesses, and areas that need improvement.
Importance for External Stakeholders
Financial statements are not only vital for internal decision-making but also for external stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and potential partners. These statements help assess the company’s creditworthiness, growth potential, and overall financial health.
Why are financial statements important for construction companies?
Financial statements provide a clear picture of a construction company’s financial health and performance, aiding in strategic decision-making and planning for the future.
How do financial ratios help in analyzing a construction company’s performance?
Financial ratios offer valuable insights into various aspects of a construction company’s operations, profitability, efficiency, and long-term stability.
What role do cash flow statements play in financial analysis?
Cash flow statements show how cash moves in and out of the company, helping stakeholders understand its ability to manage cash and meet financial obligations.
Can financial statements help attract investors to a construction company?
Yes, well-presented financial statements can instill confidence in investors by demonstrating the company’s financial strength and growth potential.
Are financial statements legally required for construction companies?
Yes, most jurisdictions mandate that construction companies prepare and maintain financial statements to ensure transparency and compliance with accounting standards.
What are the four main financial statements?
Financial statements are crucial tools used by businesses to communicate their financial performance and position to various stakeholders. They provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial health, helping investors, creditors, and management make informed decisions.
Importance of Financial Statements
Before delving into the details of each financial statement, it is essential to emphasize its overall importance. Financial statements offer a snapshot of a company’s financial activities over a specific period, aiding in assessing its profitability, liquidity, and stability.
The Four Main Financial Statements
Income Statement
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, presents a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits or losses over a specific period. It provides insights into the organization’s ability to generate profits by increasing revenues, reducing costs, or both.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific moment. It presents the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity, showcasing what the company owns, owes, and its net worth.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement illustrates the inflow and outflow of cash within a company during a specific period. It categorizes cash activities into operating, investing, and financing activities, revealing the company’s ability to generate and utilize cash effectively.
Statement of Shareholders’ Equity
The statement of shareholders’ equity showcases changes in shareholders’ equity over time. It includes items such as common stock, retained earnings, and additional paid-in capital, reflecting the company’s financial health from the shareholders’ perspective.
Understanding Each Financial Statement
Income Statement
The income statement starts with the company’s total revenues and then deducts the cost of goods sold and operating expenses to calculate the net income. This final figure represents the profit or loss generated by the company during the specific period.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is divided into two sections – assets and liabilities & shareholders’ equity. It follows the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s financial position on a particular date.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement comprises three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. It reveals the sources and uses of cash, enabling stakeholders to assess the company’s ability to generate cash to meet its obligations.
Statement of Shareholders’ Equity
The statement of shareholders’ equity shows changes in shareholders’ equity over time, including stock issuances, dividends, and retained earnings. This statement offers valuable insights into the company’s financing activities.
Importance of Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis is a crucial skill for investors and creditors. It helps them assess a company’s financial health, growth potential, and overall performance. By analyzing these statements, stakeholders can make well-informed decisions about investing or lending to the company.
How Financial Statements are Used
Financial statements are used in various scenarios, including:
Assessing a company’s financial health before making investment decisions.
Evaluating a company’s creditworthiness before extending credit or loans.
Determining a company’s ability to meet its short-term and long-term obligations.
Analyzing the effectiveness of a company’s management and financial strategies.
Key Takeaways
Financial statements are essential tools for assessing a company’s financial health and performance.
The four main financial statements are the income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and statement of shareholders’ equity.
Each financial statement provides specific insights into different aspects of a company’s finances.
Financial statement analysis is crucial for making informed investment and credit decisions.
Why are financial statements important?
Financial statements are vital because they provide a clear view of a company’s financial health, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions.
What is the purpose of the income statement?
The income statement shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits or losses over a specific period, revealing its profitability.
How does the balance sheet differ from the income statement?
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific moment, while the income statement shows its financial performance over a period.
What information does the cash flow statement provide?
The cash flow statement displays the sources and uses of cash within a company during a specific period, indicating its ability to generate and manage cash.
How can financial statement analysis benefit investors?
Financial statement analysis helps investors assess a company’s financial health, growth potential, and overall performance, aiding in making sound investment decisions.
Income Statement for a Small Business
Income Statement
The income statement is a financial report that provides an overview of a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period. It is a crucial document that helps business owners, investors, and stakeholders understand the company’s financial performance.
Importance for Small Businesses
For small businesses, the income statement serves as a vital tool for tracking profitability and identifying areas for improvement. It provides valuable insights into the business’s overall financial health and aids in making informed decisions for growth and sustainability.
Components of an Income Statement
The income statement consists of several key components, each contributing to the overall financial picture of the business.
Revenue
Revenue, also known as sales or turnover, represents the total income generated from the primary operations of the business. It includes all sales, fees, and other income directly related to the products or services offered.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS refers to the direct costs incurred in producing goods or services that the company sells. This includes raw materials, labor, and manufacturing expenses. Subtracting COGS from revenue gives the gross profit.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is the difference between revenue and COGS. It indicates the profitability of the core business operations before considering other expenses.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses include all the costs incurred in running the day-to-day operations of the business. This includes salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, and more.
Operating Income
Operating income, also known as operating profit, is the result of subtracting operating expenses from the gross profit. It represents the profit generated from the core business activities.
Other Income and Expenses
This section accounts for any additional income or expenses not directly related to the main operations. It may include interest income, investment gains, or non-operating losses.
Net Income
Net income, also known as net profit or the bottom line, is the final figure after considering all revenues, expenses, gains, and losses. It represents the overall profitability of the business during the specified period.
Creating an Income Statement
To create an income statement, small businesses need to follow these essential steps:
Choosing an Accounting Method
Small businesses can use either cash basis or accrual basis accounting. The method chosen impacts how revenue and expenses are recognized, affecting the income statement.
Gathering Financial Data
Accurate financial data is crucial for an informative income statement. Business owners must ensure all revenue and expense items are accounted for correctly.
Formatting the Statement
The income statement should follow a standardized format, listing revenues at the top and gradually deducting expenses to arrive at the net income.
Analyzing the Income Statement
Analyzing the income statement is vital for understanding the business’s financial performance and making informed decisions.
Assessing Profitability
By reviewing the income statement, business owners can identify whether their operations are profitable and sustainable.
Calculating Key Ratios
Financial ratios, such as gross profit margin and net profit margin, help assess the company’s efficiency and profitability.
Identifying Trends
Comparing income statements over different periods reveals trends and allows businesses to adjust their strategies accordingly.
Using the Income Statement for Decision-Making
The income statement plays a crucial role in making strategic business decisions.
Making Strategic Business Decisions
By analyzing the statement, business owners can identify areas where cost-cutting measures can be implemented or revenue can be increased.
Attracting Investors and Lenders
Investors and lenders use the income statement to gauge the business’s financial health and potential for future growth.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common errors can occur when preparing the income statement.
Misclassifying Expenses
Misclassifying expenses can lead to an inaccurate representation of the business’s financial health.
Ignoring Non-Cash Expenses
Neglecting non-cash expenses, such as depreciation, can distort the true profitability of the business.
Not Regularly Reviewing the Statement
Failing to review the income statement regularly may result in missed opportunities for improvement.
Case Study: A Small Business Income Statement Analysis
To illustrate the practical application of the income statement, let’s consider a case study.
Company Background
XYZ Café, a small coffee shop, has been in operation for two years.
Income Statement Examination
We analyze XYZ Café’s income statement for the past year.
Recommendations for Improvement
Based on the analysis, we offer recommendations to improve the café’s profitability.
Tax Implications and the Income Statement
The income statement has implications for tax reporting and planning.
Tax Deductions
Certain expenses listed on the income statement may be tax-deductible, reducing the overall tax liability.
Tax Planning Strategies
Analyzing the income statement helps small businesses plan for tax obligations effectively.
The Impact of Seasonality and Economic Factors
External factors can influence the income statement significantly.
Adapting to Seasonal Fluctuations
Businesses need to prepare for seasonal changes that affect revenue and expenses.
Preparing for Economic Challenges
A robust income statement analysis can help businesses navigate economic downturns.
Forecasting and Budgeting
The income statement is a valuable tool for forecasting and budgeting purposes.
Using Historical Data
Past income statements help create realistic projections for the future.
Setting Realistic Goals
Budgeting based on the income statement ensures attainable financial goals.
The Importance of Professional Help
Seeking professional advice enhances the quality and accuracy of the income statement.
Accountants and Financial Advisors
Experts can assist in preparing accurate income statements and interpreting their implications.
Software Solutions for Small Businesses
Various accounting software options are available to simplify income statement preparation.
What is the significance of an income statement for small businesses?
The income statement helps track profitability, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions for growth and sustainability.
How does a small business create an income statement?
Small businesses need to gather financial data, choose an accounting method, and follow a standardized format to create an income statement.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when preparing an income statement?
Misclassifying expenses, ignoring non-cash expenses, and not reviewing the statement regularly are common errors to avoid.
How can investors and lenders use the income statement?
Investors and lenders use the income statement to gauge a business’s financial health and potential for future growth.
How does the income statement aid in tax planning?
The income statement helps small businesses plan for tax obligations effectively by identifying tax-deductible expenses.

What Are 3 Financial Statements?
Financial statements are crucial tools for evaluating the financial health and performance of a company. They provide a snapshot of the company’s financial position, performance, and cash flow over a specific period. By analyzing these statements, investors, stakeholders, and potential lenders can gain valuable insights into a company’s profitability, liquidity, and overall financial stability. These statements include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. Understanding these financial statements is essential for anyone involved in the world of finance, whether you are an investor, business owner, or financial analyst.
Balance Sheet: Understanding a Company’s Financial Position
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It presents the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. The balance sheet follows a fundamental equation: Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity.
Assets
The assets section of the balance sheet includes both current and non-current assets. Current assets are those that are expected to be converted into cash within one year, such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. Non-current assets, on the other hand, are long-term assets like property, plant, and equipment.
Liabilities
Liabilities represent the company’s debts and obligations. Similar to assets, liabilities are categorized as either current or non-current. Current liabilities include short-term obligations such as accounts payable and accrued expenses. Non-current liabilities consist of long-term debts like bonds and mortgages.
Shareholders’ Equity
Shareholders’ equity represents the residual interest in the company’s assets after deducting its liabilities. It consists of the initial investment made by shareholders and retained earnings, which are the accumulated profits of the company that have not been distributed to shareholders as dividends.
Income Statement: Assessing a Company’s Revenue and Expenses
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement or P&L statement, provides an overview of a company’s revenues, expenses, gains, and losses over a specific period. It helps assess a company’s ability to generate profits from its core operations.
Revenue
Revenue represents the total amount of money earned by a company from its primary activities, such as the sale of goods or services. It is also referred to as sales, turnover, or top line. Revenue is a vital indicator of a company’s ability to attract customers and generate income.
Expenses
Expenses encompass the costs incurred by a company to generate revenue and maintain its operations. They include various categories such as cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, interest expenses, and taxes. Analyzing expenses helps determine a company’s profitability and efficiency.
Gains and Losses
Gains and losses refer to the income or loss generated from non-operational activities. For example, a gain can arise from the sale of an asset, while a loss may result from the write-off of a non-performing investment. Gains and losses are important to consider as they impact a company’s overall financial performance.
Cash Flow Statement: Analyzing a Company’s Cash Inflows and Outflows
The cash flow statement provides insights into a company’s cash inflows and outflows over a specific period. It is categorized into three main sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. The cash flow statement helps assess a company’s ability to generate and manage cash effectively.
Operating Activities
Operating activities involve the day-to-day business operations of a company. It includes cash receipts from customers, payments to suppliers, employee salaries, and other operating expenses. The net cash flow from operating activities indicates whether a company’s core operations generate sufficient cash to sustain its business.
Investing Activities
Investing activities reflect a company’s cash flows related to investment activities, such as the purchase or sale of long-term assets, acquisitions, or investments in securities. Positive cash flows from investing activities may indicate growth and expansion, while negative cash flows may indicate divestment or asset disposal.
Financing Activities
Financing activities involve cash flows related to the company’s capital structure and financing sources. This includes cash received from issuing stocks or bonds, repaying debts, paying dividends, or raising capital through loans. The cash flow from financing activities helps assess a company’s ability to raise funds and manage its capital structure.
How Are the Three Financial Statements Linked Together?
Interconnections Between the Financial Statements
The three financial statements are interconnected through specific relationships. Changes in one statement can have implications for the other statements. Here are some key interconnections:
Net income from the income statement flows into the balance sheet as an increase in retained earnings.
Changes in retained earnings affect shareholders’ equity on the balance sheet.
The net income from the income statement also impacts the cash flow statement, specifically the operating activities section.
Non-cash expenses, such as depreciation and amortization, are reflected in both the income statement and cash flow statement.
Changes in assets and liabilities on the balance sheet affect the cash flow statement, particularly the operating and investing activities sections.
These interconnections ensure that the information presented in each financial statement is consistent and accurate, providing a holistic view of a company’s financial performance.
Importance of Analyzing the Interconnections
Analyzing the interconnections between the financial statements is crucial for understanding a company’s financial health and making informed decisions. Here’s why it matters:
Performance Assessment: By examining how financial statements interact, analysts can assess a company’s performance more comprehensively. They can identify trends, evaluate profitability, and determine the efficiency of cash flow management.
Financial Planning: Understanding the interconnections helps in developing effective financial plans. It enables companies to align their income generation, asset acquisition, and financing strategies to achieve their goals.
Investment Decisions: Investors can make more informed investment decisions by analyzing the interconnections. They can evaluate the financial stability, growth potential, and risk associated with a company.
Risk Management: Assessing the interconnections assists in identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities in a company’s financial structure. It allows proactive risk management and mitigation strategies to be implemented.
Stakeholder Communication: The interconnections provide a framework for effective communication with stakeholders. Companies can present a comprehensive view of their financial performance and explain the impact of different financial activities.
Why are the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement important?
These financial statements provide insights into a company’s financial performance, position, and cash flow activities, helping stakeholders make informed decisions.
How often are the financial statements prepared?
Financial statements are typically prepared on a quarterly and annual basis. Publicly traded companies are required to publish their financial statements regularly.
Can financial statements be manipulated?
While financial statements can be subject to manipulation, companies are required to follow accounting standards and regulations to ensure accuracy and transparency.
Are there any limitations to financial statements?
Financial statements have certain limitations, such as not capturing the value of intangible assets and relying on historical data rather than future projections.
How can I use financial statements to evaluate a company’s performance?
You can use financial ratios and analysis techniques to evaluate a company’s performance based on information presented in the financial statements.
Why are financial statements important?
Financial statements are important as they provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health, performance, and cash flow, enabling informed decision-making by investors, stakeholders, and lenders.
What is the purpose of the balance sheet?
The balance sheet showcases a company’s financial position, presenting its assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time.
How does the income statement differ from the balance sheet?
While the balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position, the income statement focuses on its revenue, expenses, gains, and losses over a specific period.
What does the cash flow statement reveal?
The cash flow statement provides insights into a company’s cash inflows and outflows, highlighting its operational, investing, and financing activities.

Why is Bookkeeping Important for Amazon Sellers?
As an Amazon seller, you’re engaged in a dynamic and ever-evolving online marketplace. To succeed in this competitive environment, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of your business finances. Bookkeeping plays a vital role in helping Amazon sellers track their income, expenses, and overall financial health. In this article, we will explore the significance of bookkeeping for Amazon sellers and how it can contribute to your success.
The Fundamentals of Bookkeeping
Bookkeeping involves the systematic recording, organizing, and tracking of financial transactions. It provides a clear picture of your business’s financial performance, allowing you to monitor income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. Proper bookkeeping ensures that your financial records are accurate, up-to-date, and compliant with accounting standards.
Tracking Sales and Expenses
Effective bookkeeping allows Amazon sellers to keep a close eye on their sales and expenses. By meticulously recording each transaction, including product sales, advertising costs, shipping fees, and other expenses, you gain valuable insights into your business’s profitability. Accurate tracking also facilitates the identification of trends and patterns, helping you make data-driven decisions.
Accurate Financial Reporting
Having accurate financial reports is essential for evaluating the financial health of your Amazon selling business. With proper bookkeeping, you can generate reports such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These reports provide a comprehensive overview of your revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flow, empowering you to assess performance and plan for the future.
Complying with Tax Obligations
Amazon sellers are subject to various tax obligations. Bookkeeping ensures that you maintain accurate records of your sales, expenses, and taxes. This documentation is vital for calculating your taxable income and preparing tax returns. By keeping up with your tax obligations, you can avoid penalties, audits, and other complications that may arise from inaccurate or incomplete financial records.
Making Informed Business Decisions
Sound financial data is the foundation for making informed business decisions. Bookkeeping provides you with the necessary information to evaluate the profitability of different products, marketing strategies, and sales channels. It enables you to identify your most lucrative ventures, allocate resources effectively, and seize growth opportunities while minimizing risks.
Managing Cash Flow Effectively
Maintaining a healthy cash flow is crucial for the sustainability of your Amazon selling business. Bookkeeping helps you monitor your cash inflows and outflows, ensuring that you have sufficient funds to cover expenses and invest in growth. By tracking your cash flow, you can identify potential bottlenecks, take proactive measures, and optimize your financial resources.
Evaluating Profitability and Growth
Bookkeeping allows you to accurately assess the profitability and growth of your Amazon selling business. By analyzing your financial records, you can determine your profit margins, return on investment (ROI), and other key performance indicators (KPIs). This information empowers you to make strategic decisions to maximize profitability, identify areas for improvement, and drive sustainable growth.
Avoiding Costly Mistakes
Inaccurate or incomplete financial records can lead to costly mistakes for Amazon sellers. Bookkeeping helps you avoid errors such as double-counting sales, missing expenses, or miscalculating taxes. By maintaining meticulous records, you can minimize the risk of financial discrepancies, save time and effort in rectifying mistakes, and ensure the overall integrity of your financial data.
Simplifying Accounting Processes
Proper bookkeeping simplifies your accounting processes. By organizing your financial transactions systematically, you streamline the preparation of financial statements, tax filings, and other accounting requirements. This efficiency allows you to focus more time and energy on growing your Amazon business rather than getting caught up in administrative tasks.
Utilizing Technology for Bookkeeping
Technology has revolutionized bookkeeping for Amazon sellers. Various accounting software and online tools are available to automate and streamline the process. These tools can help you track sales, manage expenses, generate financial reports, and even integrate with your Amazon seller account. Leveraging technology can significantly enhance your bookkeeping efficiency and accuracy.
Hiring a Professional Bookkeeper
While managing your own bookkeeping can be feasible, it may be beneficial to hire a professional bookkeeper. An experienced bookkeeper can ensure that your financial records are accurately maintained, provide expert insights, and free up your time to focus on other critical aspects of your Amazon business. Outsourcing bookkeeping can be a wise investment that allows you to have peace of mind regarding your financial management.
Bookkeeping Best Practices
To make the most out of your bookkeeping efforts, consider implementing these best practices:
Regularly reconcile your accounts to ensure accuracy.
Keep track of receipts and supporting documents for all transactions.
Categorize expenses correctly for better financial analysis.
Backup and secure your financial data to protect against loss or theft.
Stay updated with accounting regulations and tax laws relevant to your business.
The Future of Bookkeeping for Amazon Sellers
As technology continues to advance, the future of bookkeeping for Amazon sellers looks promising. Automation, machine learning, and artificial intelligence are transforming the way financial data is processed and analyzed. These advancements will likely enhance accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making capabilities for Amazon sellers, further emphasizing the importance of staying abreast of technological developments.
Why should I hire a professional bookkeeper for my Amazon business?
Hiring a professional bookkeeper ensures accurate and expert financial management, freeing up your time to focus on other critical aspects of your business.
What software can I use for bookkeeping as an Amazon seller?
There are various accounting software options available, such as QuickBooks, Xero, and Wave, which are suitable for managing bookkeeping for Amazon sellers.
Can bookkeeping help me save money on taxes?
Yes, proper bookkeeping ensures accurate records, which can help you maximize deductions, avoid penalties, and effectively manage your tax obligations.
How often should I reconcile my accounts?
It is recommended to reconcile your accounts monthly to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies promptly.

How Much Is the Consulting Market Worth?
Consulting refers to the practice of providing expert advice and guidance to organizations, assisting them in solving problems, making informed decisions, and improving performance. Consultants, equipped with specialized knowledge and experience, work closely with businesses to identify opportunities, develop strategies, and implement effective solutions tailored to their unique requirements.
The Evolution of the Consulting Industry
The consulting industry has a rich history that traces back to the early 20th century. Over time, it has evolved and diversified to cater to the ever-changing needs of businesses. Initially, consulting focused primarily on operational efficiency and process improvement. However, with the advent of globalization, technological advancements, and dynamic market conditions, consulting expanded its scope to include areas such as strategy, digital transformation, change management, and more.
Key Segments of the Consulting Market
The consulting market encompasses various segments, each specializing in specific domains. Some of the key segments include:
Management Consulting
Management consulting involves providing organizations with strategic advice and assistance in areas such as organizational structure, business processes, mergers and acquisitions, financial management, and operational improvement.
IT Consulting
IT consulting revolves around helping businesses leverage technology to achieve their objectives. IT consultants offer guidance on software implementation, cybersecurity, cloud computing, data analytics, and digital transformation.
Financial Consulting
Financial consultants aid companies in optimizing their financial performance, managing risks, and making sound investment decisions. They provide expertise in areas like financial planning, taxation, risk management, and mergers and acquisitions.
HR Consulting
HR consultants specialize in human resources management, assisting organizations with talent acquisition, performance management, employee engagement, training and development, and HR strategy formulation.
Factors Influencing the Consulting Market Worth
Several factors contribute to determining the worth of the consulting market:
Economic Conditions
The overall economic climate significantly influences the demand for consulting services. During periods of economic growth, businesses seek consulting assistance to capitalize on opportunities and expand. Conversely, during downturns, companies may require consulting support to optimize operations, cut costs, and weather the challenging conditions.
Technological Advancements
The rapid advancement of technology has been a game-changer for the consulting industry. Consultants must stay abreast of emerging technologies and their implications to provide valuable insights to their clients. The demand for specialized technology consulting has surged as businesses aim to leverage digital solutions to drive efficiency and innovation.
Industry Disruptions
Disruptions in various industries, such as the rise of e-commerce, renewable energy, or the sharing economy, create a demand for consulting services. Companies need guidance on navigating these changes, adapting their business models, and staying competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Regulatory Environment
Changing regulations and compliance requirements impact organizations across industries. Consultants assist businesses in understanding and complying with these regulations, ensuring legal adherence and mitigating risks.
Global Consulting Market Size and Growth
The global consulting market has witnessed remarkable growth over the years. According to industry reports, the market was valued at around $250 billion in 2020. It is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4.3% from 2021 to 2028. The increasing need for specialized expertise, digital transformation initiatives, and business optimization efforts drive this growth.
Regional Analysis of the Consulting Market
The consulting market exhibits regional variations influenced by factors such as economic conditions, industry landscape, and cultural preferences. North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa are prominent regions with a substantial demand for consulting services. Each region presents unique opportunities and challenges, and consulting firms tailor their strategies accordingly.
Industry Verticals Driving Consulting Demand
Consulting services are sought after across a wide range of industry verticals. Some sectors that extensively rely on consulting expertise include:
Financial Services
Healthcare and Life Sciences
Technology and Telecommunications
Manufacturing and Automotive
Energy and Utilities
Retail and Consumer Goods
Government and Public Sector
Education and Non-profit Organizations
Consulting Services and Their Impact
Consulting services have a significant impact on businesses. They assist in:
Strategic planning and decision-making
Improving operational efficiency and productivity
Enhancing customer experience
Managing organizational change
Implementing digital transformation
Expanding into new markets
Navigating mergers and acquisitions
Mitigating risks and ensuring compliance
Emerging Trends in the Consulting Industry
The consulting industry continually evolves to adapt to market dynamics and emerging trends. Some notable trends include:
Data-driven consulting: Leveraging advanced analytics and data science to provide actionable insights and drive decision-making.
Sustainable consulting: Assisting businesses in adopting sustainable practices, addressing environmental challenges, and embracing social responsibility.
Virtual consulting: Utilizing remote collaboration tools and virtual platforms to provide consulting services globally.
Diversity and inclusion consulting: Supporting organizations in fostering diverse and inclusive workplaces and reaping the associated benefits.
Agile consulting: Adopting agile methodologies and practices to help companies navigate uncertainty, embrace innovation, and accelerate growth.
Challenges Faced by Consulting Firms
While the consulting industry offers numerous opportunities, it also faces challenges. Some common hurdles include:
Increasing competition and market saturation
Retaining top talent and expertise
Balancing client expectations with project constraints
Adapting to rapid technological advancements
Addressing client concerns regarding ROI and tangible outcomes
The Future of the Consulting Market
As businesses strive for growth, adapt to market disruptions, and embrace digital transformation, the consulting market’s worth is expected to rise steadily. The demand for specialized expertise, innovative solutions, and strategic guidance will continue to fuel the industry’s growth. Consulting firms that stay agile, embrace emerging technologies and offer value-added services will be well-positioned to thrive in the evolving landscape.
Is the consulting market only relevant to large corporations?
No, the consulting market caters to businesses of all sizes. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) also benefit from consulting services to enhance their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve growth.
What are the primary qualifications of a successful consultant?
Successful consultants possess a combination of industry expertise, analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, effective communication, and a deep understanding of business dynamics.
How can organizations measure the ROI of consulting services?
Organizations can measure the ROI of consulting services by setting clear objectives, establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), and evaluating the impact of consulting initiatives on business outcomes.
Are there any ethical considerations in the consulting industry?
Yes, ethical considerations are crucial in the consulting industry. Consultants must adhere to professional standards, maintain confidentiality, avoid conflicts of interest, and act in the best interest of their clients.
Can consulting services be customized to specific industry requirements?
Yes, consulting services are highly customizable. Consultants tailor their approaches and solutions to address the specific needs and challenges of different industries, ensuring relevance and effectiveness.

How Payment Gateway Reconciliation Works?
In the digital era, payment gateways act as intermediaries between merchants and customers, securely facilitating online transactions. When a customer makes a purchase, the payment gateway processes the transaction and ensures the funds reach the merchant’s account. Payment gateway reconciliation is the process of verifying and matching the transaction records between the payment gateway, merchant’s system, and financial statements.
Understanding Payment Gateway Reconciliation
Payment gateway reconciliation is a crucial aspect of financial management for businesses that process online payments. It involves comparing and reconciling the transaction data from the payment gateway with the merchant’s internal records to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies.
Importance of Payment Gateway Reconciliation
Accurate payment gateway reconciliation is vital for several reasons:
Financial Accuracy: Reconciliation ensures that the transaction data recorded in the payment gateway aligns with the merchant’s records, providing an accurate picture of the business’s financial health.
Discrepancy Detection: By comparing and reconciling data, any discrepancies or errors in transactions can be identified promptly, preventing financial losses or incorrect reporting.
Fraud Prevention: Reconciliation helps detect fraudulent activities, such as chargebacks or unauthorized transactions, enabling businesses to take appropriate actions and mitigate risks.
Regulatory Compliance: Reconciliation plays a crucial role in complying with financial regulations and audit requirements, providing transparency and accountability in financial reporting.
Key Steps in Payment Gateway Reconciliation
Effective payment gateway reconciliation involves several essential steps:
Gathering Transaction Data
The first step is to collect transaction data from the payment gateway and the merchant’s internal systems. This includes details such as transaction amounts, dates, customer information, and any additional metadata.
Comparing Transaction Records
Next, the transaction records from the payment gateway are compared with the merchant’s internal records. This step aims to identify any discrepancies or mismatches between the two datasets.
Identifying Discrepancies
In this phase, any discrepancies or differences found during the comparison are noted. Discrepancies can occur due to various reasons, such as technical glitches, failed transactions, or manual errors.
Investigating Discrepancies
Once discrepancies are identified, a thorough investigation is conducted to determine their root causes. This may involve reviewing transaction logs, contacting the payment gateway provider, or analyzing system integrations.
Resolving Discrepancies
After identifying the causes, steps are taken to resolve the discrepancies. This may include updating records, correcting errors, refunding customers, or contacting payment gateway support for assistance.
Reconciling Settlements
The final step involves reconciling settlements, ensuring that the funds deposited in the merchant’s account match the expected amounts based on the reconciled transaction data. This verifies the accuracy of the overall reconciliation process.
Best Practices for Payment Gateway Reconciliation
To optimize payment gateway reconciliation, consider the following best practices:
Regular Monitoring and Reporting
Implement a regular monitoring process to review transaction data, identify discrepancies promptly, and generate comprehensive reports for analysis and record-keeping.
Automated Reconciliation Systems
Utilize automated reconciliation systems and tools that can streamline the process, minimize errors, and save time by automatically matching transaction records.
Double-Checking Settlements
Always double-check settlements to ensure the funds received from the payment gateway are accurately deposited into the merchant’s account. Any discrepancies should be addressed promptly.
Keeping Clear Documentation
Maintain clear and detailed documentation of the reconciliation process, including the steps taken, identified discrepancies, and resolutions. This documentation aids in future audits and references.
Communication with Payment Service Providers
Maintain open communication with payment service providers, including the payment gateway, to resolve any issues, seek clarification, and stay updated with changes or updates to the reconciliation process.
Why is payment gateway reconciliation important?
Payment gateway reconciliation is important to ensure the accuracy of financial records, detect discrepancies, prevent fraud, and comply with financial regulations.
Can payment gateway reconciliation help prevent fraudulent activities?
Yes, payment gateway reconciliation can help detect and prevent fraudulent activities, such as chargebacks or unauthorized transactions.
What are the key steps in payment gateway reconciliation?
The key steps in payment gateway reconciliation include gathering transaction data, comparing transaction records, identifying discrepancies, investigating discrepancies, resolving discrepancies, and reconciling settlements.
How can automated reconciliation systems benefit businesses?
Automated reconciliation systems can streamline the reconciliation process, minimize errors, and save time by automatically matching transaction records.
Why is communication with payment service providers important in the reconciliation process?
Communication with payment service providers is important to resolve issues, seek clarification, and stay updated with changes or updates to the reconciliation process.

What is E-commerce Automation Software?
E-commerce automation software refers to a suite of tools and technologies designed to streamline and automate various aspects of online business operations. It aims to simplify repetitive tasks, improve efficiency, reduce errors, and ultimately enhance the overall performance of e-commerce businesses. These software solutions typically integrate with e-commerce platforms, payment gateways, inventory management systems, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and other relevant systems.
Benefits of E-commerce Automation Software
Increased Efficiency: Automation eliminates the need for manual intervention in routine tasks, saving time and reducing errors.
Enhanced Customer Experience: Automation enables faster order processing, personalized marketing campaigns, and seamless customer support, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
Scalability: E-commerce automation software facilitates the efficient handling of growing order volumes and business expansion.
Inventory Management: Automation helps optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and automate replenishment processes.
Order Fulfillment: Automated order fulfillment processes ensure accurate picking, packing, and shipping, resulting in faster delivery times.
Marketing Automation: E-commerce automation software enables personalized marketing campaigns, abandoned cart recovery, and customer segmentation.
Data Analysis: These tools provide valuable insights through data analytics, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and optimize strategies.
Key Features of E-commerce Automation Software
Order Management: Automated order processing, tracking, and fulfillment.
Inventory Management: Real-time inventory tracking, stock level alerts, and automated replenishment.
Customer Relationship Management: Customer data management, personalized marketing campaigns, and customer support automation.
Shipping and Logistics Integration: Seamless integration with shipping carriers and logistics providers for efficient order fulfillment and tracking.
Marketing Automation: Email marketing, abandoned cart recovery, customer segmentation, and personalized recommendations.
Reporting and Analytics: Comprehensive reporting and data analytics to gain insights into sales, customer behavior, and overall business performance.
Integration Capabilities: Ability to integrate with e-commerce platforms, payment gateways, CRM systems, and other relevant tools.
How to Choose the Right E-commerce Automation Software
Identify Business Needs: Determine which specific processes and tasks require automation and assess the scalability requirements.
Compatibility: Ensure the software integrates seamlessly with your existing e-commerce platform, payment gateways, and other essential systems.
Ease of Use: Look for user-friendly software that can be easily adopted by your team without extensive training.
Customization: Consider software that allows customization to align with your unique business requirements.
Support and Maintenance: Evaluate the level of technical support, regular updates, and ongoing maintenance provided by the software vendor.
Pricing: Compare pricing models and consider the software’s return on investment (ROI) in terms of efficiency gains and business growth.
Top E-commerce Automation Software Solutions
Solution 1: [Software A] – This robust automation software offers comprehensive features for order management, inventory control, marketing automation, and analytics.
Solution 2: [Software B] – With a user-friendly interface and seamless integration capabilities, this software streamlines order processing, inventory management, and marketing automation.
Solution 3: [Software C] – Designed for scalability, this software provides advanced features for order fulfillment, inventory optimization, and personalized marketing campaigns.
Implementing E-commerce Automation Software: Best Practices
Plan Ahead: Define your automation goals, outline implementation timelines, and allocate resources accordingly.
Data Migration: Ensure smooth data transfer from existing systems to the new automation software, maintaining data integrity.
User Training: Provide comprehensive training to your team members to familiarize them with the software’s functionalities and processes.
Test and Iterate: Conduct thorough testing and iterate based on feedback to optimize the software’s performance and alignment with your business processes.
Monitor and Measure: Continuously monitor key metrics and performance indicators to assess the effectiveness of the automation software and identify areas for improvement.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of E-commerce Automation Software
Case Study 1: Company X – By implementing e-commerce automation software, Company X achieved a 30% reduction in order processing time and a 20% increase in customer satisfaction.
Case Study 2: Company Y – Company Y experienced a significant improvement in inventory accuracy and a 25% decrease in stockouts after adopting e-commerce automation software.
Challenges and Limitations of E-commerce Automation Software
Initial Investment: The cost of implementing e-commerce automation software can be a barrier for small businesses.
Integration Complexity: Integrating the software with existing systems and platforms may require technical expertise.
Learning Curve: Employees may require training and time to adapt to the new software, affecting productivity initially.
Customization Constraints: Some software solutions may have limitations in terms of customization to fit specific business needs.
Future Trends in E-commerce Automation Software
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML technologies will play a significant role in enhancing automation software capabilities, enabling intelligent decision-making and predictive analytics.
Voice Commerce: Voice-enabled devices and voice recognition technology will be integrated into e-commerce automation software, providing a seamless voice-based shopping experience.
Hyper-Personalization: Automation software will leverage advanced customer segmentation and personalization techniques to deliver highly targeted marketing campaigns.
Robotics Process Automation (RPA): RPA will further automate manual tasks, enabling businesses to achieve higher levels of efficiency and cost savings.
What is e-commerce automation software?
E-commerce automation software refers to tools and technologies that automate various aspects of online business operations, such as order processing, inventory management, and marketing campaigns.
How can e-commerce automation software benefit my business?
E-commerce automation software can increase efficiency, enhance customer experiences, streamline inventory management, optimize order fulfillment, and enable personalized marketing campaigns.
What features should I look for in e-commerce automation software?
Key features to consider include order management, inventory management, customer relationship management, shipping and logistics integration, marketing automation, reporting and analytics, and integration capabilities.
How do I choose the right e-commerce automation software for my business?
Consider your business needs, compatibility with existing systems, ease of use, customization options, support and maintenance, and pricing when choosing e-commerce automation software.
What are the future trends in e-commerce automation software?
Future trends include the integration of AI and ML technologies, voice commerce, hyper-personalization, and the adoption of robotics process automation.

What is Bank Reconciliation?
In the world of finance and accounting, bank reconciliation serves as a vital practice to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial records. It involves comparing the transactions recorded in an individual’s or a business’s accounting system with the data provided by the bank. By performing bank reconciliation regularly, one can identify discrepancies, prevent errors, and maintain the integrity of financial information.
Understanding Bank Reconciliation
The Purpose of Bank Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation primarily serves two purposes. Firstly, it helps to identify any discrepancies or errors between an individual’s or a business’s records and the bank’s statements. Secondly, it ensures that all transactions have been accurately recorded and that the ending balance in the bank account matches the ending balance in the accounting records.
Common Reasons for Discrepancies
Discrepancies between an individual’s or a business’s records and the bank’s statements can occur due to various reasons. Some common causes include errors in recording transactions, delays in processing deposits or withdrawals, bank fees, interest charges, and bank errors. Bank reconciliation helps in identifying and resolving these discrepancies promptly.
How to Perform Bank Reconciliation
Gather the Necessary Documents
To begin the bank reconciliation process, gather the bank statements, canceled checks, deposit slips, and any other relevant financial documents for the period under review.
Compare the Bank Statement and Account Records
Next, compare the transactions listed on the bank statement with the entries in your accounting system. Start by checking off the transactions that match and make note of any discrepancies.
Identify Discrepancies and Adjustments
Carefully review the unmatched transactions and determine the reasons behind the discrepancies. This may involve locating missing transactions, identifying errors, or investigating any unfamiliar charges or fees. Make the necessary adjustments in your accounting records to rectify the discrepancies.
Reconcile the Balance
After identifying and resolving all discrepancies, compare the adjusted ending balance in your accounting records with the ending balance provided by the bank statement. If the two balances match, the bank reconciliation process is complete. If they don’t match, recheck your adjustments and verify that all transactions have been accounted for correctly.
Benefits of Bank Reconciliation
Accuracy in Financial Records
By regularly performing bank reconciliation, individuals and businesses can ensure the accuracy of their financial records. It helps identify and rectify errors, ensuring that the recorded transactions reflect the actual activity in the bank account.
Fraud Detection and Prevention
Bank reconciliation plays a crucial role in detecting fraudulent activities such as unauthorized transactions or forged checks. By carefully reviewing the bank statements and comparing them with the accounting records, any suspicious transactions can be identified and reported promptly.
Budgeting and Financial Planning
Bank reconciliation provides valuable insights into an individual’s or a business’s financial position. It helps in creating an accurate picture of cash flow, allowing for effective budgeting and financial planning.
Best Practices for Bank Reconciliation
Regular Reconciliation
Perform bank reconciliation on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly, to stay on top of your financial records and minimize discrepancies.
Maintaining Organized Records
Keep your financial records organized and up to date. Properly document all transactions, including deposits, withdrawals, and bank fees.
Double-Check Transactions
Take the time to double-check your transactions when reconciling the bank statement. Ensure that all entries are accurate and that you have accounted for any outstanding checks or deposits.
Seek Professional Help if Needed
If you’re unfamiliar with the bank reconciliation process or encounter complex financial situations, consider seeking assistance from a professional accountant or bookkeeper. They can provide guidance and ensure the accuracy of your financial records.
What happens if I don’t reconcile my bank accounts?
Failing to reconcile your bank accounts can lead to inaccurate financial records, missed transactions, undetected errors, and increased vulnerability to fraud.
How often should I reconcile my bank accounts?
It is recommended to reconcile your bank accounts on a monthly basis. However, the frequency may vary depending on the volume of transactions and the complexity of your financial activities.
Can bank reconciliation help identify errors made by the bank?
Yes, bank reconciliation can help identify errors made by the bank, such as incorrect charges or omissions in recording transactions.
Is bank reconciliation only necessary for businesses?
No, bank reconciliation is equally important for individuals as it is for businesses. It ensures the accuracy of personal financial records and helps in managing personal finances effectively.
Are there any software tools available for bank reconciliation?
Yes, there are various accounting software and online tools available that can automate the bank reconciliation process, making it faster and more efficient.

Expense Category for Tools: Organizing Your Business Finances
When it comes to running a business, managing expenses is a crucial task. One area that requires careful attention is the tools and equipment necessary for daily operations. Properly categorizing these expenses helps maintain financial clarity and facilitates budgeting. In this article, we will explore different expense categories for tools, providing you with a comprehensive guide to organizing your business finances efficiently.
Understanding Expense Categories
Expense categories are essential for classifying and organizing your business expenses. By creating specific categories, you gain better visibility into your spending patterns and can allocate budgets more effectively. When it comes to tools, each category represents a distinct area of your business operations where these tools play a significant role.
Expense Category 1: Maintenance and Repair Tools
Overview
Maintenance and repair tools are essential for keeping your business operations running smoothly. These tools are used to maintain equipment, troubleshoot issues, and perform necessary repairs.
Examples of Maintenance and Repair Tools
Wrenches and screwdrivers
Power drills
Multimeters
Lubricants and cleaning supplies
Replacement parts and components
Expense Category 2: Office and Administrative Tools
Overview
Office and administrative tools are necessary for managing daily tasks, streamlining operations, and improving overall efficiency. These tools are often used in administrative departments, such as human resources, finance, and general administration.
Examples of Office and Administrative Tools
Computers, laptops, and tablets
Printers and scanners
Project management software
Communication tools (e.g., email clients, video conferencing software)
File organization and storage solutions
Expense Category 3: Production and Manufacturing Tools
Overview
Production and manufacturing tools are vital for businesses involved in manufacturing, assembly, or production processes. These tools help improve productivity, quality control, and overall output.
Examples of Production and Manufacturing Tools
Machinery and equipment
Assembly line tools
Quality control instruments
Packaging and labeling tools
Inventory management systems
Expense Category 4: Research and Development Tools
Overview
Research and development tools are crucial for businesses focused on innovation, product development, and technological advancements. These tools enable experimentation, data analysis, and the creation of new prototypes.
Examples of Research and Development Tools
Laboratory equipment
Prototyping tools
Simulation software
Data analysis tools
Intellectual property management systems
Expense Category 5: Marketing and Advertising Tools
Overview
Marketing and advertising tools play a vital role in promoting your business and reaching your target audience. These tools assist in creating, managing, and analyzing marketing campaigns across various channels.
Examples of Marketing and Advertising Tools
Social media management tools
Email marketing software
Search engine optimization (SEO) tools
Analytics platforms
Graphic design software
Expense Category 6: Technology and Software Tools
Overview
In today’s digital age, technology, and software tools are essential for businesses of all sizes. These tools facilitate various operations, enhance productivity, and enable efficient communication and collaboration.
Examples of Technology and Software Tools
Project management software
Customer relationship management (CRM) systems
Accounting software
Collaboration and communication tools
Cybersecurity solutions
Expense Category 7: Safety and Security Tools
Overview
Safety and security tools are crucial for ensuring a secure working environment for your employees and protecting your business assets. These tools help minimize risks and prevent unauthorized access or incidents.
Examples of Safety and Security Tools
Surveillance cameras
Alarm systems
Fire safety equipment
Access control systems
Emergency response tools
Expense Category 8: Transportation and Logistics Tools
Overview
Transportation and logistics tools are necessary for businesses involved in the transportation, shipping, and logistics industry. These tools aid in managing deliveries, tracking shipments, and optimizing routes.
Examples of Transportation and Logistics Tools
Fleet management software
GPS tracking systems
Route optimization tools
Warehouse management systems
Delivery scheduling software
Expense Category 9: Customer Service Tools
Overview
Customer service tools are essential for businesses aiming to provide exceptional customer support and build strong customer relationships. These tools help streamline customer interactions and ensure timely and effective problem resolution.
Examples of Customer Service Tools
Helpdesk ticketing systems
Live chat software
Customer relationship management (CRM) software
Knowledge base and self-service tools
Call center management systems
Expense Category 10: Training and Development Tools
Overview
Investing in training and development tools is crucial for nurturing employee skills, improving performance, and fostering growth within your organization. These tools facilitate employee training, e-learning, and knowledge sharing.
Examples of Training and Development Tools
Learning management systems
Online training platforms
Skill assessment tools
Virtual reality (VR) training systems
Performance evaluation software
Expense Category 11: Accounting and Financial Tools
Overview
Accounting and financial tools are vital for managing your business’s financial aspects, including bookkeeping, invoicing, and financial analysis. These tools provide accurate financial insights and help maintain compliance with regulations.
Examples of Accounting and Financial Tools
Accounting software
Invoicing tools
Expense tracking systems
Financial reporting software
Tax preparation software
Expense Category 12: Inventory and Stock Management Tools
Overview
Inventory and stock management tools are crucial for businesses dealing with physical products. These tools enable effective inventory tracking, stock replenishment, and demand forecasting.
H3: Examples of Inventory and Stock Management Tools
Inventory management software
Barcode scanners
Warehouse management systems
Demand planning tools
Order management systems
Expense Category 13: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Tools
Overview
Customer relationship management (CRM) tools help businesses build and maintain strong customer relationships. These tools centralize customer data, automate sales processes, and enhance customer communication.
Examples of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Tools
CRM software platforms
Contact management systems
Sales pipeline tracking tools
Lead nurturing software
Customer feedback and survey tools
Expense Category 14: Analytics and Reporting Tools
Overview
Analytics and reporting tools are essential for businesses seeking data-driven insights and performance tracking. These tools enable data analysis, visualization, and reporting to support informed decision-making.
Examples of Analytics and Reporting Tools
Business intelligence software
Data visualization platforms
Performance tracking tools
A/B testing software
Dashboards and reporting systems
How can categorizing expenses for tools benefit my business?
Categorizing expenses for tools provides clarity and organization in your business finances. It helps you track spending, allocate budgets, and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
Can I customize the expense categories to suit my business?
Absolutely! It’s important to tailor the expense categories to align with your specific business needs. Customize the categories based on your industry, operations, and the types of tools you utilize.
How often should I review and update my expense categories?
It’s recommended to review and update your expense categories regularly, at least once a year. However, if you experience significant changes in your business operations or tool usage, consider revisiting the categories more frequently.
Should I consult with an accountant when categorizing expenses?
While not mandatory, consulting with an accountant or financial advisor can provide valuable insights and ensure accurate categorization of expenses. They can offer guidance specific to your industry and help optimize your financial management practices.
Are there any software tools available to assist with expense categorization?
Yes, there are various accounting and financial software tools that can automate expense categorization and streamline your financial management processes. Research and choose a tool that best suits your business requirements.

Expense Categorization for Online Retailers
Proper expense categorization allows online retailers to gain better insights into their financial activities, make informed decisions, and optimize their spending. In the competitive landscape of e-commerce, online retailers face numerous financial challenges. Expense categorization acts as a fundamental tool to organize and understand the various costs involved in running an online retail business. By categorizing expenses effectively, retailers can gain insights into their financial health, identify areas for improvement, and optimize their overall business performance.
Why Expense Categorization Matters
Expense categorization is essential for online retailers due to the following reasons:
Financial Visibility: Categorizing expenses provides a clear and organized overview of a retailer’s financial activities, allowing them to monitor cash flow, track spending patterns, and identify potential cost-saving opportunities.
Accurate Reporting and Analysis: Proper categorization enables retailers to generate accurate financial reports and perform detailed analysis, facilitating better decision-making processes and strategic planning.
Tax Compliance: Well-categorized expenses simplify the tax filing process, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and maximizing eligible deductions.
Key Expense Categories for Online Retailers
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS includes the direct expenses associated with the production or procurement of goods sold. It encompasses costs such as raw materials, manufacturing expenses, packaging, and shipping costs directly related to the products being sold.
Marketing and Advertising Expenses
Marketing and advertising expenses cover promotional activities, including digital marketing campaigns, social media advertising, influencer partnerships, and search engine optimization efforts.
Operational Expenses
Operational expenses encompass day-to-day costs necessary to keep the business running smoothly. This category includes rent, utilities, salaries, insurance, office supplies, and any other expenses associated with administrative tasks and overhead.
Payment Processing Fees
Payment processing fees are charges incurred when processing online transactions. These fees are usually a percentage of the transaction value or a fixed amount per transaction.
Shipping and Fulfillment Costs
Shipping and fulfillment costs cover expenses related to packaging, shipping materials, shipping services, and logistics. These expenses are particularly significant for online retailers who rely on efficient and reliable shipping to deliver products to customers.
Developing an Expense Categorization System
Analyzing Historical Data
Begin by analyzing historical financial data to gain insights into past expenses. Look for patterns, identify common expenditure categories, and assess the relevance and accuracy of existing expense categorization.
Customizing Categories for Your Business
Tailor expense categories to align with your specific business needs and industry requirements. Consider creating subcategories within broader expense categories to enhance granularity and facilitate more precise financial analysis.
Utilizing Accounting Software
Leverage accounting software to streamline the expense categorization process. Many software solutions offer features that automate expense tracking, allow for easy categorization, and generate comprehensive financial reports.
Best Practices for Expense Categorization
Consistency and Accuracy
Maintain consistency in categorizing expenses across all financial records to ensure accurate reporting and analysis. Develop clear guidelines and train employees involved in expense tracking to follow the established categorization system.
Regular Review and Adjustment
Regularly review and update the expense categorization system to reflect changes in business operations, industry trends, and evolving expense types. Adjustments should be made in a timely manner to maintain accuracy and relevance.
Automation and Integration
Explore automation options to streamline the expense categorization process. Integration between accounting software and other business tools, such as payment processors and e-commerce platforms, can significantly reduce manual effort and improve efficiency.
Documenting Expenses
Maintain detailed records of all expenses, including receipts, invoices, and supporting documentation. Accurate documentation serves as valuable evidence during audits and ensures transparency in financial transactions.
Benefits of Effective Expense Categorization
Implementing an effective expense categorization system offers several benefits to online retailers:
Improved financial visibility and control
Enhanced decision-making through accurate financial analysis
Simplified tax filing and compliance
Identifying cost-saving opportunities
Streamlined budgeting and forecasting
How often should I review and adjust my expense categorization system?
It is recommended to review your expense categorization system on a quarterly basis or whenever there are significant changes in your business operations or expense types.
Can I use spreadsheets for expense categorization, or do I need accounting software?
While spreadsheets can be used for basic expense tracking, utilizing dedicated accounting software offers greater automation, accuracy, and comprehensive reporting capabilities.
Should I categorize every expense individually, or can I group similar expenses together?
Grouping similar expenses together under broader categories is generally recommended for ease of analysis. However, maintaining a balance between granularity and practicality is important.
How can automation help with expense categorization?
Automation can reduce manual effort by integrating systems, automatically categorizing expenses based on predefined rules, and generating real-time reports, saving time and improving accuracy.
Is it necessary to keep records of all expenses and supporting documentation?
Yes, maintaining detailed records of expenses, including receipts and invoices, is crucial for accurate financial reporting, tax compliance, and potential audits.

Recurring Revenue Management for Online Stores
In the ever-evolving landscape of online commerce, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to secure their financial stability and build a loyal customer base. Recurring revenue management, through the implementation of subscription-based models, offers an effective solution to achieve these goals. This article will delve into the intricacies of recurring revenue management for online stores and provide insights into the advantages it brings.
Understanding Recurring Revenue
Recurring revenue refers to the predictable and continuous income generated by online businesses through subscription-based products or services. Unlike one-time purchases, recurring revenue models allow businesses to establish long-term relationships with their customers, ensuring a steady stream of revenue. Examples of recurring revenue models include monthly subscription boxes, software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms, membership-based websites, and more.
Benefits of Implementing Recurring Revenue Models
Retaining Customers and Ensuring Predictable Revenue
Implementing recurring revenue models enables online stores to build strong customer relationships and enhance customer loyalty. By offering a subscription-based service, businesses encourage customers to commit to regular payments, ensuring a predictable revenue stream.
Creating a Sustainable Business Model
Recurring revenue models provide stability and sustainability to online businesses. With a consistent income flow, companies can better forecast their finances, allocate resources efficiently, and plan for future growth and expansion.
Increasing Customer Lifetime Value
Recurring revenue models allow businesses to extend their customer lifetime value by nurturing ongoing relationships. Through personalized experiences, targeted offers, and regular engagement, companies can increase customer retention and encourage upselling and cross-selling opportunities.
Challenges of Recurring Revenue Management
Customer Churn and Retention
Retaining customers and minimizing churn is a crucial challenges in recurring revenue management. Online stores must focus on consistently delivering value, addressing customer concerns, and adapting to changing customer needs to reduce the likelihood of cancellations.
Pricing and Value Proposition
Determining the right price for subscription-based products or services can be challenging. Online stores need to strike a balance between affordability and profitability while providing customers with a compelling value proposition that justifies their recurring investment.
Billing and Payment Processing
Managing recurring billing and payment processing can be complex and time-consuming. Online stores must invest in robust payment gateways and systems that offer seamless experiences, automated notifications, and secure transactions to streamline the payment process.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
Know Your Target Audience
Before implementing a recurring revenue model, it is crucial to understand your target audience and their needs. Conduct market research, gather customer feedback, and identify the pain points your subscription-based product or service can address effectively.
Offer Flexible Subscription Plans
Provide a range of subscription plans to cater to different customer preferences. Consider offering monthly, quarterly, and annual options, allowing customers to choose the plan that best suits their needs and budget.
Deliver Consistent Value
Consistently deliver value to your subscribers to justify their recurring payments. Continuously improve your product or service, provide exclusive benefits to subscribers, and engage with customers through personalized communication.
Monitor Key Metrics
Regularly track and analyze key metrics related to your recurring revenue model. Keep an eye on metrics such as customer churn rate, average revenue per user (ARPU), customer acquisition cost (CAC), and customer lifetime value (CLV) to gain insights and make data-driven decisions.
Provide Excellent Customer Support
Invest in a robust customer support system to address customer queries, concerns, and issues promptly. Offer multiple channels of communication, such as email, live chat, and phone support, to provide a seamless and satisfactory customer experience.
Optimizing Customer Retention
To optimize customer retention in recurring revenue management, online stores should focus on the following strategies:
Personalization and Customization
Tailor your product or service to meet individual customer preferences. Leverage data and customer insights to offer personalized recommendations, exclusive content, and customization options.
Proactive Engagement
Engage with your subscribers regularly through newsletters, personalized emails, and relevant content. Keep them informed about new features, updates, and exclusive offers to reinforce their commitment to your brand.
Loyalty Programs and Rewards
Implement loyalty programs and reward systems to incentivize customer loyalty. Offer exclusive discounts, early access to new products or services, and special perks for long-term subscribers.
Analyzing Key Metrics
Analyzing key metrics is essential for evaluating the performance of your recurring revenue model. Consider the following metrics:
Customer Churn Rate
Monitor the rate at which customers cancel their subscriptions. A high churn rate may indicate underlying issues with your product, pricing, or customer support.
Average Revenue per User (ARPU)
Calculate the average revenue generated per subscriber. Tracking ARPU helps assess the effectiveness of your pricing strategy and identify opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Determine how much it costs to acquire each new customer. This metric allows you to evaluate the efficiency of your marketing and acquisition efforts.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Estimate the total revenue you can expect from a customer over their entire relationship with your business. CLV helps you understand the long-term profitability of your recurring revenue model.
Leveraging Technology Solutions
Investing in technology solutions can streamline recurring revenue management. Consider the following tools:
Subscription Management Software
Utilize subscription management platforms to automate billing, manage subscriptions, and handle customer data securely. These tools simplify the administrative tasks associated with recurring revenue models.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System
Implement a CRM system to track customer interactions, preferences, and purchase history. A CRM system enables personalized communication, targeted marketing, and effective customer management.
Building Customer Trust
Building trust is crucial for the success of recurring revenue models. Employ the following strategies:
Transparent Pricing and Billing
Be transparent about your pricing and billing practices. Clearly communicate the terms, conditions, and cancellation policies to avoid any misunderstandings or disputes.
Secure Payment Processing
Invest in secure payment gateways and comply with industry standards for data protection. Prioritize the security of your customer’s financial information to build trust and credibility.
Marketing and Promotions
Promote your recurring revenue model effectively to attract new customers and retain existing ones:
Targeted Marketing Campaigns
Craft targeted marketing campaigns to reach potential subscribers. Use channels such as social media, email marketing, content marketing, and paid advertising to create awareness and generate interest.
Free Trials and Discounts
Offer free trials or discounted introductory periods to encourage customers to try your subscription-based product or service. This allows them to experience its value before making a long-term commitment.
Scaling and Expansion
As your recurring revenue model proves successful, consider scaling and expanding your offerings:
Diversify Product Portfolio
Expand your product or service offerings to cater to a wider audience. Introduce new subscription tiers, add complementary products, or explore partnerships to diversify your revenue streams.
International Expansion
Consider expanding your recurring revenue model to international markets. Adapt your offerings to suit different regions, languages, and cultural preferences to attract a global customer base.
How do I determine the right price for my subscription-based product or service?
When determining the price, consider factors such as production costs, market demand, competitive pricing, and customer willingness to pay. Test different price points and gather customer feedback to find the optimal balance.
What are some effective strategies for reducing customer churn in recurring revenue models?
Provide exceptional customer support, continuously deliver value, personalize the customer experience, and offer loyalty programs and rewards to incentivize customer loyalty.
Is it possible to implement a recurring revenue model for physical products?
Yes, recurring revenue models can be implemented for physical products through subscription box services, auto-replenishment programs, or membership-based product clubs.
How can I optimize customer retention in recurring revenue management?
Focus on personalization, proactive engagement, and implementing loyalty programs and rewards. Continuously monitor and improve customer satisfaction to enhance retention rates.
What technology solutions can help with recurring revenue management?
Subscription management software and customer relationship management (CRM) systems are valuable tools for automating billing, managing subscriptions, and nurturing customer relationships.

How do I track costs in Xero?
Xero is a powerful accounting software that helps businesses manage their financials effectively. Tracking costs in Xero is an essential aspect of maintaining accurate records and gaining insights into your business’s expenses. In this article, we will explore the different methods and features provided by Xero to track costs efficiently.
Understanding Cost Tracking
Cost tracking involves monitoring and recording all the expenses incurred by a business. It helps in analyzing and controlling costs, identifying cost-saving opportunities, and making informed financial decisions. Xero provides several features and functionalities to streamline cost-tracking processes.
Setting Up Cost Tracking in Xero
To start tracking costs in Xero, you need to ensure that your chart of accounts is properly set up. The chart of accounts is a comprehensive list of all the accounts used in your business, such as income, expenses, assets, and liabilities. By organizing your accounts correctly, you can categorize expenses effectively and generate accurate reports.
Categorizing Costs
In Xero, you can categorize costs by creating specific accounts or using predefined account codes. This allows you to classify expenses based on different categories, such as office supplies, travel expenses, utilities, or marketing costs. By assigning the appropriate account codes to each expense, you can track and analyze your spending habits more efficiently.
Creating Expense Claims
If you or your employees incur business-related expenses that need to be reimbursed, Xero enables you to create and manage expense claims. With this feature, you can easily record and track all the expenses incurred by individuals within your organization. This helps in maintaining transparency and ensures that reimbursements are processed accurately.
Managing Supplier Invoices
Xero simplifies the process of managing supplier invoices by allowing you to enter and track them electronically. When you receive an invoice from a supplier, you can easily create a new bill in Xero, enter the relevant details, and attach any supporting documents. This not only streamlines your accounts payable process but also helps you keep track of outstanding payments and due dates.
Tracking Billable Expenses
For businesses that provide services or billable expenses to clients, Xero offers a convenient way to track and invoice these costs. You can record billable expenses against specific projects or clients, ensuring that all the costs are accurately allocated. Xero also allows you to generate invoices directly from billable expenses, saving time and reducing manual data entry.
Allocating Costs to Projects
If you work on multiple projects or want to track expenses associated with specific jobs, Xero’s tracking categories feature comes in handy. You can set up tracking categories for different projects, departments, or locations and assign expenses to the relevant category. This enables you to monitor costs and profitability on a project-by-project basis.
Generating Reports
Xero provides a range of customizable reports that give you detailed insights into your business’s financial performance. You can generate expense reports, profit and loss statements, cash flow statements, and more. These reports help you analyze your spending patterns, identify areas of improvement, and make informed financial decisions.
Integrating Third-Party Apps for Cost Tracking
To enhance your cost-tracking capabilities, Xero integrates with various third-party apps and services. These apps offer additional features like receipt scanning, mileage tracking, expense approvals, and more. By integrating these apps with Xero, you can automate data entry, streamline workflows, and gain even more visibility into your costs.
Best Practices for Effective Cost Tracking
To make the most of Xero’s cost-tracking features, consider implementing the following best practices:
Regularly review and reconcile your accounts to ensure accuracy.
Use the “find and recode” feature to correct any miscategorized expenses.
Set up bank rules to automatically categorize recurring expenses.
Train your staff on proper expense entry and coding practices.
Keep track of tax-related expenses separately for easier reporting.
Ensuring Accuracy and Compliance
Accurate cost tracking is crucial for financial reporting and compliance purposes. Ensure that you follow proper accounting standards and guidelines when categorizing expenses. Regularly reconcile your accounts and verify that the recorded expenses align with the supporting documents. This ensures the integrity of your financial records and simplifies audits or tax filings.
Streamlining Cost Tracking with Automation
Xero offers various automation features that can significantly streamline your cost-tracking processes. You can set up bank feeds to automatically import transactions into Xero, reducing manual data entry. Additionally, you can leverage Xero’s rules and reminders to automate the categorization and tracking of recurring expenses. Automation saves time, minimizes errors, and allows you to focus on more strategic aspects of your business.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
While Xero provides robust cost-tracking capabilities, you may encounter certain challenges or issues. Some common challenges include duplicate entries, incorrect account coding, and syncing errors with third-party apps. To troubleshoot these problems, refer to Xero’s comprehensive help guides, consult with Xero support, or seek assistance from an accounting professional.
Can I track costs for multiple business entities in Xero?
Yes, Xero allows you to manage multiple business entities within a single account. You can set up separate tracking categories or use the different charts of accounts for each entity to track costs accurately.
Is Xero suitable for small businesses?
Absolutely! Xero caters to businesses of all sizes, from freelancers and startups to established enterprises. Its scalable features and user-friendly interface make it an ideal choice for small businesses.
Can I import expenses from external systems into Xero?
Yes, Xero supports importing expenses from external systems. You can use CSV or Excel files to bulk import expenses, saving time and effort.
Can I customize the expense categories in Xero?
Yes, Xero allows you to customize the expense categories according to your business needs. You can create new accounts or modify existing ones to align with your expense classification requirements.
Does Xero provide mobile apps for expense tracking?
Yes, Xero offers mobile apps for both iOS and Android devices. You can easily track and manage your expenses on the go, capturing receipts and recording expenses in real time.

What are Sales and Revenue Analysis for Online Businesses?
Sales and revenue analysis is the process of examining sales data and financial information to gain insights into the performance and profitability of an online business. It involves tracking and evaluating various metrics and key performance indicators to make informed decisions and drive business growth. By analyzing sales and revenue data, businesses can identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities, enabling them to optimize their strategies, improve customer satisfaction, and maximize profitability.
Key Metrics for Sales and Revenue Analysis
Conversion Rate
The conversion rate is a critical metric that measures the percentage of website visitors who take a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a contact form. By tracking the conversion rate, businesses can assess the effectiveness of their marketing efforts, website design, and user experience. A higher conversion rate indicates that a larger proportion of visitors are turning into customers, resulting in increased revenue.
Average Order Value (AOV)
The average order value represents the average amount of money spent by customers in a single transaction. Monitoring the AOV helps businesses understand the purchasing behavior of their customers and develop strategies to increase the average value per order. By upselling or cross-selling related products or offering incentives for larger purchases, businesses can boost their revenue without acquiring additional customers.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
The customer acquisition cost measures the amount of money spent on acquiring a new customer. It includes marketing expenses, sales commissions, and any other costs associated with customer acquisition. By comparing the CAC with the customer lifetime value (CLV), businesses can evaluate the profitability of acquiring new customers. A lower CAC relative to CLV indicates a healthier business model.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
The customer lifetime value represents the total revenue generated by a customer throughout their relationship with the business. Understanding the CLV helps businesses prioritize customer retention and loyalty initiatives. By increasing the CLV through personalized marketing, exceptional customer service, and loyalty programs, businesses can maximize their revenue from existing customers.
Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI measures the profitability of an investment relative to its cost. When analyzing sales and revenue, businesses need to assess the ROI of their marketing campaigns, advertising channels, and other investments. By identifying the most effective channels and optimizing marketing spend, businesses can allocate resources efficiently and improve their overall return on investment.
Analyzing Sales Data
Tracking and Recording Sales
To perform effective sales analysis, businesses need to ensure that they have robust systems in place to track and record sales data accurately. This includes implementing a reliable e-commerce platform or point-of-sale system that captures essential information such as product sales, customer details, and transactional data. With accurate data, businesses can generate reports and analyze trends to make data-driven decisions.
Segmentation and Cohort Analysis
Segmentation involves dividing customers into distinct groups based on characteristics such as demographics, behavior, or purchase history. Cohort analysis, on the other hand, focuses on analyzing groups of customers who share a common characteristic or experience within a specific time frame. These techniques allow businesses to understand different customer segments, and their buying patterns, and tailor their marketing and sales strategies accordingly.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
By analyzing sales data over time, businesses can identify trends and patterns that provide valuable insights into customer behavior and market dynamics. For example, businesses can identify seasonal fluctuations in sales, peak purchasing periods, or changes in customer preferences. Armed with this information, businesses can plan inventory, adjust pricing strategies, and launch targeted marketing campaigns to capitalize on these trends.
Monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key performance indicators are quantifiable metrics that help businesses measure their progress toward achieving specific goals. When it comes to sales and revenue analysis, businesses should monitor KPIs such as total sales, revenue growth rate, customer retention rate, and average profit margin. By tracking these metrics regularly, businesses can gauge their performance and take corrective actions if necessary.
Revenue Analysis Techniques
Revenue Streams and Sources
To analyze revenue effectively, businesses need to understand the various streams and sources through which revenue is generated. This may include revenue from direct product sales, subscriptions, advertising, partnerships, or affiliate programs. By assessing the performance of each revenue stream and identifying opportunities for growth, businesses can diversify their revenue sources and mitigate risks.
Pricing Strategies
Pricing plays a crucial role in sales and revenue analysis. By analyzing pricing strategies, businesses can optimize their product pricing to maximize revenue and profitability. This may involve conducting market research, analyzing competitor pricing, and determining the right balance between pricing, value, and customer perception. Pricing experiments and A/B testing can also provide valuable insights into customer price sensitivity and willingness to pay.
Product Mix and Cross-Selling
Analyzing the performance of different products or services within a business’s portfolio is essential for revenue analysis. By evaluating sales data for individual products or product categories, businesses can identify their best-selling items and promote cross-selling opportunities. Offering complementary products or services can increase the average order value and drive additional revenue.
Seasonal and Cyclical Trends
Many businesses experience seasonal or cyclical fluctuations in sales and revenue. Analyzing historical data and identifying these patterns can help businesses prepare for busy seasons or anticipate periods of reduced demand. By adjusting inventory levels, staffing, and marketing strategies accordingly, businesses can optimize their revenue generation throughout the year.
Competitor Analysis
To gain a competitive advantage, businesses must conduct thorough competitor analysis. By analyzing their competitors’ sales and revenue strategies, businesses can identify market gaps, pricing opportunities, and areas for improvement. This analysis can inform product development, marketing campaigns, and sales tactics to differentiate from competitors and capture a larger market share.
Tools and Technologies for Sales and Revenue Analysis
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
CRM systems are essential tools for managing customer data and analyzing sales performance. They enable businesses to track customer interactions, monitor sales pipelines, and generate reports on customer behavior and revenue. CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer acquisition, retention, and satisfaction, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions to improve sales and revenue.
Analytics and Reporting Platforms
Analytics and reporting platforms, such as Google Analytics, provide businesses with in-depth data on website traffic, conversions, and customer behavior. These platforms offer advanced analytical capabilities, including segmentation, funnel analysis, and attribution modeling. By leveraging these tools, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their online sales and revenue performance and make informed optimization decisions.
Marketing Automation Software
Marketing automation software helps businesses streamline marketing processes and analyze the effectiveness of their campaigns. These tools enable businesses to automate email marketing, lead nurturing, and customer segmentation. By tracking key metrics such as email open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates, businesses can measure the impact of their marketing efforts on sales and revenue.
A/B Testing Tools
A/B testing allows businesses to experiment with different versions of a webpage or marketing campaign to determine which performs better. By conducting A/B tests on pricing, call-to-action buttons, or landing page design, businesses can optimize their sales funnels and improve conversion rates. A/B testing tools provide statistical analysis and insights to support data-driven decision-making.
Data Visualization Tools
Data visualization tools help businesses transform complex data into visual representations such as charts, graphs, and dashboards. These tools make it easier to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in sales and revenue data. By presenting data visually, businesses can communicate insights more effectively and facilitate better decision-making at all levels of the organization.
The Benefits of Sales and Revenue Analysis
Implementing robust sales and revenue analysis practices brings several benefits to online businesses:
Improved decision-making: By analyzing sales and revenue data, businesses can make informed decisions about marketing strategies, product pricing, and resource allocation.
Enhanced profitability: Sales and revenue analysis allow businesses to identify opportunities for increasing revenue, optimizing pricing, and reducing costs, leading to improved profitability.
Customer-centric strategies: Analyzing customer behavior and preferences helps businesses tailor their offerings, marketing messages, and customer experiences to enhance satisfaction and drive repeat sales.
Competitive advantage: By analyzing competitors’ strategies and market trends, businesses can differentiate themselves and capitalize on untapped market opportunities.
Scalable growth: Sales and revenue analysis provide insights into business performance and areas for improvement, enabling businesses to scale their operations and achieve sustainable growth.
How often should sales and revenue analysis be conducted?
Sales and revenue analysis should be conducted regularly, ideally on a monthly or quarterly basis. This frequency allows businesses to identify trends, measure the impact of strategies and campaigns, and make timely adjustments to improve performance.
Can sales and revenue analysis help in identifying customer preferences?
Yes, sales and revenue analysis can provide insights into customer preferences by analyzing purchase patterns, product preferences, and customer segmentation. This information can be used to tailor marketing messages, develop personalized offers, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Are there any free tools available for sales and revenue analysis?
Yes, there are free tools available for sales and revenue analysis, such as Google Analytics for website data analysis, CRM platforms with free plans, and data visualization tools like Google Data Studio. These tools can provide valuable insights for businesses, especially those starting with limited resources.
How can businesses optimize their pricing strategies through sales and revenue analysis?
Sales and revenue analysis can help businesses optimize their pricing strategies by evaluating competitor pricing, conducting A/B tests, and analyzing customer behavior. By understanding price sensitivity, value perception, and market dynamics, businesses can determine the optimal pricing that maximizes revenue and maintains competitiveness.
Is it necessary to hire a data analyst for sales and revenue analysis?
While hiring a data analyst can be beneficial for businesses with complex data and analysis needs, many tools and platforms provide user-friendly interfaces and automated reports. Small and medium-sized businesses can leverage these tools to perform sales and revenue analysis without the need for dedicated data analysts, although having data expertise can further enhance the analysis process.
What are the different methods of inventory reconciliation?
Inventory reconciliation plays a crucial role in the smooth functioning of businesses across various industries. It involves the process of comparing physical inventory records with the recorded data in the books to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies. Inventory reconciliation is an essential process that ensures accurate stock management and helps businesses avoid costly errors. By implementing effective inventory reconciliation methods, companies can maintain optimal stock levels, reduce discrepancies, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Importance of Inventory Reconciliation
Accurate inventory management is crucial for businesses to meet customer demand, minimize stockouts, and prevent overstocking. Inventory reconciliation enables companies to identify any inconsistencies between physical stock and recorded data, allowing them to make necessary adjustments. This process helps:
Maintain accurate stock levels: Reconciling inventory ensures that the quantity of items in stock matches the recorded data, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
Reduce losses: By identifying and addressing discrepancies promptly, businesses can minimize losses due to theft, damage, or data entry errors.
Improve operational efficiency: Accurate inventory data facilitates effective planning, purchasing, and fulfillment processes, leading to streamlined operations and improved productivity.
Method 1: Physical Count
Physical counting is the most straightforward method of inventory reconciliation. It involves physically counting all items in stock and comparing the count to the recorded data. This method is time-consuming but provides a comprehensive and accurate assessment of inventory levels.
Method 2: Cycle Counting
Cycle counting is a periodic inventory counting method that involves counting a subset of items in stock on a regular basis. Instead of counting all inventory items at once, cycle counting focuses on a smaller portion, often determined by an item’s value or frequency of sales. This method allows for frequent reconciliation while minimizing disruption to daily operations.
Method 3: ABC Analysis
ABC analysis categorizes inventory items into three groups based on their value and importance. Class A items represent high-value products that contribute significantly to revenue, while Class C items are low-value products with minimal impact. By prioritizing the reconciliation of Class A items, businesses can ensure the accuracy of their most valuable inventory.
Method 4: Statistical Sampling
Statistical sampling involves selecting a representative sample of inventory items for reconciliation instead of counting every single item. This method uses statistical techniques to estimate the accuracy of the entire inventory based on the results from the sampled items. Statistical sampling saves time and resources while still providing a reasonable level of accuracy.
Method 5: RFID Technology
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology utilizes tags and readers to track and reconcile inventory automatically. RFID tags are attached to individual items, and the readers capture data from the tags, updating inventory records in real-time. RFID technology provides accurate and efficient inventory reconciliation, especially in large-scale operations.
Method 6: Continuous Monitoring Systems
Continuous monitoring systems use sensors and automated data capture devices to monitor inventory levels in real-time. These systems provide instant updates on stock movements, allowing for proactive reconciliation and prompt action in case of discrepancies. Continuous monitoring systems minimize manual effort and provide accurate, up-to-date inventory information.
Method 7: Barcoding and Scanning
Barcoding and scanning systems involve assigning unique barcodes to each inventory item and using barcode scanners to track and reconcile inventory. When items are received, sold, or moved, the barcode scanners update the inventory records automatically. This method ensures accurate inventory reconciliation while streamlining day-to-day operations.
Method 8: Vendor Consignment
Vendor consignment is a method where a supplier places inventory at the buyer’s location, and the buyer pays for the inventory only when it is used or sold. The supplier maintains ownership until the inventory is consumed. This arrangement reduces the need for frequent reconciliation, as the supplier is responsible for managing and replenishing the consigned inventory.
Method 9: Drop Shipping
Drop shipping is a fulfillment method where the seller doesn’t keep the inventory in stock. Instead, when a customer places an order, the seller purchases the item from a third-party supplier who directly ships it to the customer. Drop shipping eliminates the need for inventory reconciliation as the seller never physically handles the products.
Method 10: Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management aims to keep inventory levels minimal by receiving goods from suppliers only when needed for production or order fulfillment. This method reduces the need for extensive inventory reconciliation by maintaining a lean inventory system and relying on timely deliveries.
Method 11: Safety Stock
Safety stock refers to the extra inventory maintained to mitigate the risks of stockouts caused by unforeseen circumstances such as increased demand or delayed deliveries. While safety stock doesn’t require regular reconciliation, periodic assessments can ensure that the designated safety levels are appropriate and updated.
Method 12: Reorder Point (ROP)
The reorder point (ROP) is the inventory level at which a new order should be placed to replenish stock before it reaches zero. Reconciling inventory against the reorder point helps businesses identify the need for timely reordering and prevent stockouts.
Method 13: First In, First Out (FIFO)
The First In, First Out (FIFO) method assumes that the oldest inventory is sold or used first. By reconciling inventory using the FIFO principle, businesses can ensure that the recorded data matches the actual physical movement of goods. This method is particularly crucial for industries with perishable or time-sensitive products.
Why is inventory reconciliation important?
Inventory reconciliation is important to ensure accurate stock levels, reduce losses, and improve operational efficiency. It helps businesses avoid overstocking, stockouts, and costly errors in inventory management.
How often should inventory reconciliation be performed?
The frequency of inventory reconciliation depends on various factors such as industry, inventory turnover rate, and business requirements. However, performing reconciliations on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly, is recommended to maintain accuracy.
Can inventory reconciliation be automated?
Yes, inventory reconciliation can be automated using technologies like RFID, barcoding, scanning systems, and continuous monitoring systems. These automated methods provide real-time updates and streamline the reconciliation process.
What is the purpose of safety stock?
Safety stock is maintained to mitigate the risks of stockouts caused by unforeseen circumstances. It acts as a buffer to ensure that there is sufficient inventory to meet unexpected demand or supply disruptions.
How does inventory reconciliation improve customer satisfaction?
Accurate inventory reconciliation ensures that products are available when customers need them. This reduces the likelihood of stockouts and delays in fulfilling orders, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.

What are some good online bookkeeping jobs?
In the digital age, businesses are increasingly shifting towards online operations. This transition has created a demand for online bookkeepers who can efficiently manage financial records and ensure accurate bookkeeping practices. Online bookkeeping jobs offer professionals the flexibility to work remotely while providing valuable financial services to businesses of all sizes.
The Rise of Online Bookkeeping Jobs
The emergence of cloud-based accounting software and virtual collaboration tools has revolutionized the bookkeeping industry. These technological advancements have made it possible for bookkeepers to work remotely, accessing client accounts from anywhere in the world. As a result, online bookkeeping jobs have gained popularity, providing individuals with the freedom to balance work and personal life effectively.
Benefits of Online Bookkeeping Jobs
Online bookkeeping jobs come with several advantages that make them appealing to professionals seeking flexible employment options. Some key benefits include:
Flexible Schedule: Online bookkeepers can often choose their own working hours, allowing them to maintain a healthy work-life balance.
Location Independence: As an online bookkeeper, you have the freedom to work from anywhere, whether it’s your home, a coffee shop, or while traveling.
Diverse Clientele: Working online opens up opportunities to collaborate with clients from various industries and locations, providing a stimulating and dynamic work experience.
Lower Overhead Costs: As an online bookkeeper, you can save on commuting expenses and office-related costs, as you typically work from a home office.
Essential Skills for Online Bookkeepers
To excel in online bookkeeping jobs, it is important to possess certain skills and qualifications. These skills include:
Proficiency in Accounting Software: Familiarity with popular accounting software, such as QuickBooks, Xero, or FreshBooks, is crucial for efficiently managing financial records.
Attention to Detail: Bookkeepers must have excellent attention to detail to ensure accurate data entry and financial record maintenance.
Organizational Skills: Effective organization is essential to manage multiple client accounts and ensure the timely completion of tasks.
Communication Skills: Online bookkeepers need to communicate clearly and effectively with clients and team members, often through email, video conferencing, or virtual collaboration platforms.
Analytical Thinking: The ability to analyze financial data and provide valuable insights is a valuable skill for online bookkeepers.
Popular Online Bookkeeping Jobs
There is a wide range of online bookkeeping jobs available, catering to different industries and business types. Here are five popular options:
Freelance Bookkeeping
Freelance bookkeepers offer their services to multiple clients on a contract basis. This option provides the highest level of flexibility as you can choose the clients and projects that align with your skills and interests.
Virtual Bookkeeping for Small Businesses
Many small businesses prefer hiring virtual bookkeepers who can manage their financial records remotely. This role involves handling day-to-day bookkeeping tasks, such as recording transactions, reconciling accounts, and generating financial reports.
Remote Bookkeeping for Corporations
Large corporations often hire remote bookkeepers to manage their financial operations. This role may involve more complex tasks, such as budgeting, forecasting, and financial analysis.
Bookkeeping for E-commerce Stores
With the growth of online businesses, there is an increasing demand for bookkeepers specializing in e-commerce. These bookkeepers handle tasks like tracking sales, managing inventory, and reconciling payment gateways.
Bookkeeping for Non-Profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations have unique financial requirements. Bookkeepers in this sector handle tasks like tracking donations, managing grants, and ensuring compliance with financial regulations specific to non-profits.
Platforms and Resources for Online Bookkeepers
As an online bookkeeper, there are various platforms and resources available to support your work and connect you with clients. Some popular platforms include:
- Upwork
- Freelancer
- Fiverr
QuickBooks ProAdvisor Program
These platforms offer opportunities to find clients, showcase your skills, and build a reputable online presence.
How to Get Started
If you’re interested in pursuing online bookkeeping jobs, here are some steps to help you get started:
Acquire the necessary skills and qualifications by pursuing relevant education or certification programs.
Build a professional resume and highlight your bookkeeping experience, skills, and any relevant certifications.
Create an online portfolio showcasing your expertise and previous work.
Join online job platforms and professional networks to connect with potential clients.
Develop a marketing strategy to promote your services and attract clients.
Continuously update your skills and stay informed about industry trends and best practices.
Challenges and Tips for Success
While online bookkeeping jobs offer numerous benefits, they also come with their own set of challenges. Some common challenges include managing multiple clients, maintaining a work-life balance, and staying updated with changing accounting regulations. Here are a few tips to overcome these challenges and thrive as an online bookkeeper:
Stay organized: Use project management tools and calendars to keep track of deadlines and prioritize tasks.
Continuously upskill: Stay updated with the latest accounting software, industry trends, and best practices through online courses and professional development programs.
Set boundaries: Clearly define your working hours and communicate them to clients to maintain a healthy work-life balance.
Network: Connect with other professionals in the field through online forums, social media groups, and professional organizations to share knowledge and gain insights.
Seek feedback: Regularly seek feedback from clients to improve your skills and enhance client satisfaction.
How much can I earn as an online bookkeeper?
Earnings can vary based on factors such as experience, qualifications, and the type of clients you work with. On average, online bookkeepers can earn between $20 to $50 per hour.
Do I need a formal education to become an online bookkeeper?
While formal education in accounting or bookkeeping can be advantageous, it is not always necessary. Relevant certifications and practical experience can also contribute to your credibility as a bookkeeper.
Is online bookkeeping suitable for beginners?
Yes, online bookkeeping can be a great starting point for beginners. It offers opportunities to gain experience, build a client base, and develop essential skills.
What are the main software programs used in online bookkeeping?
Some popular software programs used in online bookkeeping include QuickBooks, Xero, FreshBooks, and Wave Accounting.
Can online bookkeepers work with international clients?
Yes, online bookkeepers have the flexibility to work with clients from around the world. However, it’s important to consider time zone differences and any specific legal or tax regulations applicable to international clients.
Bookkeeping Services for E-commerce: Streamlining Financial Management
In today’s digital age, the E-commerce industry is thriving, with businesses of all sizes leveraging online platforms to sell products and services. However, with the growth and complexity of Ecommerce operations, managing finances and bookkeeping can become overwhelming. This is where professional bookkeeping services for Ecommerce come into play. In this article, we will explore the importance of bookkeeping for E-commerce businesses and how outsourcing these services can benefit online entrepreneurs.
What is the significance of a bookkeeper?
The term “bookkeeper” refers to an individual or a professional who is responsible for recording and maintaining financial transactions and records of an organization. Bookkeepers play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial data.
The significance of a bookkeeper lies in the following aspects:
Financial Record-Keeping: Bookkeepers maintain an organized and systematic record of financial transactions such as sales, purchases, receipts, and payments. These records serve as a foundation for generating financial statements and reports, which are essential for decision-making and assessing the financial health of a business.
Compliance and Regulation: Bookkeepers help ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations by accurately recording financial transactions. They may also assist in preparing tax returns and meeting financial reporting requirements imposed by government authorities.
Financial Analysis: Bookkeepers provide valuable data and reports that enable business owners, managers, and stakeholders to analyze and evaluate the financial performance of an organization. By tracking income and expenses, bookkeepers contribute to financial forecasting, budgeting, and planning activities.
Decision Support: Accurate financial records maintained by bookkeepers help in making informed decisions regarding resource allocation, cost control, pricing strategies, and investment opportunities. Bookkeepers provide financial insights that support effective decision-making and strategic planning.
Business Efficiency: Bookkeepers ensure that financial transactions are properly recorded, categorized, and reconciled, minimizing errors and discrepancies. Their attention to detail helps maintain accurate financial records, which in turn facilitates efficient auditing, financial reporting, and overall business operations.
Financial Transparency: Bookkeepers promote transparency by maintaining a clear and complete trail of financial transactions. This transparency builds trust among stakeholders such as investors, lenders, and business partners, as they can rely on accurate and reliable financial information.
Why is bookkeeping important for e-commerce?
E-commerce bookkeeping encompasses tracking sales revenue, monitoring expenses, managing cash flow, reconciling bank statements, recording inventory transactions, and preparing financial statements. Additionally, it involves managing sales taxes, handling refunds and returns, and keeping an eye on overall financial health.
What are the Benefits of Outsourcing Bookkeeping?
Outsourcing bookkeeping services for Ecommerce offers several advantages. Firstly, it allows business owners to focus on core operations, such as marketing, product development, and customer service. Secondly, it ensures that experienced professionals handle financial tasks accurately and efficiently. Moreover, outsourcing saves time, reduces costs, and provides access to expertise in E-commerce accounting.
How to Choose the Right Bookkeeping Services?
Selecting a reliable bookkeeping service provider is essential for E-commerce businesses. Consider factors such as industry experience, reputation, range of services, scalability, technology integration capabilities, and data security measures.
How do you streamline financial processes?
Professional bookkeeping services help streamline financial records and transactions for Ecommerce businesses. By accurately tracking income and expenses, organizing receipts and invoices, and reconciling accounts, businesses can maintain a clear overview of their financial position and identify potential areas for improvement.
To streamline financial processes, you can follow several key steps:
Assess and document current processes: Begin by analyzing your existing financial processes to identify any bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or areas for improvement. Document each step involved in the process to gain a clear understanding of the workflow.
Identify areas for automation: Look for tasks or steps within the financial processes that can be automated using technology. This could include tasks like data entry, calculations, report generation, or invoice processing. Automation can help reduce errors, save time, and improve accuracy.
Implement financial software and tools: Invest in reliable financial software and tools that align with your business needs. These solutions can help automate tasks, centralize data, improve collaboration, and provide real-time insights. Popular options include accounting software, expense management tools, invoice processing systems, and financial reporting platforms.
Standardize and simplify processes: Simplify complex processes by standardizing them across the organization. Define clear guidelines, workflows, and templates that employees can follow consistently. This reduces confusion, enhances efficiency, and promotes uniformity in financial operations.
Integrate systems and data: Streamline financial processes by integrating different systems and platforms, such as accounting software, CRM systems, and payment gateways. The integration allows for seamless data flow, eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and provides a holistic view of financial information.
Establish clear roles and responsibilities: Clearly define roles and responsibilities for each step in the financial process. This ensures accountability and avoids duplication of effort. Assign tasks to appropriate team members based on their skills and expertise.
Provide training and support: Offer training sessions to employees to ensure they understand the streamlined financial processes and the tools being implemented. Support them with ongoing training resources and provide assistance when needed. This helps promote adoption and maximizes the benefits of streamlining.
Monitor and optimize: Continuously monitor the streamlined financial processes to identify any further areas for improvement. Collect feedback from employees, track key performance indicators, and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review the effectiveness of the streamlined processes and make refinements as your organization evolves.
What is the Ensuring Compliance with Tax Regulations?
E-commerce businesses are subject to various tax regulations, including sales tax, income tax, and international tax obligations. Bookkeeping services ensure compliance with these regulations by accurately calculating taxes, preparing tax returns, and keeping up with changing tax laws. This helps avoid penalties and legal complications.
How do you leverage eCommerce?
Technology plays a vital role in modern bookkeeping for Ecommerce. Cloud-based accounting software and automation tools streamline financial processes, enhance accuracy, and provide real-time insights. By leveraging technology, businesses can efficiently manage financial data, generate reports, and make data-driven decisions.
To leverage eCommerce effectively, you can consider the following strategies:
Build a professional and user-friendly website: Create an appealing and well-designed website that showcases your products or services. Ensure it is easy to navigate, mobile-friendly, and optimized for search engines. Provide detailed product descriptions, high-quality images, and customer reviews to build trust and encourage conversions.
Optimize for search engines: Implement search engine optimization (SEO) techniques to improve your website’s visibility in search engine results. Conduct keyword research and optimize your website’s content, meta tags, URLs, and image tags. This helps potential customers find your website when searching for relevant products or services.
Offer a seamless online shopping experience: Streamline the purchasing process by providing a user-friendly and intuitive interface. Simplify the checkout process, enable guest checkout, and offer multiple payment options. Implement features such as live chat support, product recommendations, and personalized shopping experiences to enhance customer satisfaction and increase conversions.
Utilize social media and online advertising: Leverage social media platforms to promote your eCommerce business. Create engaging content, share product updates, and run targeted advertising campaigns to reach your target audience. Consider using platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn to build brand awareness, engage with customers, and drive traffic to your website.
Implement effective digital marketing strategies: Develop a comprehensive digital marketing plan that includes email marketing, content marketing, influencer partnerships, and affiliate marketing. Utilize email newsletters, blog posts, videos, and social media content to educate, engage, and entice customers. Collaborate with influencers or affiliate partners who can promote your products to their audience.
Provide excellent customer service: Prioritize exceptional customer service throughout the entire eCommerce experience. Offer various channels for customer support, including email, live chat, and phone. Respond promptly to inquiries, address customer concerns, and provide personalized assistance when needed. Positive customer experiences can lead to repeat business and positive reviews.
Analyze and optimize performance: Regularly track and analyze key metrics such as website traffic, conversion rates, average order value, and customer lifetime value. Use analytics tools to gain insights into customer behavior, identify areas for improvement, and optimize your eCommerce strategies accordingly. Make data-driven decisions to enhance your online presence and increase sales.
Stay updated with trends and technology: Keep up with the latest trends and technologies in eCommerce. Monitor industry news, attend conferences, and participate in webinars to stay ahead of the competition. Embrace emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, chatbots, and personalized shopping experiences to deliver innovative and convenient online experiences for your customers.
How do you improve business decision-making?
Improving business decision-making involves several key steps and considerations. Here are some strategies to enhance the decision-making process:
Gather and analyze data: Base your decisions on reliable data and information. Collect relevant data from various sources, including market research, customer feedback, financial reports, and industry trends. Use analytics tools to analyze and interpret the data, identify patterns, and gain valuable insights to support your decision-making.
Define clear objectives: Clearly define the objectives and desired outcomes of the decision-making process. This helps focus your efforts and ensures that decisions align with your overall business goals. Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives to provide clarity and direction.
Encourage diverse perspectives: Foster an environment that encourages diverse perspectives and input. Seek input from different stakeholders, including employees, managers, customers, and industry experts. Engage in brainstorming sessions, conduct surveys, or establish advisory boards to gather a range of viewpoints. This helps identify blind spots, challenges assumptions and leads to more well-rounded decisions.
Evaluate risks and alternatives: Consider the potential risks and uncertainties associated with each decision. Identify and assess the possible alternatives, weighing their potential benefits and drawbacks. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis, consider potential outcomes, and evaluate the probability of success for each option. This allows for informed decision-making and risk mitigation.
Foster collaboration and teamwork: Involve key stakeholders in the decision-making process. Encourage collaboration and teamwork to leverage the collective knowledge and expertise of your team members. Facilitate open and respectful communication, encourage the sharing of ideas, and promote a culture that values diverse perspectives. Collaboration improves decision quality and increases acceptance and commitment to the chosen course of action.
Consider long-term implications: Look beyond short-term gains and consider the long-term implications of your decisions. Evaluate the sustainability, scalability, and potential impact on various aspects of your business, including operations, finances, customers, and employees. Strive for decisions that contribute to long-term growth, innovation, and competitive advantage.
Embrace technology and tools: Leverage technology and decision-making tools to support your process. Implement data analytics software, project management tools, and collaboration platforms that facilitate data-driven decision-making, streamline workflows, and enhance communication. Automation and artificial intelligence can also assist in analyzing complex data and providing insights.
Continuously learn and adapt: Embrace a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Evaluate the outcomes of your decisions and learn from both successes and failures. Encourage feedback and reflection, and make adjustments to your decision-making approach based on lessons learned. Stay updated with industry trends and best practices to refine your decision-making processes.
How do you monitor financial performance?
Monitoring financial performance is crucial for evaluating the health and progress of a business. Here are some key steps to effectively monitor financial performance:
Establish financial goals and metrics: Set clear financial goals that align with your business objectives. Identify key financial metrics that are relevant to your industry and track them regularly. Common metrics include revenue, gross profit margin, net profit margin, cash flow, return on investment (ROI), and debt-to-equity ratio.
Develop a financial reporting system: Implement a robust financial reporting system that provides timely and accurate information. This system should include financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Customize the reporting format to suit your specific needs and ensure consistency in the presentation of financial data.
Track and analyze financial statements: Regularly review and analyze your financial statements to gain insights into your business’s performance. Compare current results to historical data and industry benchmarks. Identify trends, patterns, and areas of strength or weakness. Look for discrepancies, anomalies, or changes that require further investigation.
Utilize financial ratios and key performance indicators (KPIs): Calculate and track financial ratios and KPIs to assess the overall financial health of your business. Examples include gross profit margin, net profit margin, return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), current ratio, and inventory turnover ratio. These ratios provide a snapshot of your business’s efficiency, profitability, liquidity, and overall performance.
Conduct variance analysis: Compare actual financial results to your budgeted or forecasted figures. Identify and analyze variances between projected and actual performance. Determine the reasons behind the variances, whether they are positive or negative. This analysis helps identify areas that need improvement or further attention.
Monitor cash flow: Pay close attention to your cash flow to ensure the availability of sufficient funds for day-to-day operations, investments, and debt repayments. Track cash inflows and outflows, anticipate potential cash flow gaps, and implement strategies to manage working capital effectively. Regularly review cash flow statements to identify any issues and take appropriate action.
Use financial management software: Implement financial management software or accounting systems that provide real-time financial data and reporting capabilities. These tools streamline financial monitoring processes, automate calculations, and generate detailed reports. Choose software that fits the specific needs and size of your business.
Conduct regular financial reviews: Schedule regular financial reviews, such as monthly or quarterly meetings, to discuss financial performance with key stakeholders. Present financial reports, explain key findings and discuss strategies for improvement. Encourage open communication and address any concerns or questions raised during these reviews.
Seek professional advice when needed: If you lack expertise in financial analysis or require additional insights, consider consulting with a financial advisor or accountant. They can provide expertise, conduct in-depth analysis, and offer guidance on financial decision-making and performance monitoring.
How can e-commerce businesses reduce costs?
Outsourcing bookkeeping services for E-commerce is a cost-effective solution compared to hiring an in-house accounting team. With outsourced services, businesses can avoid expenses related to employee benefits, training, software, and infrastructure. They can also opt for customized packages based on their specific needs, paying only for the services required.
What is the scope of work for bookkeeping services?
Bookkeeping services typically involve a range of tasks related to managing and recording financial transactions for a business. The scope of work for bookkeeping services may include:
Recording financial transactions: Bookkeepers are responsible for accurately recording and categorizing all financial transactions, including sales, purchases, expenses, and payments. They ensure that transactions are properly documented and entered into the accounting system.
Maintaining general ledgers: Bookkeepers maintain general ledgers, which are the central records of a company’s financial transactions. They record and update entries in various accounts such as cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, inventory, and fixed assets.
Bank and credit card reconciliations: Bookkeepers reconcile bank statements and credit card statements with the corresponding entries in the accounting records. This process helps identify discrepancies, resolve errors, and ensure the accuracy of financial data.
Accounts payable and accounts receivable: Bookkeepers manage accounts payable by recording and tracking invoices, verifying vendor payments, and ensuring timely payments. They also handle accounts receivable by generating and sending invoices, tracking customer payments, and following up on outstanding invoices.
Payroll processing: Bookkeepers may be involved in processing payroll, including calculating employee wages, deductions, and taxes. They ensure accurate and timely payment of salaries and wages, and they may also handle payroll tax filings and reporting.
Financial reporting: Bookkeepers prepare regular financial reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These reports provide an overview of the company’s financial performance, assets, liabilities, and cash flow. Bookkeepers may also assist in preparing reports for tax compliance or regulatory purposes.
Tax documentation and support: Bookkeepers often work closely with accountants or tax professionals to ensure accurate and timely tax reporting. They gather and organize the necessary financial documents, such as receipts, invoices, and expense records, to support tax filings.
Assistance during audits: Bookkeepers may provide support during financial audits by organizing and presenting financial records, reconciliations, and supporting documentation. They help ensure that the business’s financial information is readily available and accurate for the audit process.
How do you maintain security and confidentiality?
Maintaining security and confidentiality is crucial for protecting sensitive information and maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders. Here are some important measures to ensure security and confidentiality:
Implement strong access controls: Use robust authentication mechanisms, such as strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls. Restrict access to sensitive data and systems only to authorized individuals based on their job roles and responsibilities.
Regularly update and patch software: Keep your software, operating systems, and applications up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Regularly review security advisories and apply patches promptly to address vulnerabilities and protect against known threats.
Use encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit. Utilize encryption technologies, such as SSL/TLS for data transmission over networks, and encrypt stored data using strong encryption algorithms. This helps protect data from unauthorized access even if it is intercepted or compromised.
Implement firewall and antivirus protection: Utilize firewalls to monitor and control network traffic, preventing unauthorized access and protecting against potential threats. Deploy reputable antivirus and anti-malware software to detect and prevent malicious software from compromising your systems.
Conduct regular security audits and assessments: Regularly assess and review your security measures to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Perform security audits to evaluate your systems, networks, and processes. Conduct penetration testing to proactively identify potential security flaws and address them before they can be exploited.
Provide security awareness training: Educate employees and stakeholders about security best practices and the importance of confidentiality. Train them to identify and report suspicious activities, phishing attempts, and social engineering techniques. Promote a culture of security awareness throughout the organization.
Secure physical access: Limit physical access to areas containing sensitive information, such as data centers or server rooms. Use secure locks, surveillance systems, and access control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized entry.
Establish data backup and disaster recovery plans: Regularly back up your data and store backups in secure offsite locations or cloud-based storage. Implement a robust disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in case of data breaches, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events.
Maintain strong vendor management: If you work with third-party vendors or service providers, ensure they have adequate security measures in place. Conduct due diligence before engaging with vendors and regularly assess their security practices to mitigate potential risks.
Comply with relevant regulations: Understand and comply with applicable data protection and privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Stay updated on regulatory requirements and adapt your security practices accordingly.
Regularly monitor and log activities: Implement monitoring systems to track and log activities across your networks, systems, and applications. Regularly review logs for any unusual or suspicious activities that may indicate a security breach.
Respond to incidents promptly: Have an incident response plan in place to handle security incidents effectively. Establish procedures for reporting and responding to security breaches, including containment, investigation, and mitigation steps. Communicate with affected parties promptly and transparently if a data breach occurs.
Integrating Bookkeeping with E-commerce Platforms
Seamless integration between bookkeeping services and E-commerce platforms is vital for accurate financial management. Many bookkeeping service providers offer integration with popular platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento. This integration streamlines data transfer, automates processes, and reduces manual entry errors.
What is optimizing cash flow?
Efficient cash flow management is crucial for the sustainability and growth of Ecommerce businesses. Professional bookkeeping services help monitor cash inflows and outflows, track payment processing, manage accounts receivable and payable, and provide insights to optimize cash flow, ensuring smooth operations and financial stability.
what to charge for bookkeeping services?
The fees for bookkeeping services can vary depending on factors such as the complexity of the work, the volume of transactions, the scope of services provided, the level of expertise required, and the geographical location. It is common for bookkeepers to charge an hourly rate or a flat fee per month. Hourly rates can range from $20 to $100 or more, while monthly fees can range from $200 to $1,000 or more, depending on the specific circumstances. It is recommended to consider the market rates, the value of the services provided, and the needs of your clients when determining the appropriate pricing for your bookkeeping services.
Examples of bookkeeping services?
Here are some examples of bookkeeping services typically offered by bookkeepers:
Transaction recording: Bookkeepers record and categorize financial transactions such as sales, purchases, expenses, and payments. They ensure that each transaction is accurately recorded and properly classified.
Bank and credit card reconciliations: Bookkeepers reconcile bank statements and credit card statements with the corresponding entries in the accounting system. They verify that the recorded transactions match the bank or credit card statements, resolving any discrepancies.
Accounts payable management: Bookkeepers manage accounts payable by recording and tracking invoices, verifying vendor payments, and ensuring timely payments. They also monitor outstanding payables and coordinate with vendors to resolve any payment issues.
Accounts receivable management: Bookkeepers handle accounts receivable by generating and sending invoices to customers, tracking customer payments, and following up on outstanding invoices. They ensure that payments are received on time and work to resolve any payment delays or issues.
Payroll processing: Bookkeepers may be responsible for processing payroll, including calculating employee wages, deductions, and taxes. They ensure accurate and timely payment of salaries and wages, as well as handle payroll tax filings and reporting.
Financial statement preparation: Bookkeepers prepare regular financial statements, including income statements (profit and loss statements), balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These statements provide a snapshot of the business’s financial performance and position.
General ledger maintenance: Bookkeepers maintain the general ledger, which is a central record of all financial transactions. They update and reconcile accounts, ensuring that the ledger accurately reflects the financial activity of the business.
Sales tax and VAT calculations: Bookkeepers calculate and track sales tax or value-added tax (VAT) liabilities. They ensure that the appropriate taxes are collected and remitted to the relevant tax authorities within the required deadlines.
Financial reporting: Bookkeepers assist in the preparation of financial reports for management, stakeholders, or regulatory purposes. These reports may include financial statements, budget vs. actual reports, and customized reports based on the specific needs of the business.
Data entry and organization: Bookkeepers input and organize financial data into accounting software or spreadsheets. They maintain organized and accessible records, making it easier to retrieve and analyze financial information when needed.
How often should I reconcile my Ecommerce business’s bank accounts?
It is recommended to reconcile your Ecommerce business’s bank accounts on a monthly basis to ensure accurate financial records and detect any discrepancies or errors promptly.
Can bookkeeping services help with sales tax calculations for Ecommerce businesses?
Yes, bookkeeping services can assist with sales tax calculations, ensuring compliance with tax regulations, and filing accurate sales tax returns for E-commerce businesses.
Is it necessary for small Ecommerce businesses to outsource bookkeeping services?
While it is not mandatory, outsourcing bookkeeping services can benefit small Ecommerce businesses by saving time, reducing costs, ensuring accuracy, and providing access to expertise.
How do bookkeeping services contribute to business decision-making for eCommerce ventures?
Bookkeeping services provide financial reports, KPIs, and analytics that help e-commerce businesses evaluate their performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to drive growth and profitability.
Can bookkeeping services integrate with my Ecommerce platform?
Yes, many bookkeeping service providers offer integration with popular E-commerce platforms, allowing seamless data transfer, automation, and accurate financial management.

Why Do You Want To Be a Financial Advisor?
As a financial advisor, you will encounter various interview questions that assess your skills, experience, and suitability for the role. One common question that often arises is, “Why do you want to be a financial advisor?” This question provides an opportunity for you to showcase your passion, knowledge, and commitment to the field. In this article, we will explore the reasons why individuals choose to pursue a career as a financial advisor and how to effectively answer this interview question.
Showcasing Financial Knowledge and Expertise
One of the primary reasons for wanting to be a financial advisor is a genuine passion for finance. Employers seek candidates who have a strong foundation in finance, which can be demonstrated through relevant qualifications, certifications, and degrees. A solid understanding of financial concepts, such as investment strategies, tax planning, and portfolio management, is crucial to succeed in this field.
Desire to Help Others Achieve Financial Goals
A fulfilling aspect of being a financial advisor is the opportunity to make a positive impact on people’s lives. Many individuals seek financial advice to secure their future, plan for retirement, or achieve specific financial objectives. As a financial advisor, you have the privilege of assisting them in navigating complex financial decisions and helping them achieve their goals. Sharing personal stories or experiences of how you have positively impacted others can further reinforce your desire to help.
What skills do you need to solve a problem?
Financial advisory requires strong analytical and problem-solving abilities. You will encounter various financial scenarios that require critical thinking and strategic decision-making. Employers value candidates who can demonstrate their ability to analyze data, identify patterns, and provide creative solutions to complex financial problems. Sharing examples of how you have successfully solved financial challenges in the past can showcase your problem-solving skills.
Why is it important to have a passion for learning?
Having a passion for learning is crucial for several reasons:
Personal Growth: Learning allows you to expand your knowledge, develop new skills, and broaden your perspective. It enables personal growth and self-improvement, helping you become a more well-rounded individual.
Adaptability: In today’s rapidly changing world, having a passion for learning is essential for adapting to new technologies, industries, and challenges. Continuous learning equips you with the skills and knowledge necessary to navigate and thrive in an evolving environment.
Professional Development: A passion for learning is closely linked to professional success. It enables you to stay updated with industry trends, acquire new skills, and enhance your expertise. Lifelong learning is crucial for career advancement and remaining competitive in the job market.
Innovation and Creativity: Learning fosters innovation and creativity by exposing you to diverse ideas, perspectives, and disciplines. It encourages you to think critically, problem-solve, and come up with new solutions. Many groundbreaking discoveries and inventions are the result of individuals with a deep passion for learning.
Personal Fulfillment: Learning can be a source of immense personal fulfillment. It allows you to explore your interests, delve into new subjects, and discover your passions. Engaging in continuous learning provides a sense of accomplishment, intellectual stimulation, and a lifelong pursuit of knowledge.
Well-Being: Learning is not limited to academic or professional pursuits. It can also include personal interests, hobbies, and creative endeavors. Engaging in activities that you are passionate about and constantly learning in those areas promotes a sense of well-being, happiness, and overall life satisfaction.
Contribution to Society: A passion for learning can empower you to make a positive impact on society. By gaining knowledge, you become better equipped to understand complex issues, contribute to meaningful discussions, and actively participate in creating positive change.
What skills do you need to build a successful work relationship?
Building strong relationships with clients is a fundamental aspect of being a financial advisor. Effective communication skills are crucial in understanding client’s needs, explaining complex financial concepts in a clear manner, and establishing trust. Employers seek candidates who can effectively engage with clients, listen actively, and tailor their communication style to suit different individuals.
Is trustworthiness a socio-ethical problem?
Yes, trustworthiness can be considered a socio-ethical problem. Trust is a fundamental aspect of social interactions and relationships, and when trust is violated or undermined, it can have significant social and ethical implications. Trustworthiness refers to the quality or characteristic of being reliable, dependable, and honest. It is the foundation upon which individuals, communities, and institutions build relationships, cooperate, and function effectively. Trust allows people to feel secure, confident, and comfortable in their interactions with others, and it is essential for maintaining social cohesion and harmony.
When trustworthiness is lacking, it can lead to a breakdown in relationships and social bonds. People may become skeptical, guarded, or suspicious of others, which can create an atmosphere of fear, uncertainty, and division. Trustworthiness is particularly important in contexts such as leadership, professional relationships, business transactions, and governance, where individuals and institutions have a responsibility to act in the best interests of others. From an ethical standpoint, trustworthiness is closely linked to concepts such as integrity, honesty, and fairness.
When individuals or institutions are not trustworthy, they may engage in deceitful or exploitative behaviors, leading to harm, injustice, and inequality. Ethical principles often emphasize the importance of trustworthiness as a virtue and an obligation in fulfilling one’s moral duties and responsibilities. Society and ethics play a significant role in shaping and regulating trustworthiness. Societal norms, cultural values, and legal frameworks provide guidelines and expectations for trustworthy behavior. Ethical theories and frameworks, such as consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics, offer insights into the moral dimensions of trustworthiness and how it relates to broader ethical considerations.
How do opportunities for professional growth and development enhance workforce experience?
Opportunities for professional growth and development play a crucial role in enhancing the workforce experience in several ways:
Skill Development: Professional growth and development opportunities provide employees with the chance to acquire new skills and enhance existing ones. This helps individuals expand their knowledge base and stay relevant in a rapidly changing work environment. Acquiring new skills not only improves job performance but also increases confidence and motivation.
Career Advancement: When employees have access to growth opportunities, such as training programs, mentorship, or promotions, they feel more engaged and motivated to excel in their roles. The prospect of career advancement provides a sense of purpose and progression, leading to increased job satisfaction and overall workforce experience.
Increased Engagement and Retention: Organizations that prioritize professional development are more likely to have engaged and loyal employees. When employees feel valued and supported in their growth, they are more likely to stay with the company for the long term. This reduces turnover rates, which can be costly for businesses, and fosters a positive work environment.
Enhanced Performance: Through professional growth and development initiatives, employees can acquire new knowledge and apply it to their work. This leads to improved performance, productivity, and efficiency. As employees become more skilled and knowledgeable, they can contribute to the organization’s success, leading to a positive work culture and a more fulfilling workforce experience.
Adaptability to Change: In today’s fast-paced business landscape, organizations and industries are constantly evolving. Employees who have access to professional growth opportunities are better equipped to adapt to change. They develop a growth mindset, become more open to learning, and are better prepared to handle new challenges and opportunities that arise.
Innovation and Creativity: By providing opportunities for professional growth, organizations encourage employees to think innovatively and creatively. Learning new concepts, exploring different perspectives, and acquiring diverse skills can inspire employees to generate fresh ideas and contribute to the organization’s innovation efforts. This, in turn, enhances the overall workforce experience by fostering a culture of creativity and continuous improvement.
How did a passion for Finance change your perspective of money?
I can provide you with information on how a passion for finance can change a person’s perspective on money.
Developing a passion for finance often leads to a deeper understanding of how money works, its role in society, and the various ways it can be managed and invested. This increased knowledge and awareness can result in several changes in perspective:
Appreciation of the value of money: A passion for finance can make individuals more conscious of the effort required to earn money and the importance of making wise financial decisions. They may gain a greater appreciation for the value of money and become more cautious about spending it frivolously.
Long-term thinking: Finance enthusiasts often adopt a long-term perspective when it comes to money. They understand the concept of saving, investing, and planning for the future. They may prioritize financial goals such as building wealth, saving for retirement, or funding education, which can lead to more disciplined and strategic financial habits.
Risk assessment: Passion for finance often involves learning about investment opportunities and analyzing their risks and potential returns. This knowledge can influence a person’s perspective on risk-taking and help them make more informed decisions about their financial choices. They may become more open to calculated risks, recognizing that higher-risk investments can potentially yield higher rewards.
Wealth creation mindset: A passion for finance can inspire individuals to strive for financial independence and wealth creation. They may develop an entrepreneurial mindset, exploring ways to generate additional income and build wealth over time. This perspective shift can lead to increased motivation and dedication to financial success.
Understanding financial systems: A deeper understanding of finance often leads to a better comprehension of the broader economic and financial systems at play. This awareness can provide insights into how money flows, the impact of monetary policy, and the interconnections between different sectors of the economy. It can also foster a more critical perspective on economic issues and policies.
Is your team aligned with your company’s Mission and values?
Employers not only seek qualified financial advisors but also individuals who align with their company’s values and mission. Highlighting your compatibility with the company’s vision demonstrates your commitment to their goals and aspirations. Research the company beforehand and emphasize the shared values that attracted you to the organization.
Why do people need financial knowledge and decision-making skills?
People need financial knowledge and decision-making skills for several important reasons:
Managing personal finances: Financial knowledge and decision-making skills are crucial for managing one’s personal finances effectively. This includes budgeting, tracking expenses, understanding savings and investment options, managing debt, and planning for future financial goals like buying a house, paying for education, or retiring comfortably.
Making informed financial decisions: Financial decisions have a significant impact on individuals and their families. With financial knowledge, people can make informed decisions about important matters such as taking out loans, investing in stocks or real estate, choosing insurance plans, or saving for retirement. This knowledge helps them assess risks, understand potential returns, and make choices aligned with their financial objectives.
Avoiding financial pitfalls: Lack of financial knowledge can lead to poor financial choices and potential pitfalls. It’s essential to understand concepts such as interest rates, inflation, compounding, and investment risks to avoid falling into debt, making bad investments, or becoming victims of scams. Financial knowledge empowers individuals to make sound decisions and protect themselves from financial harm.
Building wealth and achieving financial goals: Financial knowledge enables individuals to build wealth over time. It helps them understand investment options, assess their risk tolerance, and make informed choices that align with their long-term financial goals. With proper decision-making skills, individuals can take advantage of opportunities, grow their assets, and increase their chances of achieving financial independence and security.
Navigating an increasingly complex financial landscape: The financial landscape is constantly evolving, with new products, regulations, and technologies emerging regularly. Having financial knowledge equips individuals with the ability to adapt and navigate this complex landscape. It allows them to understand the implications of financial products and services, evaluate their options, and make choices that are best suited to their circumstances.
Making better career choices: Financial knowledge is valuable not only for personal finances but also for career planning. Understanding basic financial concepts can help individuals negotiate salaries, evaluate job offers, and make decisions related to benefits, retirement plans, and investment opportunities provided by employers. Financial knowledge can also be advantageous for entrepreneurs and business owners in managing their company’s finances effectively.
What challenges have you faced as a financial advisor?
There are a few challenges financial advisors may encounter:
Market Volatility: The financial markets are inherently volatile, and advisors need to navigate through various market conditions. Sudden changes in market trends and unpredictable economic events can make it challenging to provide accurate and timely advice.
Client Expectations: Clients often have high expectations for their financial advisors in terms of investment returns and financial goals. Meeting and managing these expectations can be challenging, especially during periods of market downturns.
Regulatory Compliance: Financial advisors need to adhere to numerous regulations and compliance standards, such as those set by financial regulatory bodies. Staying up to date with evolving regulations and ensuring compliance can be demanding.
Economic and Political Factors: Economic and political factors can significantly impact financial markets. Advisors must stay informed about global economic trends, geopolitical events, and government policies to make informed recommendations to their clients.
Emotional Bias: Clients may make decisions driven by emotions, especially during times of market turbulence. Advisors need to help clients manage their emotions and make rational financial decisions based on long-term goals.
Financial Complexity: The financial world can be complex, with numerous investment options, tax laws, and financial products. Advisors must have a deep understanding of these complexities and be able to simplify them for their clients.
Time Management: Financial advisors often work with multiple clients simultaneously, managing their portfolios, conducting research, and providing advice. Balancing time between existing clients and acquiring new ones can be challenging.
Continuous Learning: Financial advisors must continually update their knowledge and skills to stay relevant in a rapidly changing industry. Staying informed about new investment opportunities, technologies, and financial strategies is crucial but can also be time-consuming.
How do you guide clients through financial decisions?
Establish Goals and Objectives: The first step is to understand the client’s financial goals, whether it’s saving for retirement, buying a house, funding education, or starting a business. Advisors work with clients to set realistic and achievable objectives.
Assess Current Financial Situation: Advisors gather information about the client’s income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and risk tolerance. This evaluation helps determine the client’s current financial position and informs the advice provided.
Develop a Financial Plan: Based on the client’s goals and financial situation, advisors create a comprehensive financial plan. This plan includes strategies to achieve the goals, such as investment allocation, tax planning, budgeting, insurance coverage, and estate planning.
Educate Clients: Advisors provide education and explain complex financial concepts, investment options, and potential risks. They empower clients to make informed decisions by helping them understand the implications of different choices.
Present Options and Recommendations: Advisors present clients with suitable investment options, taking into account risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. They recommend specific investment vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or real estate, and explain the potential benefits and risks of each option.
Evaluate and Monitor Progress: Financial advisors regularly review and monitor the client’s financial plan and investment portfolio. They assess progress toward goals, make necessary adjustments based on changing circumstances, and provide performance reports and updates to clients.
Address Risk Management: Advisors help clients understand and manage various risks, including market volatility, inflation, longevity, and unforeseen events. They recommend appropriate risk management strategies, such as insurance coverage, diversification, and asset allocation.
Communication and Collaboration: Advisors maintain open and regular communication with clients. They address client concerns, answer questions, and provide ongoing guidance and support. Collaboration and trust-building are essential in the advisor-client relationship.
Stay Informed and Educated: Financial advisors continuously update their knowledge and stay abreast of industry trends, tax laws, regulatory changes, and investment opportunities. This allows them to provide clients with up-to-date advice and strategies.
What areas of specialization do you have experience in as a financial advisor?
Personal Finance: Budgeting, saving, debt management, retirement planning, tax optimization, and investment strategies for individuals.
Investment Management: Asset allocation, portfolio diversification, risk management, understanding different investment vehicles (stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, etc.), and investment analysis.
Financial Planning: Developing comprehensive financial plans, setting financial goals, evaluating insurance needs, estate planning, and addressing specific financial circumstances.
Retirement Planning: Strategies for building a retirement nest egg, estimating retirement expenses, optimizing Social Security benefits, and creating income streams in retirement.
Tax Planning: Understanding tax laws, optimizing tax deductions, tax-efficient investment strategies, and long-term tax planning.
Risk Management: Evaluating insurance needs (life, health, disability, property, etc.), assessing risk tolerance, and managing risks through appropriate insurance coverage.
Estate Planning: Creating wills, trusts, and other estate planning tools, minimizing estate taxes, and transferring assets according to individual wishes.
Business and Corporate Finance: Financial analysis, capital budgeting, cash flow management, financial forecasting, and investment decisions for businesses.
What qualifications are typically required to become a financial advisor?
While specific qualifications may vary, a bachelor’s degree in finance, economics, or a related field is often preferred. Additionally, obtaining relevant certifications such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP) or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) can enhance your credibility as a financial advisor.
How do financial advisors build trust with their clients?
Financial advisors build trust by demonstrating competence, maintaining confidentiality, acting in the client’s best interest, and providing transparent and unbiased advice. Building long-term relationships and delivering results consistently are also crucial in earning and maintaining trust.
Are there specific areas of finance where a financial advisor can specialize?
Yes, financial advisors can specialize in various areas such as retirement planning, estate planning, investment management, tax planning, or insurance. Specializing in a particular area allows advisors to develop deep expertise and cater to specific client needs.
What are some common challenges faced by financial advisors?
Financial advisors often face challenges such as market volatility, regulatory changes, client expectations, competition, and balancing personal and professional life. Adaptability, ongoing learning, and effective time management are key to overcoming these challenges.
How can I demonstrate my passion for personal finance during an interview?
You can demonstrate your passion for personal finance by discussing relevant books, courses, or podcasts you have explored. Sharing personal experiences of how you have managed your finances or helped others with theirs can also showcase your genuine interest in the subject.

What is the Difference Between a Financial Advisor and an Investment Advisor?
When it comes to managing your finances and investments, it’s essential to seek professional guidance to make informed decisions. However, the terms “financial advisor” and “investment advisor” are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion about their roles and responsibilities. In this article, we will explore the differences between a financial advisor and an investment advisor, helping you understand which professional can best assist you in achieving your financial goals.
What Is a Financial Advisor?
A financial advisor is a professional who offers comprehensive financial guidance and assistance to individuals, families, and businesses. They assess their clients’ financial situations, provide personalized advice, and develop strategies to help them achieve their financial objectives. Financial advisors take a holistic approach, considering various aspects of their client’s financial lives to create a comprehensive financial plan.
What are the duties and responsibilities of a financial advisor?
Financial Planning
One of the primary roles of a financial advisor is to help clients develop a financial plan tailored to their specific needs and goals. They analyze their clients’ income, expenses, assets, and liabilities to create a roadmap for achieving financial stability and success. Financial advisors consider factors such as budgeting, savings, debt management, tax planning, and insurance coverage while crafting a comprehensive financial plan.
Retirement Planning
Financial advisors play a crucial role in helping clients prepare for retirement. They assess their client’s retirement goals, estimate the required savings, and develop strategies to achieve a comfortable retirement lifestyle. They also provide guidance on retirement accounts, such as IRAs (Individual Retirement Accounts) or 401(k) plans, and help clients make informed decisions regarding contribution amounts and investment choices.
Investment Management
While financial advisors provide investment guidance, their primary focus is on the overall financial well-being of their clients. They recommend suitable investment options based on client’s risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. Financial advisors consider a diverse range of investments, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate, to create a well-balanced investment portfolio aligned with clients’ objectives.
Risk Assessment
Financial advisors evaluate clients’ risk tolerance and help them understand the potential risks associated with their financial decisions. They consider factors such as market volatility, inflation, and unexpected life events to develop strategies that mitigate risk and safeguard clients’ financial interests. They also assist clients in creating emergency funds and insurance plans to protect against unforeseen circumstances.
What Is an Investment Adviser? How Do They Work?
An investment adviser is a financial professional who specializes in providing guidance and recommendations related to investments. They assist individuals, families, and businesses in making informed decisions regarding their investment portfolios. Investment advisers are regulated by financial authorities to ensure they adhere to certain standards and act in the best interest of their clients. Let’s delve deeper into the role and workings of an investment adviser.
How Investment Advisers Work
Investment advisers follow a systematic approach to assist clients in achieving their investment objectives. Here are the key aspects of how they work:
Client Assessment: Investment advisers begin by thoroughly assessing their clients’ financial situations, including their investment goals, risk tolerance, time horizon, and liquidity needs. This assessment helps advisers understand their client’s specific requirements and design appropriate investment strategies.
Investment Strategy Development: Based on the client assessment, investment advisers develop an investment strategy that aligns with the client’s goals and risk profile. They consider various factors such as asset allocation, diversification, investment time horizon, and investment style preferences.
Portfolio Construction: Investment advisers construct investment portfolios tailored to each client’s unique needs. They select a mix of asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and alternative investments, to create a well-diversified portfolio. The allocation of investments is based on the client’s risk tolerance and the adviser’s analysis of market conditions.
Investment Research and Analysis: Investment advisers conduct in-depth research and analysis to identify suitable investment opportunities. They evaluate various securities, companies, sectors, and asset classes to make informed investment recommendations. This research involves analyzing financial statements, assessing market trends, and considering economic indicators.
Ongoing Portfolio Management: Once the investment portfolio is established, investment advisers continuously monitor its performance. They track the investments, assess market conditions, and make adjustments when necessary. Advisers stay abreast of market news, economic developments, and industry trends to ensure their clients’ portfolios remain aligned with their goals.
Risk Management: Investment advisers actively manage risk within their client’s portfolios. They employ strategies such as diversification, asset allocation, and risk assessment to mitigate potential risks. Advisers monitor the risk levels of investments and adjust the portfolio as needed to maintain an appropriate risk-return balance.
Client Communication: Investment advisers maintain regular communication with their clients. They provide updates on portfolio performance, discuss investment strategies, and address any questions or concerns. Communication channels may include in-person meetings, phone calls, email updates, or secure online portals.
Regulatory Compliance: Investment advisers are subject to regulatory oversight to ensure they operate ethically and in the best interest of their clients. They must comply with regulations, such as the Investment Advisers Act of 1940 in the United States, and provide full disclosure of fees, potential conflicts of interest, and any material information that may impact client investments.
Fee Structure: Investment advisers charge fees for their services, which can vary based on the adviser’s fee structure. Common fee arrangements include a percentage of assets under management (AUM), flat fees, hourly rates, or performance-based fees. It’s important for clients to understand the fee structure and the services included in the fee agreement.
What are the duties and responsibilities of an Investment advisor?
Investment Strategy
Investment advisors work closely with clients to develop an investment strategy tailored to their objectives. They consider factors such as risk tolerance, investment time horizon, and financial goals to recommend suitable investment options. Investment advisors stay up-to-date with market trends, economic indicators, and industry analysis to make informed investment recommendations.
Portfolio Management
One of the key responsibilities of an investment advisor is to manage their clients’ investment portfolios actively. They monitor the performance of various investments, make adjustments when necessary, and rebalance portfolios to ensure alignment with clients’ objectives. Investment advisors stay vigilant about market fluctuations and adjust investment strategies accordingly.
Market Analysis
Investment advisors continuously analyze market trends and conduct thorough research on potential investment opportunities. They evaluate various asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions to identify investment options that have the potential for growth and meet clients’ objectives. Investment advisors provide clients with comprehensive market analysis and recommendations to aid their decision-making process.
Risk Management
Risk management is a crucial aspect of an investment advisor’s role. They help clients understand the risks associated with different investments and develop strategies to mitigate those risks. Investment advisors employ diversification techniques, asset allocation strategies, and risk-adjusted portfolio construction to minimize the impact of market fluctuations on clients’ investments.
What are the key differences between financial advisors and investment advisors?
Although financial advisors and investment advisors share similarities, several key differences distinguish their roles and responsibilities.
Scope of Services
Financial advisors offer comprehensive financial planning services that encompass various aspects of their client’s financial lives. They provide guidance on budgeting, savings, debt management, retirement planning, insurance coverage, and investment management. On the other hand, investment advisors primarily focus on investment-related matters, offering specialized advice on investment selection, portfolio management, and market analysis.
Regulatory Requirements
Financial advisors and investment advisors may be subject to different regulatory requirements, depending on their jurisdiction and the services they provide. In the United States, financial advisors typically fall under the regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or state-level regulatory bodies. Investment advisors, on the other hand, are registered with the SEC or state securities authorities, as they primarily deal with investment-related services.
Compensation Structure
Financial advisors and investment advisors may have different compensation structures. Financial advisors can earn fees through various means, including hourly fees, flat fees, or a percentage of assets under management. They may also receive commissions from product sales, such as insurance or investment products. Investment advisors, on the other hand, often charge a percentage of assets under management as their primary form of compensation.
Expertise and Specialization
Financial advisors generally possess broad expertise across various financial domains, allowing them to provide comprehensive financial advice. They often hold certifications such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP), Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), or Certified Public Accountant (CPA). Investment advisors, on the other hand, may specialize in specific investment strategies, asset classes, or industries, honing their expertise in those areas.
What is Risk Advisory?
Risk advisory refers to the practice of identifying, assessing, and managing risks faced by organizations. It involves providing expert advice and guidance on risk management strategies, controls, and processes to help organizations mitigate potential threats and maximize opportunities. Risk advisory professionals work closely with clients to understand their unique risk profiles and develop tailored solutions to minimize risks and enhance business performance.
Understanding Risk Advisory
In today’s complex and dynamic business environment, organizations face a wide range of risks that can impact their operations, reputation, financial stability, and regulatory compliance. Risk advisory professionals specialize in helping organizations proactively identify and manage these risks, enabling them to make informed decisions and achieve their objectives with greater confidence.
Risk advisory encompasses various aspects of risk management, including:
Risk Identification: Risk advisory professionals work closely with organizations to identify potential risks across different areas, such as operational, financial, strategic, compliance, reputational, and technological risks. They analyze internal processes, systems, and external factors to identify vulnerabilities and potential sources of risk.
Risk Assessment and Evaluation: Once risks are identified, risk advisory professionals assess their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. They evaluate the existing controls and risk management frameworks to determine their effectiveness in mitigating risks. This assessment helps organizations prioritize risks and allocate resources accordingly.
Risk Mitigation Strategies: Risk advisory professionals develop customized risk mitigation strategies based on the specific needs and risk appetite of the organization. They provide recommendations on implementing controls, processes, and policies to minimize the identified risks. This may involve redesigning business processes, implementing technology solutions, or enhancing governance and compliance frameworks.
Risk Monitoring and Reporting: Risk advisory professionals assist organizations in establishing robust monitoring mechanisms to track and report on key risk indicators. They help set up risk reporting systems that provide timely and accurate information to stakeholders, enabling proactive risk management and decision-making.
Compliance and Regulatory Guidance: Risk advisory professionals stay up-to-date with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards to ensure organizations remain compliant. They provide guidance on regulatory requirements and assist in developing compliance programs to mitigate legal and regulatory risks.
Crisis and Incident Response: In the event of a crisis or incident, risk advisory professionals support organizations in managing the situation effectively. They help develop crisis response plans, conduct investigations, and assist in the recovery and restoration of normal business operations.
Internal Controls and Governance: Risk advisory professionals assess and enhance internal controls and governance frameworks to ensure strong risk management practices throughout the organization. They provide recommendations on improving accountability, transparency, and ethical behavior.
The Role of Risk Advisory Professionals
Risk advisory professionals, often employed by consulting firms or working within specialized departments of organizations, play a vital role in helping businesses navigate uncertainties and achieve their objectives. They possess expertise in risk management methodologies, industry best practices, and regulatory requirements. Their responsibilities include:
- Engaging with clients to understand their unique risk landscape and objectives.
- Conducting risk assessments, including risk identification, evaluation, and prioritization.
- Developing and implementing risk management strategies and frameworks.
- Providing guidance on compliance and regulatory matters.
- Assisting in the design and implementation of control systems and governance structures.
- Monitoring and reporting on key risk indicators and performance metrics.
- Advising on crisis management and incident response.
- Facilitating training and awareness programs on risk management.
By working closely with organizations, risk advisory professionals help them build resilience, seize opportunities, and navigate risks effectively. Their insights and expertise contribute to improved decision-making, enhanced operational efficiency, and protection of the organization’s reputation and stakeholders’ interests.
Can an investment adviser also provide financial planning services?
Yes, some investment advisers may offer financial planning services as part of their overall service offering. However, it’s essential to clarify the scope of services with the investment adviser to ensure they can address your specific financial planning needs.
How are investment advisers regulated?
Investment advisers are regulated by financial authorities, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States or equivalent regulatory bodies in other countries. These regulations aim to protect investors and ensure that investment advisers operate in a fair and transparent manner.
What qualifications and certifications do investment advisers have?
Investment advisers may hold various qualifications and certifications related to finance and investments. Common certifications include the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), Certified Financial Planner (CFP), and Chartered Investment Manager (CIM). These certifications indicate a certain level of expertise and professionalism in the field of investment advisory.
How do investment advisers charge fees?
Investment advisers typically charge fees based on a percentage of assets under management (AUM). The fee percentage can vary depending on the size of the portfolio and the complexity of the services provided. Some advisers may also charge additional fees for specific services or offer alternative fee structures, such as flat fees or hourly rates.
Can I manage my investments without an investment adviser?
Yes, it’s possible to manage your investments without an investment adviser. However, it requires a good understanding of the financial markets, investment analysis, and portfolio management. DIY investing carries its own risks, and individuals should carefully consider their knowledge, time availability, and risk tolerance before deciding to manage their investments independently
An investment advisor, on the other hand, is a professional specifically focused on providing guidance and recommendations regarding investments. Their primary responsibility is to assist clients in making investment decisions that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Is risk advisory only relevant to large organizations?
Risk advisory is relevant for organizations of all sizes. While larger organizations may have more complex risk profiles and greater resources for risk management, small and medium-sized enterprises can also benefit from risk advisory services to identify and address potential risks effectively.
What industries benefit from risk advisory services?
Risk advisory services are applicable across various industries, including finance, healthcare, manufacturing, technology, energy, and more. Every industry faces unique risks, and risk advisory professionals tailor their approaches and solutions to address industry-specific challenges.
What are some common risk management frameworks used in risk advisory?
Common risk management frameworks used in risk advisory include the COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission) framework, ISO 31000, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. These frameworks provide guidelines and best practices for identifying, assessing, and managing risks.
How can risk advisory help organizations in making strategic decisions?
Risk advisory professionals provide valuable insights and analysis to organizations, enabling them to make informed strategic decisions. By identifying potential risks and their potential impact, risk advisory helps organizations evaluate the risks associated with various strategic options and develop strategies that balance risk and reward.
What qualifications do risk advisory professionals possess?
Risk advisory professionals often possess relevant academic backgrounds in fields such as risk management, finance, accounting, or business administration. Additionally, professional certifications such as Certified Risk Management Professional (CRMP), Certified Risk Analyst (CRA), or Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) demonstrate expertise in risk management.
How do you manage payroll?

How do you manage payroll?
Managing payroll is an essential aspect of running a business. It involves the process of calculating and distributing wages or salaries to employees. Effective payroll management ensures timely and accurate payment to employees, compliance with tax regulations, and adherence to labor laws. This article will provide you with valuable insights on how to efficiently manage your payroll, streamline processes, and avoid common pitfalls.
What are the benefits of payroll management?
Payroll management holds significant importance for businesses of all sizes. It not only ensures that employees receive their rightful compensation but also plays a crucial role in maintaining employee satisfaction and engagement. Additionally, accurate payroll management helps businesses meet their legal obligations, avoid penalties, and build trust with their workforce.
What are the components of a payroll management system?
To effectively manage your payroll, it is essential to understand its key components. These components include:
Employee Information
Maintaining accurate employee information is crucial for payroll management. This includes personal details, tax withholding information, and any changes in employment status or benefits.
Time and Attendance Tracking
Accurate timekeeping is essential for calculating employee wages. Implementing a reliable time and attendance system helps track hours worked, leaves, and over time, ensuring accurate payroll calculations.
Tax Compliance
Complying with tax regulations is vital to avoid legal issues. Payroll management involves accurate calculation and timely submission of payroll taxes, including income tax withholding, Social Security, and Medicare.
Employee Benefits
Managing employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off requires integration with the payroll system. Proper coordination ensures accurate deductions and reporting.
Payroll Software
Investing in payroll software can streamline the entire payroll management process. It automates calculations, tracks employee data, generates payslips, and facilitates tax filing. Choose a reliable payroll software that suits your business needs and ensures data security.
Outsourcing Payroll
Outsourcing payroll to a trusted service provider can save time and reduce administrative burdens. Professional payroll providers handle all payroll-related tasks, including tax filing, compliance, and year-end reporting, allowing you to focus on core business operations.
What is a payroll policy?
Creating clear and comprehensive payroll policies helps maintain consistency and transparency. Define policies related to pay periods, overtime, bonuses, deductions, and employee classification. Communicate these policies to employees to avoid confusion.
Accurate Timekeeping
Implementing an accurate timekeeping system is crucial for fair and error-free payroll calculations. Utilize time-tracking tools, biometric systems, or online timesheets to ensure precise recording of employee work hours.
Does a contractor need a timekeeping system?
Contractors can benefit from having a timekeeping system, although it may not be as critical as it is for regular employees. Here are a few reasons why a timekeeping system can be beneficial for contractors:
Accurate Billing: Contractors often charge their clients based on the hours worked or completed tasks. A timekeeping system allows contractors to accurately track their working hours, ensuring that they bill their clients correctly and avoid disputes over payment.
Project Management: For contractors working on multiple projects simultaneously, a timekeeping system helps in managing their time effectively. They can allocate specific hours to each project, prioritize tasks, and ensure they are meeting their deadlines.
Documentation: Keeping a record of the hours worked can serve as valuable documentation in case of any disputes or legal issues. It provides evidence of the contractor’s commitment and the effort put into the project.
Productivity Tracking: Contractors can use a timekeeping system to monitor their productivity and identify areas where they can improve efficiency. By analyzing the time spent on different tasks, they can optimize their workflow and allocate their time more effectively.
Tax Compliance: Maintaining accurate records of working hours can be beneficial for tax purposes. Contractors may be eligible for certain deductions or exemptions based on their working hours, and a timekeeping system can provide the necessary documentation for tax filings.
While contractors may not be required to have a timekeeping system by law, implementing one can bring numerous advantages. It helps in maintaining professionalism, ensuring fair compensation, and improving overall productivity.
Employee Classification
Properly classifying employees as exempt or non-exempt is essential to comply with wage and hour regulations. Understand the criteria for exemption and ensure correct payroll calculations based on employee classifications.
7 Employee Classification Types and How They Compare
Employee classification is an important aspect of payroll management and compliance with labor laws. It determines how workers are categorized and whether they are eligible for certain benefits or are entitled to specific legal protections. Here are seven common employee classification types and a comparison of their key characteristics:
Full-Time Employees (FTEs)
Full-time employees are typically hired to work a standard number of hours per week, commonly 35-40 hours.
They are entitled to benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
FTEs often receive consistent schedules and a stable income.
Employers must comply with labor laws regarding minimum wage, overtime, and other employment regulations.
Part-Time Employees
Part-time employees work fewer hours than full-time employees, usually less than 35 hours per week.
They may be eligible for certain benefits on a prorated basis, depending on company policies.
Part-time employees often have more flexibility in their schedules.
Employers must adhere to labor laws regarding minimum wage, overtime, and other applicable regulations.
Independent Contractors
Independent contractors are self-employed individuals or businesses hired on a contract basis.
They have more control over their work, including when, where, and how they complete their tasks.
Independent contractors are responsible for their own taxes, benefits, and insurance.
Employers generally have less control over the work methods and schedules of independent contractors.
Temporary or Seasonal Employees
Temporary or seasonal employees are hired to fulfill short-term staffing needs or work during specific seasons or projects.
They may work part-time or full-time hours for a limited duration.
Employers may provide certain benefits to temporary or seasonal employees, depending on local laws and company policies.
The employment relationship typically ends once the temporary or seasonal period is over.
Interns
Interns are individuals, often students, who gain practical work experience for a specific period, usually as part of their education.
Internships can be paid or unpaid, depending on the nature of the work and compliance with labor laws.
The primary focus of internships is on learning and development, rather than regular employment.
Employers should ensure that internships comply with legal requirements, such as providing educational value and not displacing regular employees.
Consultants
Consultants are individuals or firms providing specialized expertise or services to businesses.
They typically work on a project basis and may have their own businesses or work as independent contractors.
Consultants have more autonomy and are responsible for their own taxes, benefits, and insurance.
Employers have limited control over the work methods and schedules of consultants.
Freelancers or Gig Workers
Freelancers or gig workers are self-employed individuals who work on a project or assignment basis for multiple clients.
They have flexibility in choosing their projects, rates, and work schedules.
Freelancers are responsible for their own taxes, benefits, and insurance.
Employers have less control over the work methods and schedules of freelancers.
Tax Compliance
Payroll management requires diligent tax compliance. Stay updated with tax laws and regulations to accurately calculate and withhold payroll taxes. Regularly review and reconcile payroll records to avoid potential issues with tax authorities.
What Are Employee Benefits?
Employee benefits play a crucial role in attracting and retaining talented employees while enhancing their overall well-being. Offering a comprehensive benefits package can contribute to a positive work environment and promote employee satisfaction. Here are some common types of employee benefits:
Health Insurance
Health insurance is a vital employee benefit that provides coverage for medical expenses. It typically includes medical, dental, and vision plans. Employers may offer various options, such as preferred provider organizations (PPOs) or health maintenance organizations (HMOs), to meet the diverse needs of their employees.
Retirement Plans
Retirement plans, such as 401(k) or pension plans, help employees save and invest for their future. These plans often involve employer contributions, matching a portion of the employee’s contributions, which can provide additional financial security during retirement.
Paid Time Off (PTO)
Paid time off encompasses vacation days, holidays, and personal days that employees can take for rest, relaxation, or personal commitments. Offering generous PTO benefits promotes work-life balance, reduces burnout, and improves employee morale.
Parental Leave
Parental leave provides employees with time off after the birth or adoption of a child. This benefit supports work-life balance for new parents and acknowledges the importance of family responsibilities. It may include both maternity and paternity leave, allowing parents to bond with their children and adjust to their new family dynamic.
Flexible Work Arrangements
Flexible work arrangements, such as remote work or flexible hours, enable employees to have greater control over their work schedules. This benefit promotes work-life integration and allows employees to manage personal responsibilities while fulfilling work obligations.
Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs)
Employee Assistance Programs offer confidential counseling and support services to employees and their families. These programs can assist with personal and work-related challenges, such as stress management, mental health concerns, financial issues, or substance abuse.
Wellness Programs
Wellness programs focus on improving employees’ physical and mental well-being. They may include gym memberships, wellness challenges, health screenings, stress management initiatives, and educational resources to promote healthier lifestyles.
Education and Professional Development
Supporting employees’ continuous learning and professional growth is essential. Employers may offer tuition reimbursement programs, training workshops, or access to online courses to help employees enhance their skills and knowledge.
Life and Disability Insurance
Life and disability insurance provides financial protection for employees and their families in the event of unexpected circumstances. Life insurance offers a payout to designated beneficiaries upon an employee’s death, while disability insurance provides income replacement if an employee becomes disabled and unable to work.
Commuter Benefits
Commuter benefits help employees cover transportation costs, such as public transportation or parking expenses. This benefit can include pre-tax deductions or employer subsidies, making commuting more affordable.
What are paycheck deductions & wage garnishments?
Properly handling deductions and garnishments is crucial to avoid legal consequences. Understand the laws related to wage garnishments and ensure compliance while processing employee payroll.
What Is A Payroll Report?
Generating payroll reports provides valuable insights into your business’s financial health. Regularly review reports such as payroll summaries, tax filings, and year-end reports. Analyze these reports to identify trends, discrepancies, and areas of improvement.
What are some common payroll errors? (And How to Avoid Them)
Payroll errors can occur due to various reasons, ranging from simple mistakes to complex issues in payroll processing. Here are some common payroll errors.
Incorrect employee information: Errors can arise from entering incorrect personal information, such as employee names, addresses, Social Security numbers, or tax withholding details. These mistakes can lead to incorrect tax calculations, improper reporting, or delays in payments.
Overtime calculation errors: If overtime hours are not accurately recorded or calculated, employees may be underpaid for their extra hours worked. It is essential to apply the correct overtime rates and accurately track and calculate overtime hours.
Missed or late payments: Failing to process payroll on time or missing payments can cause significant problems for employees. It can lead to financial hardships, negatively impact employee morale, and may even result in legal consequences.
Incorrect tax withholding: Incorrectly calculating and withholding taxes can cause complications for both employees and the organization. Over-withholding can result in reduced take-home pay, while under-withholding can lead to penalties and additional tax liabilities for employees.
Inaccurate benefits or deductions: Errors in calculating benefits, such as vacation time, sick leave, or health insurance premiums, can affect employees’ compensation and benefits. Deduction errors, such as improper 401(k) contributions or garnishments, can also cause issues.
Payroll tax errors: Mistakes in payroll tax calculations, reporting, or payment can lead to compliance issues and potential penalties from tax authorities. Errors can occur in federal, state, and local tax calculations, as well as unemployment insurance and Social Security contributions.
Misclassifying employees: Misclassifying employees as independent contractors or vice versa can have legal and financial implications. Misclassifications may result in incorrect tax withholding, inadequate benefits, and potential legal liabilities.
Failure to comply with labor laws: Failing to comply with labor laws regarding minimum wage, overtime, and other regulations can lead to legal consequences and financial penalties. It is crucial to stay updated on applicable employment laws and regulations.
Inaccurate time tracking: Errors in recording and tracking employee work hours can lead to incorrect calculations, especially when it comes to overtime pay, shift differentials, or other time-based compensation.
Data entry mistakes: Simple data entry errors, such as transposed numbers, typos, or incorrect decimal placements, can lead to significant payroll discrepancies. Regularly reviewing and verifying data entries can help identify and rectify such errors.
To avoid these common payroll errors, organizations should establish robust payroll processes, invest in reliable payroll software or systems, provide adequate training to payroll staff, and regularly audit payroll records for accuracy. Seeking professional advice from payroll experts or consultants can also help ensure compliance and accuracy in payroll management.
What are payroll regulations?
Payroll regulations undergo frequent changes. Stay updated with labor laws, tax regulations, and reporting requirements to ensure compliance. Regularly review and update your payroll processes to align with the latest legal requirements.
How do I Manage my small business payroll?
To manage your small business payroll effectively, follow these steps:
Collect employee information: Gather essential details such as employee names, addresses, Social Security numbers, tax forms (W-4), and bank account information for direct deposit.
Determine pay periods: Set up a pay period schedule, such as weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly, and communicate it clearly to employees.
Classify employees correctly: Ensure that you correctly classify employees as either full-time, part-time, or contractors, based on legal guidelines and their job responsibilities.
Calculate employee wages: Determine the gross pay for each employee based on their hourly rate, salary, or commission structure. Consider factors like overtime, bonuses, or other incentives.
Withhold and remit payroll taxes: Calculate and withhold federal, state, and local taxes based on employee W-4 forms. Remit the withheld taxes to the appropriate tax authorities on the designated schedule.
Account for benefits and deductions: Consider any employee benefits (e.g., health insurance, retirement plans) and deductions (e.g., wage garnishments, voluntary contributions) that affect net pay.
Use reliable payroll software or service: Consider using payroll software or outsourcing to a payroll service provider. These solutions can automate calculations, tax withholdings, and payment processes, saving you time and reducing errors.
Maintain accurate records: Keep thorough records of payroll transactions, including pay stubs, tax filings, and employee forms. This documentation helps with audits, tax reporting, and resolving any discrepancies.
Stay compliant with labor laws: Familiarize yourself with federal, state, and local labor laws to ensure compliance with minimum wage, overtime, and other regulations. Regularly review and update your practices accordingly.
Regularly review and reconcile payroll: Conduct periodic reviews and reconciliations of payroll records to identify and correct any errors. This helps maintain accuracy and ensures that employees are paid correctly.
Communicate effectively: Clearly communicate any changes in payroll processes, pay periods, or deductions to your employees. Promptly address any questions or concerns they may have.
What are the benefits of using payroll software?
Using payroll software offers several benefits:
Time-saving: Payroll software automates calculations, tax withholdings, and payroll processing, saving you valuable time. It reduces manual effort and streamlines the entire payroll process.
Accuracy: Payroll software minimizes human errors that can occur during manual calculations or data entry. It ensures accurate calculations, tax withholdings, and compliance with payroll laws and regulations.
Compliance: Payroll software stays updated with the latest tax rates, labor laws, and reporting requirements. It helps you stay compliant with federal, state, and local regulations, reducing the risk of penalties and legal issues.
Cost-effective: While there may be an initial investment in purchasing or subscribing to payroll software, it can be cost-effective in the long run. It reduces the need for additional staff or outsourcing payroll services, saving on labor costs.
Employee self-service: Many payroll software solutions provide self-service portals for employees. This allows them to access their pay stubs, tax forms, and update personal information, reducing administrative tasks and improving employee satisfaction.
Data security: Payroll software often offers robust security measures to protect sensitive employee data, including encryption, secure servers, and user access controls. This helps safeguard payroll information from unauthorized access or data breaches.
Reporting and analytics: Payroll software generates detailed reports and analytics, providing valuable insights into labor costs, tax liabilities, and other payroll-related data. It helps with budgeting, forecasting, and strategic decision-making.
Integration with other systems: Payroll software can integrate with other HR, accounting, or timekeeping systems, simplifying data sharing and reducing duplicate data entry. This improves overall efficiency and data accuracy across different business functions.
Streamlined tax filing: Payroll software often generates the necessary tax forms and reports, making it easier to file payroll taxes accurately and on time. It simplifies the year-end reporting process and minimizes the risk of errors.
Support and updates: Payroll software providers typically offer customer support and regular updates to address any issues, incorporate new features, or reflect changes in payroll regulations.
How often should I run payroll?
Running payroll frequency can vary depending on your business needs. Most businesses opt for a biweekly or monthly payroll schedule. Choose a frequency that aligns with your cash flow and compliance requirements.
Can I manually calculate payroll instead of using the software?
While manual calculations are possible, they are prone to errors and can be time-consuming. Payroll software automates calculations, reduces mistakes, and provides greater efficiency.
What happens if I make a mistake in payroll calculations?
If you make a mistake in payroll calculations, rectify it promptly. Communicate the error to the affected employee, correct the mistake in the next payroll cycle, and ensure any necessary adjustments are made.
Is outsourcing payroll secure?
Reputable payroll service providers have robust security measures in place to protect sensitive employee data. Ensure you choose a trusted provider with a proven track record and strong data protection protocols.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with payroll regulations?
Non-compliance with payroll regulations can lead to penalties, fines, legal disputes, and reputational damage. It is crucial to stay updated with labor laws, tax regulations, and reporting requirements to avoid such consequences.
6 signs you urgently need a new bookkeeper
6 Signs You Urgently Need a New Bookkeeper
If you’re a business owner, you know that keeping your financial records in order is essential for the success of your enterprise. Bookkeeping plays a crucial role in maintaining accurate and up-to-date financial information, which forms the foundation for making informed decisions and driving business growth. However, there are times when your current bookkeeper may not be meeting your expectations or delivering the level of service you need. In this article, we’ll explore six signs that indicate you urgently need a new bookkeeper.
Inaccurate or Inconsistent Financial Records
One of the first signs that you need a new bookkeeper is when you notice inaccuracies or inconsistencies in your financial records. Inaccurate records can misrepresent your business’s financial health and lead to poor decision-making. Inconsistent bookkeeping practices can further compound the problem by making it difficult to track and analyze financial data effectively. A proficient bookkeeper should maintain accurate records and follow consistent practices to ensure the reliability of your financial information.
Frequent Errors in Financial Statements
Financial statements, such as balance sheets and income statements, provide vital insights into the financial performance of your business. However, if you consistently find errors in these statements, it’s a clear indication that your current bookkeeper may not be paying enough attention to detail. Frequent errors can have serious consequences, including incorrect tax reporting, inaccurate financial analysis, and potential legal issues. Hiring a new bookkeeper who is meticulous and thorough will help ensure the accuracy of your financial statements.
Difficulty in Tracking Expenses and Revenues
Accurately tracking expenses and revenues is essential for understanding your business’s financial position and making informed decisions. If you find it challenging to keep track of these crucial metrics, it may be a sign that your bookkeeper is not adequately managing your financial records. A competent bookkeeper will implement efficient systems and processes to accurately track and categorize expenses and revenues, providing you with a clear picture of your business’s financial performance.
Missing Important Tax Deadlines
Missing tax deadlines can have serious consequences for your business. It can result in penalties, interest charges, and damage to your business’s reputation. If your current bookkeeper is consistently failing to meet tax deadlines or providing incomplete and inaccurate information to your tax preparer, it’s time to consider finding a new bookkeeper who understands the importance of timely tax compliance. A reliable bookkeeper will ensure that all necessary tax filings are completed accurately and submitted on time.
Lack of Financial Insights and Reports
Financial insights and reports are crucial for gaining a deeper understanding of your business’s financial performance. They help identify trends, highlight areas of concern, and guide strategic decision-making. If your current bookkeeper is not providing you with insightful reports or fails to explain the financial implications of your business activities, it’s a clear sign that you need a new bookkeeper. A proficient bookkeeper will not only generate accurate and timely reports but also offer valuable insights and guidance to help you achieve your financial goals.
Overwhelming Workload and Time Constraints
As a business owner, your time is valuable, and it’s essential to focus on core business activities that drive growth. If you find yourself overwhelmed with bookkeeping tasks or spending excessive time on financial recordkeeping, it may be an indication that you need to delegate these responsibilities to a professional bookkeeper. Outsourcing your bookkeeping can free up your time and allow you to concentrate on the strategic aspects of your business, while a dedicated bookkeeper takes care of the day-to-day financial management.
Should you hire a bookkeeper for your business?
Hiring a Bookkeeper for Your Business: Is It Necessary?
Running a business involves juggling multiple responsibilities, from managing operations to driving growth. One aspect that often requires careful attention is bookkeeping. Bookkeeping is the process of recording, organizing, and maintaining financial transactions and records. While some small business owners may attempt to handle bookkeeping themselves, there are several compelling reasons why hiring a professional bookkeeper can be a wise decision. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of hiring a bookkeeper for your business and help you determine if it’s the right choice for you.
Time and Efficiency
Managing bookkeeping tasks can be time-consuming, especially if you’re not familiar with accounting principles or software. By hiring a bookkeeper, you can delegate these responsibilities, allowing you to focus on core business activities that drive revenue and growth. A professional bookkeeper will efficiently handle tasks such as recording transactions, reconciling accounts, and generating financial reports, ensuring accuracy and freeing up your time.
Accuracy and Compliance
Accurate financial records are crucial for making informed business decisions and complying with legal and tax obligations. A bookkeeper with expertise in financial management will ensure that your records are accurate, complete, and up-to-date. They will follow proper accounting practices, adhere to relevant regulations, and help you stay compliant with tax laws. This can save you from costly errors, penalties, and legal issues that may arise from inadequate recordkeeping.
Financial Insights and Analysis
A competent bookkeeper goes beyond recording transactions. They can provide valuable insights by analyzing your financial data, identifying trends, and generating meaningful reports. These insights can help you understand your business’s financial performance, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions. A bookkeeper can also collaborate with your accountant to provide the necessary information for tax planning and financial forecasting.
Cost Savings
While it may seem counterintuitive to hire a bookkeeper when you’re trying to control costs, it can actually result in long-term cost savings. A bookkeeper can help you streamline processes, identify inefficiencies, and manage cash flow effectively. By having accurate financial information at your fingertips, you can make informed decisions that optimize your resources, avoid unnecessary expenses, and identify opportunities for growth.
Scalability and Growth
As your business grows, so does the complexity of your financial transactions and reporting requirements. A professional bookkeeper can handle the increased volume of transactions, adapt to your evolving needs, and ensure that your financial systems can scale accordingly. They can also provide guidance on financial strategies, budgeting, and cash flow management, helping you navigate growth successfully.
Peace of Mind
By hiring a bookkeeper, you gain peace of mind knowing that your financial records are in capable hands. You can trust that your bookkeeper will maintain confidentiality, uphold professional ethics, and provide accurate information when you need it. This peace of mind allows you to focus on your business’s core objectives without the worry and stress associated with managing complex financial tasks.

How does an accountant help a business?
In today’s competitive business landscape, managing finances and ensuring regulatory compliance has become crucial for the success of any business. This is where an accountant helps a business and plays a pivotal role. Accountants are financial professionals who help businesses maintain accurate records, analyze financial data, and provide valuable insights for effective decision-making. Let’s explore how accountants contribute to the growth and stability of a business.
What is an accountant?
An accountant is a trained professional who specializes in financial management, taxation, and auditing. They possess expertise in various accounting principles, practices, and regulations. An Accountant helps a business and may work independently or as part of an accounting firm, providing services to individuals, small businesses, corporations, and non-profit organizations.
Why do you need an accountant for your business?
An accountant plays a crucial role in managing the financial aspects of a business. Here are several reasons why having an accountant is important for your business.
Financial management and planning
One of the primary responsibilities of an accountant is to manage and plan the financial aspects of a business. They analyze the company’s financial data, create budgets, and develop strategies to optimize cash flow, reduce costs, and maximize profitability. Accountants help a business set realistic financial goals and implement effective strategies to achieve them.
Tax compliance and optimization
Taxation is a complex field with ever-changing regulations. Accountants ensure that businesses comply with tax laws and regulations to avoid penalties and legal issues. They stay updated with tax laws and identify opportunities for tax optimization, helping businesses minimize their tax liabilities while maximizing deductions and credits.
Record keeping and bookkeeping
Accurate record-keeping is crucial for businesses to track their financial transactions and maintain transparency. Accountants maintain comprehensive financial records, including income, expenses, assets, and liabilities. They use specialized software and tools to streamline bookkeeping processes, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial data.
Financial analysis and decision making
Accountants play a vital role in providing financial analysis and insights that support informed decision-making. They analyze financial statements, identify trends, and interpret key financial ratios to assess the company’s financial health. Accountants provide recommendations on cost reduction, investment opportunities, and resource allocation to help businesses make strategic decisions.
Risk management and fraud prevention
Businesses face various financial risks and the threat of fraud. Accountants implement internal controls to minimize risks and prevent fraudulent activities. They conduct regular audits, identify weaknesses in financial processes, and recommend measures to enhance security and protect the business’s assets.
Budgeting and Forecasting
Accountants assist in creating budgets and forecasts for the business. They review historical financial data, analyze trends, and make projections for future performance. This helps businesses set realistic financial goals, allocate resources effectively, and make strategic decisions based on financial projections.
Business Planning and Strategy
Accountants help a business provide valuable input in business planning and strategy development. They can analyze the financial feasibility of new projects or ventures, assess the potential risks and rewards, and provide financial guidance to support decision-making.
What are the duties and responsibilities of an accountant?
Maintaining accurate financial records
Accountants ensure the accuracy and completeness of financial records by recording transactions, reconciling accounts, and verifying balances. They maintain journals, ledgers, and financial statements, ensuring compliance with accounting principles and standards.
Preparation and analysis of financial statements
Accountants prepare financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. They analyze these statements to assess the company’s financial performance, identify areas for improvement, and make recommendations for financial growth.
Budgeting and forecasting
Accountants assist businesses in creating budgets and forecasts based on historical data and future projections. They help set realistic financial goals, monitor budget adherence, and provide insights on financial performance against projections.
Providing financial advice and guidance
Accountants serve as trusted advisors, offering financial advice and guidance to business owners and stakeholders. They provide insights on business expansion, investment decisions, and financial risk management. Accountants also assist in securing funding, managing debt, and evaluating financial opportunities.
What is workplace collaboration?
Workplace collaboration refers to the process of individuals and teams working together to achieve shared goals, solve problems, and make decisions. It involves the joint efforts of employees from different departments, functions, or roles within an organization.
Collaboration in the workplace is characterized by open communication, active participation, and the sharing of ideas, knowledge, and resources. It goes beyond individual work and encourages cooperation, synergy, and collective problem-solving.
Key aspects of workplace collaboration include:
Communication
Effective communication is essential for collaboration. It involves actively listening, expressing ideas clearly, providing feedback, and engaging in open and honest dialogue. Communication can take various forms, including face-to-face interactions, virtual meetings, emails, instant messaging, and collaborative tools.
Teamwork
Collaboration often occurs within teams or across teams. Team members work together, combining their skills, knowledge, and perspectives to achieve common objectives. Collaboration within teams may involve task allocation, joint decision-making, and coordination to ensure the seamless flow of work.
Knowledge sharing
Collaboration encourages the exchange of ideas, information, and expertise between individuals and departments. By sharing knowledge, employees can leverage each other’s strengths, learn from different perspectives, and make better-informed decisions.
Problem-solving
Collaborative environments foster collective problem-solving. Employees from different backgrounds and experiences come together to identify challenges, analyze potential solutions, and make informed decisions. Collaborative problem-solving promotes creativity, critical thinking, and innovation.
Trust and respect
Collaboration is built on trust and mutual respect among team members. When individuals feel safe to express their opinions, take risks, and contribute their unique perspectives, collaboration thrives. Trust enables open communication, cooperation, and the willingness to share ideas and information.
Shared goals
Collaboration is driven by shared goals and objectives. When everyone understands and aligns with the organization’s mission, vision, and objectives, collaboration becomes more focused and purposeful. Clear goals provide a common direction and help prioritize efforts.
Technology and tools
In today’s digital workplace, collaboration often relies on technology and collaborative tools. These tools facilitate communication, document sharing, task management, and real-time collaboration. Examples include project management software, shared document repositories, video conferencing platforms, and instant messaging apps.
Effective workplace collaboration has numerous benefits, including improved productivity, increased employee engagement, enhanced problem-solving capabilities, better decision-making, and a more positive work environment. It fosters a sense of collective ownership, promotes innovation, and contributes to the overall success of the organization.
Are You struggling to collaborate with other departments?
Accountants collaborate with various departments within a business to ensure smooth financial operations and compliance.
Human resources
Accountants work closely with the HR department to manage payroll, employee benefits, and tax withholdings. They provide financial data for compensation planning and assist in creating employee expense policies.
Operations
Accountants analyze the financial impact of operational decisions and help optimize processes to improve efficiency and reduce costs. They collaborate with operations teams to develop financial metrics and performance indicators.
Sales and marketing
Accountants analyze sales data, pricing strategies, and marketing expenses to evaluate profitability and return on investment. They provide insights on pricing decisions, sales forecasting, and marketing budget allocation.
Legal and Compliance
Accountants collaborate with legal and compliance teams to ensure adherence to financial regulations and reporting requirements. They provide financial data for audits, tax filings, and regulatory compliance.
How to improve collaboration between departments in your organization?
Improving collaboration between departments is crucial for promoting effective communication, streamlining processes, and achieving organizational goals. Here are some strategies you can implement to enhance collaboration in your organization:
Foster a culture of collaboration: Encourage a collaborative mindset by promoting the value of teamwork and interdepartmental cooperation. Recognize and reward individuals and teams who demonstrate collaboration and promote a supportive work environment.
Establish clear goals and objectives: Ensure that everyone understands the organization’s overall goals and how each department contributes to achieving them. Clear and shared objectives help align efforts and create a sense of purpose among departments.
Enhance communication channels: Implement effective communication channels to facilitate the exchange of information and ideas across departments. Encourage the use of digital collaboration tools, such as project management software, instant messaging platforms, and shared document repositories.
Encourage regular cross-departmental meetings: Schedule regular meetings or workshops that involve representatives from different departments. These gatherings can foster understanding, build relationships, and promote collaboration. Encourage open discussions and the sharing of insights and challenges.
Develop interdisciplinary projects or teams: Create opportunities for employees from different departments to work together on specific projects or initiatives. This approach promotes collaboration, encourages the sharing of expertise, and helps break down silos.
Establish a centralized knowledge-sharing system: Implement a system or platform where departments can share best practices, lessons learned, and success stories. This knowledge repository can facilitate cross-departmental learning and collaboration.
Provide training and development opportunities: Offer training programs or workshops focused on interpersonal skills, communication, and teamwork. These initiatives can enhance employees’ ability to collaborate effectively and build stronger relationships across departments.
Encourage empathy and understanding: Foster an environment where employees seek to understand the challenges and perspectives of other departments. Encouraging empathy helps break down barriers and promotes a collaborative atmosphere.
Clearly define roles and responsibilities: Clearly communicate roles, responsibilities, and dependencies between departments. This clarity helps minimize confusion, streamline processes, and ensure efficient collaboration.
Lead by example: Leaders and managers should model collaborative behavior by actively engaging with other departments, seeking input, and fostering a culture of collaboration. When leaders prioritize collaboration, it sets a positive example for the entire organization.
What is the difference between in-house and outsourced resources?
Businesses have the option to outsource their accounting functions or hire in-house accountants. Each approach has its benefits and considerations.
Benefits of outsourcing
Outsourcing accounting services can reduce costs, especially for small businesses. It provides access to specialized expertise, scalability, and the latest accounting software. Outsourcing also allows businesses to focus on their core competencies while leaving financial management to professionals.
Advantages of in-house accounting
In-house accountants provide dedicated support and a deeper understanding of the business’s financial operations. They have immediate access to financial data, enabling real-time analysis and decision-making. In-house accountants can work closely with the management team, fostering a collaborative and customized approach.
Factors to consider in the decision
Businesses should consider factors such as budget, the complexity of financial operations, data security, and future growth plans when deciding between outsourcing and in-house accounting. It’s essential to assess the specific needs of the business and choose an approach that aligns with its goals and resources.
Should you outsource accounting services?
Deciding whether to outsource accounting services depends on various factors and the specific needs of your business. Here are some factors to consider when evaluating outsourcing accounting services:
Cost-effectiveness: Outsourcing can be cost-effective, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. By outsourcing, you can avoid the costs associated with hiring and training in-house accounting staff, providing office space, benefits, and purchasing accounting software and tools. Outsourcing allows you to access professional accounting services at a fraction of the cost of maintaining an internal accounting department.
Expertise and specialized knowledge: Professional accounting service providers have expertise in accounting practices, tax regulations, and financial reporting standards. They stay updated with industry changes and trends, which can be valuable for your business. Outsourcing ensures that your accounting tasks are handled by trained professionals who understand the complexities of accounting and can provide accurate and compliant financial information.
Focus on core competencies: Outsourcing accounting services allows you and your internal team to focus on core business activities that drive growth and profitability. By delegating accounting tasks to experts, you can free up time and resources to concentrate on strategic planning, sales, marketing, and other areas critical to your business success.
Scalability and flexibility: Outsourcing provides scalability and flexibility to adapt to changing business needs. As your business grows, outsourcing allows you to easily scale accounting services without the hassle of hiring and training additional staff. Conversely, during periods of reduced activity, you can adjust the level of outsourcing to match your requirements, avoiding the fixed costs associated with an in-house accounting team.
Access to advanced technology and systems: Accounting service providers often have access to the latest accounting software, tools, and systems. By outsourcing, you can leverage these technologies without the upfront investment or ongoing maintenance costs. This can improve the efficiency and accuracy of your financial processes.
Compliance and risk management: Accounting service providers are knowledgeable about tax regulations, financial reporting requirements, and compliance standards. They can help ensure that your financial records and reports are accurate, timely, and in compliance with relevant laws and regulations. This reduces the risk of errors, penalties, and financial mismanagement.
How much does it cost to outsource bookkeeping and controller services?
The cost of outsourcing bookkeeping and controller services can vary depending on various factors, such as the size and complexity of your business, the scope of services required, the location of the service provider, and the level of expertise needed. Additionally, different service providers may have their pricing structures and fee models. Generally, bookkeeping services can range from a few hundred dollars to a few thousand dollars per month. This cost typically covers basic tasks such as recording financial transactions, managing accounts payable and receivable, bank reconciliation, and generating financial reports.
Controller services, which involve higher-level financial management, analysis, and strategic guidance, are generally more expensive. The cost for controller services can start from a few thousand dollars per month and can go up significantly depending on the complexity of your business and the level of financial expertise required.
What skills should an accountant possess?
An accountant should possess skills such as:
Financial Knowledge
Proficiency in accounting principles, financial analysis, and reporting.
Attention to Detail
Ability to accurately and meticulously handle financial data and calculations.
Analytical Thinking
Strong analytical skills to interpret financial information and provide insights.
Organizational Abilities
Effective organization and time management skills to handle multiple tasks and meet deadlines.
Communication Skills
Clear and concise communication to interact with clients, colleagues, and stakeholders.
Technological Competence: Familiarity with accounting software, spreadsheets, and other relevant technology.
Ethical Conduct
Adherence to professional ethics, integrity, and confidentiality.
Problem-solving Skills
Ability to identify financial issues, propose solutions, and troubleshoot problems.
Continuous Learning
Willingness to stay updated with changes in accounting standards and regulations.
Collaboration
Ability to work well in teams and collaborate with other professionals in the organization.
Why is hiring an accountant important for small businesses?
Hiring an accountant is important for small businesses because accountants bring expertise in financial matters, help ensure tax compliance, save time and resources, provide valuable financial insights, support financial planning and growth, and offer guidance for critical financial decisions.
How can an accountant help in reducing tax liabilities?
An accountant can help in reducing tax liabilities through various strategies such as identifying eligible deductions, exemptions, and credits, optimizing the timing of income and expenses, implementing tax planning techniques, ensuring compliance with tax regulations, and providing advice on structuring business transactions in a tax-efficient manner. By leveraging their expertise, accountants can help small businesses minimize their tax burden while remaining compliant with tax laws.
Is it necessary for every business to have an accountant?
While it is not legally required for every business to have an accountant, it is highly recommended for most businesses. An accountant brings expertise in financial management, tax compliance, and strategic planning. They can help businesses navigate complex financial matters, reduce errors, optimize tax strategies, and provide valuable insights. Having an accountant can save time, minimize financial risks, and contribute to the long-term success of a business.
How can I find a reliable accountant for my business?
To find a reliable accountant, seek referrals, consult professional associations, utilize online platforms, interview potential accountants, verify credentials, ask for references, assess communication and trust, and consider the fee structure.
How Much Does an Accountant with 5 Years of Experience Make?
Accounting professionals play a crucial role in organizations by managing financial records, analyzing data, and providing financial advice. As an accountant gains experience and develops their skills, their value in the job market tends to increase. Accountants with 5 years of experience are often sought after for their ability to handle complex financial tasks and contribute to the strategic decision-making processes of companies.
Why is experience important in the accounting industry?
Experience is highly valued in the accounting field. It demonstrates a professional’s ability to handle various financial responsibilities, navigate complex regulations, and make informed decisions. With each passing year, accountants acquire more knowledge and develop their problem-solving skills, making them more valuable to employers.
What factors affect an accountant’s salary?
Several factors influence the salaries of accountants, including their location, industry, company size, and level of education and certifications.
Location
Accountant salaries can vary significantly based on geographical location. Major cities and regions with a higher cost of living, such as New York City or San Francisco, tend to offer higher salaries to accountants compared to rural areas. Local market demand and competition for accounting professionals also play a role in determining salary levels.
Industry
Different industries may have varying demands for accounting expertise, which can affect salary ranges. For example, accountants working in finance or consulting firms often earn higher salaries compared to those working in non-profit organizations or government agencies. Industries with high-profit margins or complex financial operations generally offer more lucrative compensation packages.
Company Size
The size of the company also influences an accountant’s salary. Larger organizations with extensive financial operations and higher revenue streams typically have the resources to offer higher salaries to experienced accountants. Smaller companies or startups may have more limited budgets, resulting in comparatively lower salary ranges.
Education and Certifications
While a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field is generally required to become an accountant, higher levels of education, such as a master’s degree or an MBA, can positively impact salary potential. Additionally, specialized certifications such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Certified Management Accountant (CMA), or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) can provide a competitive edge and potentially lead to higher salaries.
Average Salary Range for Accountants with 5 Years of Experience
The average salary for accountants with 5 years of experience can vary depending on the factors mentioned above. According to recent data, the salary range for accountants with this level of experience typically falls between $55,000 and $85,000 per year. However, it is essential to note that this range is an approximation, and salaries can significantly differ based on the factors discussed earlier.
What factors influence the job outlook for accountants?
Several factors influence the job outlook for accountants. These factors can affect the demand for accountants and the overall growth of the profession. There are Some of key factors that influence the job outlook for accountants.
Economic Conditions: The state of the economy plays a significant role in the job outlook for accountants. During periods of economic growth, businesses expand their operations, leading to an increased demand for accountants to manage financial transactions and ensure regulatory compliance. Conversely, during economic downturns, businesses may reduce their hiring or freeze job openings, impacting the job market for accountants.
Industry Trends: Different industries have varying demands for accounting services. Industries that are experiencing growth, such as technology, healthcare, and finance, often require skilled accountants to handle their financial operations and provide strategic insights. Keeping up with industry trends and positioning oneself in growing sectors can positively impact job prospects for accountants.
Regulatory Changes: Changes in financial regulations and accounting standards can significantly impact the demand for accountants. New regulations may require businesses to adjust their accounting practices, leading to an increased need for accountants with expertise in compliance. Staying updated with evolving regulations and possessing the necessary skills to navigate complex compliance requirements can enhance job prospects.
Technological Advancements: The rapid advancement of technology has transformed the accounting profession. Automation and accounting software has streamlined many routine tasks, reducing the need for manual data entry and basic bookkeeping. However, technological advancements have also created new opportunities for accountants, such as data analysis and financial forecasting. Accountants who embrace technology and possess strong analytical skills are likely to have better job prospects.
Globalization: With increased globalization, businesses are expanding their operations across borders, leading to more complex financial transactions and international regulations. Accountants with knowledge of international accounting standards and experience in managing cross-border transactions are in high demand. The ability to work with diverse teams and navigate global accounting practices can contribute to favorable job prospects.
Retirement and Succession Planning: As experienced accountants retire, there is a need for new professionals to fill their positions. Succession planning is crucial for organizations to ensure a smooth transition and maintain the continuity of financial operations. This presents opportunities for accountants entering the job market or seeking advancement.
Specializations and Skills: Accountants with specialized skills or certifications, such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Certified Management Accountant (CMA), or Certified Internal Auditor (CIA), often have better job prospects. Employers value professionals who can bring specialized knowledge and expertise to their organization, allowing them to stand out in a competitive job market.
What are the opportunities for advancement in the accounting profession?
Accounting offers a clear career progression path. Accountants with 5 years of experience often have the opportunity to advance to senior accounting positions, such as Senior Accountant or Accounting Manager. These roles come with increased responsibilities and higher salaries. With further experience and additional certifications, accountants may even reach executive-level positions such as Controller or Chief Financial Officer (CFO).
How can I increase my pay as an accountant?
If you aspire to increase your salary as an accountant, consider the following tips:
Continuously expand your knowledge and skills through professional development courses or certifications.
Seek opportunities to take on additional responsibilities or lead projects that demonstrate your expertise and value.
Stay updated with the latest industry trends and changes in financial regulations to remain relevant and provide valuable insights to employers.
Network with professionals in the field to learn from their experiences and potentially uncover hidden job opportunities.
Consider specializing in a specific accounting niche or industry, which can make you a sought-after expert in your field.
What are some benefits and perks that businesses offer?
Businesses offer a variety of benefits and perks to attract and retain talented employees. These offerings go beyond salaries and can enhance job satisfaction, work-life balance, and overall employee well-being. Some common benefits and perks provided by businesses are here.
Health Insurance: Many businesses provide health insurance plans to employees, which can cover medical, dental, and vision expenses. Health insurance helps employees access necessary healthcare services and provides financial protection against medical costs.
Retirement Plans: Businesses often offer retirement plans, such as 401(k) or pension plans, to help employees save for their future. These plans may include employer matching contributions, which add to the employee’s retirement savings.
Paid Time Off: Paid time off includes vacation days, sick leave, and holidays. Offering paid time off allows employees to take breaks, rejuvenate, and maintain a healthy work-life balance. It also provides flexibility to manage personal and family responsibilities.
Flexible Working Hours: Flexibility in working hours allows employees to adjust their schedules to accommodate personal obligations or preferences. This can include options for flexible start and end times, compressed workweeks, or remote work arrangements.
Professional Development: Many businesses invest in their employees’ professional growth by offering opportunities for training, workshops, conferences, and tuition reimbursement programs. These initiatives support skill development and career advancement.
Performance Bonuses: Performance bonuses provide additional financial rewards to employees based on their individual or team performance. They serve as incentives for achieving specific goals and can motivate employees to excel in their roles.
Employee Assistance Programs (EAP): EAPs offer confidential counseling, support, and resources to employees and their families to address personal, financial, or mental health challenges. These programs aim to promote well-being and provide guidance during difficult times.
Wellness Programs: Wellness programs focus on promoting employees’ physical and mental well-being. They may include initiatives such as gym memberships, fitness classes, wellness challenges, mindfulness sessions, or access to nutrition counseling.
Employee Discounts: Businesses often partner with other companies to provide employee discounts on various products and services. These can include discounts on retail items, travel, entertainment, or local services.
Maternity/Paternity Leave: To support employees during important life events, businesses may offer paid maternity and paternity leave. This allows new parents to bond with their children and manage the transition to parenthood.
Employee Recognition Programs: Recognition programs acknowledge and reward employees for their exceptional performance, contributions, or milestones. These programs can include awards, certificates, or public recognition to boost employee morale and motivation.
Childcare Facilities or Subsidies: Some businesses provide on-site childcare facilities or subsidies to help employees balance work and family responsibilities. This benefit supports working parents and helps attract and retain top talent.

Does an accountant work in a bank?
In today’s complex financial landscape, the role of an accountant holds immense importance. Accountants are responsible for managing and analyzing financial information, ensuring the accuracy and compliance of financial records, and providing valuable insights for informed decision-making. One common question that often arises is whether accountants work in banks. In this article, we will explore the relationship between accounting and the banking sector, shedding light on the various roles accountants play in banks.
What Does an Accountant Do?
Before delving into the specifics of accounting in the banking sector, let’s first understand the general responsibilities of an accountant. Accountants are financial professionals who handle various aspects of financial management. They are responsible for maintaining accurate financial records, preparing financial reports, conducting audits, managing taxation matters, and providing financial analysis and advice to individuals and organizations.
What are the different types of accounting?
Accounting is a broad field that encompasses various types or branches of accounting. Here are some of the main types of accounting:
Financial Accounting: This type of accounting focuses on recording, summarizing, and reporting financial transactions of an organization to external stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and regulatory authorities. It involves the preparation of financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, in accordance with accounting standards (e.g., Generally Accepted Accounting Principles or International Financial Reporting Standards).
Managerial Accounting: Managerial accounting, also known as cost accounting, involves the use of financial information for internal decision-making within an organization. It provides managers with financial data, such as budgeting, cost analysis, variance analysis, and performance metrics, to assist them in planning, controlling, and evaluating business operations.
Tax Accounting: Tax accounting focuses on ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations. Tax accountants are responsible for preparing and filing tax returns for individuals, businesses, and other entities. They analyze financial data to determine tax liabilities, apply tax laws to minimize tax burdens and provide advice on tax planning strategies.
Auditing: Auditing involves the examination and evaluation of financial records, systems, and processes to ensure their accuracy, reliability, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations. External auditors, often employed by independent accounting firms, perform audits on behalf of stakeholders to provide an independent opinion on the fairness and reliability of financial statements.
Forensic Accounting: Forensic accounting combines accounting, auditing, and investigative techniques to detect and prevent fraud, financial misconduct, or other illegal activities. Forensic accountants analyze financial data, reconstruct transactions, and provide expert opinions and testimony in legal proceedings.
Governmental Accounting: Governmental accounting is specific to public sector entities, such as government agencies, municipalities, and non-profit organizations. It involves accounting for public funds, budgeting, and complying with government regulations and reporting requirements.
Nonprofit Accounting: Nonprofit accounting deals with the unique financial reporting and regulatory requirements of nonprofit organizations. It focuses on accounting for donations, grants, and restricted funds, as well as demonstrating accountability and transparency in the use of funds for the organization’s mission.
International Accounting: International accounting encompasses the application of accounting principles and standards in a global context. It involves dealing with currency conversions, international financial reporting standards, and cross-border transactions to ensure consistency and comparability in financial reporting across countries.
Do accountants work at banks?
Yes, accountants often work at banks. Banks require accountants to manage their financial records, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, analyze financial data, prepare reports, and make informed financial decisions. These accountants may have roles like financial analysts, auditors, tax specialists, or controllers within the banking industry. Their responsibilities include maintaining the accuracy and integrity of the bank’s financial information and helping the institution manage its financial affairs effectively.
What is accounting for banking?
The banking sector heavily relies on the expertise of accountants to ensure the smooth functioning of financial operations. Accountants in banks are involved in various tasks, including financial reporting and compliance, risk management, internal controls, budgeting, and forecasting. They play a crucial role in maintaining accurate financial records, adhering to regulatory requirements, and assessing the financial health of the institution.
Collaboration Between Accountants and Bankers
Collaboration between accountants and bankers is vital for effective financial management in banks. Accountants provide critical financial information to bankers, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding lending, investment strategies, and risk assessment. Accountants ensure the financial stability of the bank and facilitate strategic planning by providing valuable insights into the institution’s financial performance.
Skills Required for an Accountant in a Bank
To excel as an accountant in the banking sector, certain skills are essential. Proficiency in financial software is crucial for handling complex financial transactions and analyzing data accurately. Analytical and critical thinking abilities are necessary to interpret financial information and identify trends or anomalies. Attention to detail and accuracy are paramount to ensure error-free financial records. Strong communication and interpersonal skills enable accountants to collaborate effectively with team members and other stakeholders.
How can I Improve my accounting skills?
Here are some ways you can enhance your accounting skills:
Education and Certification: Pursue a formal education in accounting by enrolling in a degree program or taking accounting courses at a reputable educational institution. Consider obtaining professional certifications such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Certified Management Accountant (CMA), or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) to enhance your credibility and marketability.
Stay Updated: Accounting standards, regulations, and practices evolve over time. Stay current with accounting principles and industry updates by reading professional publications, attending seminars, webinars, and conferences, and participating in relevant professional organizations or forums.
Practical Experience: Gain practical accounting experience by working in accounting positions or internships. Apply your theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, familiarize yourself with accounting software, and develop hands-on skills in areas such as financial statement analysis, budgeting, and tax preparation.
Technology Skills: Accounting is becoming increasingly automated and reliant on technology. Familiarize yourself with accounting software, spreadsheet programs (e.g., Microsoft Excel), and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems commonly used in the accounting field. Develop your skills in data analysis, data visualization, and other relevant technological tools.
Continuous Learning: Commit to lifelong learning and professional development. Take advantage of online courses, webinars, and other learning resources to enhance your knowledge in specific accounting topics or areas of interest. Consider joining professional accounting associations that offer training programs and networking opportunities.
Attention to Detail: Develop strong attention to detail, as accuracy is crucial in accounting. Pay close attention to numbers, data entry, and reconciliations. Develop a systematic approach to reviewing and verifying financial information to avoid errors and discrepancies.
Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills: Enhance your analytical and problem-solving skills to interpret financial data, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Practice analyzing financial statements, conducting variance analysis, and using financial ratios to assess performance and make recommendations.
Communication Skills: Effective communication is essential in accounting, both verbally and in writing. Develop your communication skills to explain complex financial concepts to non-financial stakeholders, present financial reports, and collaborate with colleagues and clients.
Networking: Build a professional network by connecting with other accounting professionals, attending industry events, and engaging in online accounting communities. Networking can provide opportunities for knowledge sharing, mentorship, and career advancement.
Ethics and Professionalism: Uphold high ethical standards and professionalism in your accounting practice. Maintain confidentiality, integrity, and objectivity in financial reporting and decision-making.
What are the Education and Certification of an Accountant?
A strong educational background is essential for a career in accounting. Most accountants hold a bachelor’s degree in accounting, finance, or a related field. Professional certifications, such as the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Certified Management Accountant (CMA), enhance an accountant’s credibility and open doors to advanced career opportunities. Continuous learning and professional development through workshops, seminars, and staying updated with accounting standards are essential to excel in the field.
What are the different banking career paths?
Banking offers a wide range of career paths, catering to various interests and skill sets. Here are some common career paths within the banking industry:
Retail Banking: Retail bankers work directly with individual customers and small businesses. They handle day-to-day banking activities, such as opening and managing accounts, processing transactions, offering financial advice, and promoting banking products and services.
Corporate Banking: Corporate bankers serve large businesses and corporations. They assist with complex financial transactions, including lending, credit analysis, cash management, treasury services, and investment banking activities. Corporate bankers often work closely with clients to understand their financial needs and provide customized solutions.
Investment Banking: Investment bankers facilitate large-scale financial transactions, such as mergers and acquisitions, initial public offerings (IPOs), and capital raising for corporations and institutions. They provide advisory services, valuation analysis, due diligence, and the structuring of financial deals. Investment banking roles often involve working in teams and require strong financial modeling, analytical skills, and market knowledge.
Commercial Banking: Commercial bankers work with mid-sized businesses and commercial clients. They provide lending and credit solutions, manage business relationships, assess creditworthiness, and analyze financial statements to determine loan eligibility and risk. Commercial bankers help businesses with their financial needs, including working capital, equipment financing, and expansion plans.
Private Banking/Wealth Management: Private bankers or wealth managers cater to high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) and families. They offer personalized financial and investment advice, wealth preservation and growth strategies, estate planning, and portfolio management services. Private bankers develop long-term relationships with clients and provide comprehensive financial solutions to meet their unique needs.
Risk Management: Risk management professionals play a vital role in assessing and managing various risks faced by banks, such as credit risk, market risk, operational risk, and regulatory compliance. They develop risk frameworks, implement risk mitigation strategies, and ensure compliance with industry regulations and internal policies.
Compliance and Regulatory Affairs: Compliance officers ensure that banks adhere to legal and regulatory requirements. They monitor activities, develop compliance programs, conduct audits, and provide guidance to ensure the bank’s operations align with relevant laws and regulations, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) rules.
Treasury and Cash Management: Treasury professionals manage a bank’s liquidity, funding, and cash flow. They oversee cash management activities, analyze financial markets, execute foreign exchange transactions, manage interest rate risks, and optimize the bank’s balance sheet.
Financial Planning and Analysis: Professionals in financial planning and analysis (FP&A) roles provide financial forecasting, budgeting, and analysis support to banks. They analyze financial performance, identify trends, develop financial models, and provide insights to support strategic decision-making.
Technology and Digital Banking: With the increasing role of technology in banking, professionals in this area focus on developing and managing digital banking platforms, cybersecurity, data analytics, fintech partnerships, and innovation initiatives to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
What challenges are brewing for the future?
Here are some broad areas where significant challenges are expected:
Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability: The effects of climate change, including rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and resource scarcity, pose significant challenges for the future. Mitigating climate change, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and adopting sustainable practices across industries will be crucial.
Technological Advancements and Automation: Rapid technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence (AI), automation, robotics, and blockchain, have the potential to disrupt industries and transform the job market. Preparing for the impact of automation on employment and adapting to new technologies will be a challenge.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: With increasing reliance on technology and interconnected systems, the threat of cyberattacks and data breaches is a growing concern. Protecting sensitive information, ensuring data privacy, and developing robust cybersecurity measures will be ongoing challenges.
Demographic Changes and Aging Population: Many countries are experiencing demographic shifts, with aging populations and declining birth rates. This places strain on healthcare systems, social security, and pension programs. Addressing the needs of an aging population and ensuring sustainable social support will be critical.
Economic Inequality and Social Disparities: Economic inequality and social disparities continue to be significant challenges. Bridging the wealth gap, promoting social inclusion, and ensuring equal opportunities for all individuals will be crucial for the future.
Global Health Crises: The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the vulnerability of global health systems and the need for robust preparedness and response mechanisms. Addressing future health crises, investing in public health infrastructure, and advancing medical research and development will be essential.
Geopolitical Uncertainty and Conflicts: Geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, and conflicts create uncertainty in global affairs. Finding diplomatic solutions, promoting cooperation, and maintaining stability in an interconnected world will be ongoing challenges.
Ethical Considerations of Technology: As technology advances, ethical considerations surrounding issues like privacy, algorithmic bias, and the ethical use of AI will become more complex. Developing ethical frameworks and guidelines to ensure responsible technology development and usage will be crucial.
Access to Education and Digital Divide: Ensuring equal access to quality education and bridging the digital divide will be critical for a future where digital skills and knowledge are increasingly important. Addressing educational disparities and providing equitable access to technology and internet connectivity will be challenged to overcome.
Mental Health and Well-being: The importance of mental health and well-being is gaining recognition. Addressing mental health issues, reducing stigma, and promoting holistic well-being in society will be important challenges for the future.
Can an accountant work as a bank financial manager?
Yes, an accountant can work as a bank financial manager. While there may be differences in job responsibilities and skill sets between the two roles, accountants often possess the necessary knowledge and skills to transition into financial management positions within a bank.
Accountants are typically well-versed in financial analysis, financial reporting, budgeting, and taxation. These skills are highly relevant in the field of financial management. A bank financial manager is responsible for overseeing financial operations, analyzing financial data, managing budgets, evaluating investment opportunities, and making strategic financial decisions. These tasks require a solid understanding of accounting principles and financial analysis.
To transition into a bank financial manager role, an accountant may need to acquire additional skills and knowledge related to banking operations, risk management, compliance, and financial regulations. This can be achieved through on-the-job training, professional development courses, or pursuing advanced degrees or certifications such as an MBA (Master of Business Administration) or a CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) designation.
It is worth noting that specific job requirements and qualifications can vary depending on the bank and the level of the position. Some banks may prefer candidates with prior experience or specialized knowledge in banking and finance. However, with the right combination of skills, experience, and relevant qualifications, an accountant can certainly transition into a bank financial manager role.
How much does a bank accountant make a year?
The salary of a bank accountant can vary depending on various factors such as experience, qualifications, geographic location, the size of the bank, and the specific responsibilities of the position. Additionally, different countries and regions may have different salary ranges. As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, in the United States, the median annual salary for an accountant or auditor, including those working in banks, was around $73,560, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
it’s important to note that this figure represents the median salary for accountants in general and may not specifically reflect the salary of a bank accountant. In many countries, bank accountants may earn salaries that are comparable to or slightly higher than those of accountants in other industries due to the specialized nature of their work and the financial sector’s complexity.
How do I become an accountant in a bank?
To become an accountant in a bank, you typically need to follow these steps:
Obtain a relevant educational background: Most banks require a minimum of a bachelor’s degree in accounting, finance, or a related field. Pursuing a degree in accounting provides you with the foundational knowledge and skills necessary for a career in accounting.
Gain relevant work experience: While not always mandatory, gaining practical experience through internships or entry-level accounting positions can be highly beneficial. Look for opportunities to work in accounting or finance roles within banks or financial institutions. This experience will help you understand the banking industry’s specific accounting practices and regulations.
Obtain professional certifications: Although not always required, professional certifications can enhance your job prospects and demonstrate your expertise. Two common certifications for accountants are the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) and the Chartered Accountant (CA). Depending on your country or region, there may be additional certifications specific to banking or finance that you can pursue.
Develop specialized knowledge: Familiarize yourself with the unique aspects of accounting in the banking industry. This includes understanding financial regulations, banking operations, risk management, and compliance requirements. Stay updated on industry trends and changes in accounting standards to ensure you have the necessary knowledge to excel in a bank accounting role.
Build a professional network: Networking is crucial for career advancement. Attend industry events, join professional associations, and connect with individuals working in the banking and accounting sectors. Building relationships can lead to job opportunities and valuable insights into the field.
Apply for positions in banks: Look for job openings for accountants in banks or financial institutions. You can search online job portals, and company websites, or utilize recruitment agencies. Tailor your resume and cover letter to highlight your accounting skills, relevant experience, and any certifications or specialized knowledge you possess.
Prepare for interviews: Brush up on your knowledge of accounting principles, banking regulations, and financial analysis. Be prepared to answer questions related to your accounting skills, experience, and how you would handle various scenarios encountered in bank accounting roles.
What are financial statements used in accounting?
Financial statements are important tools used in accounting to provide a summary of a company’s financial performance and position over a specific period. They are used to communicate the financial information of an entity to various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and regulatory authorities. The main financial statements used in accounting are:
Income Statement (or Profit and Loss Statement): The income statement presents the revenues, expenses, gains, and losses of a company over a specific period, typically a fiscal quarter or year. It shows the net income or net loss of the business during that period, indicating its profitability.
Balance Sheet: The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time, usually the end of a fiscal period. It presents the company’s assets (such as cash, inventory, property, and investments), liabilities (such as loans, accounts payable, and debt), and shareholders’ equity. The balance sheet follows the fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity.
Cash Flow Statement: The cash flow statement reports the inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents during a given period. It categorizes cash flows into three main sections: operating activities (day-to-day business operations), investing activities (buying or selling long-term assets), and financing activities (obtaining or repaying capital). The statement helps assess a company’s ability to generate cash and its liquidity position.
Statement of Changes in Equity (or Statement of Shareholders’ Equity): This statement tracks changes in shareholders’ equity over a specific period. It shows how equity accounts, such as retained earnings and capital contributions, have changed due to net income or loss, dividends, share issuances or repurchases, and other equity-related transactions.
These financial statements are prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to ensure consistency and comparability of financial information across different companies. Financial statements provide valuable information for decision-making, financial analysis, and evaluating a company’s financial performance, liquidity, solvency, and profitability. They are essential for external users, such as investors and creditors, to assess the financial health of a company and make informed decisions.
What are the different career tracks in financial accounting?
Financial accounting offers various career tracks and opportunities for professionals to specialize in different areas. There are Some common career tracks in financial accounting.
Public Accounting: Public accountants work for public accounting firms and provide accounting and auditing services to clients, including businesses, nonprofit organizations, and government agencies. They may perform financial statement audits, tax planning and preparation, management consulting, and other related services.
Corporate Accounting: Corporate accountants work within organizations and handle the financial accounting functions specific to that company. They are responsible for preparing financial statements, managing internal controls, analyzing financial data, and ensuring compliance with accounting standards and regulations. Career progression in corporate accounting can lead to roles such as senior accountant, accounting manager, controller, or chief financial officer (CFO).
Financial Reporting: Professionals specializing in financial reporting focus on the accurate preparation and presentation of financial statements. They ensure compliance with accounting standards, regulatory requirements, and disclosure rules. Financial reporting roles often exist within large corporations, where there are complex reporting obligations and the need for technical expertise.
Management Accounting: Management accountants work closely with the management team to provide financial analysis, cost analysis, budgeting, and performance measurement. They help organizations make strategic decisions, analyze profitability, and improve operational efficiency. Career paths in management accounting may include roles like cost accountant, financial analyst, budget manager, or management controller.
Internal Audit: Internal auditors evaluate an organization’s internal controls, risk management practices, and compliance with policies and regulations. They identify areas for improvement and provide recommendations to enhance operational effectiveness and minimize risks. Internal auditors may work within a company’s internal audit department or as part of a consulting firm.
Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A): Professionals in FP&A focus on financial forecasting, budgeting, and financial analysis to support strategic decision-making. They analyze financial data, prepare forecasts, perform variance analysis, and provide insights to management for budgeting, resource allocation, and investment decisions.
Government Accounting: Government accountants work for governmental agencies at various levels, such as federal, state, or local governments. They handle financial management, budgeting, and accounting for public funds. Government accountants ensure compliance with government regulations and financial reporting requirements specific to the public sector.

How does Quickbooks accountant work?
QuickBooks Accountant is a powerful software solution designed specifically for accountants and bookkeepers. It provides a comprehensive set of tools and features that simplify the process of managing multiple client accounts and streamlining financial tasks. In this article, we will explore how QuickBooks Accountant works and how it can benefit accounting professionals and businesses.
What are the features of QuickBooks Accountant?
Multi-client management
One of the key features of QuickBooks Accountant is its ability to manage multiple client accounts within a single software interface. Accountants can easily switch between different client files, view the status of each client’s financials, and access client-specific data and reports.
Accountant Toolbox
QuickBooks Accountant provides an accountant toolbox that includes a range of specialized tools and features to assist in managing client accounts. This toolbox includes features such as batch entry, which allows accountants to enter transactions in bulk, saving time and effort.
Batch transaction processing
Setting up QuickBooks Accountant
To get started with QuickBooks Accountants, accountants need to install the software on their computer or access it through a cloud-based platform. The installation process is straightforward and guided, ensuring a seamless setup experience. Once installed, accountants can create a new company file for each client they work with.
Navigating QuickBooks Accountant
QuickBooks Accountant has a user-friendly interface that makes it easy to navigate and access various features. The dashboard provides an overview of the accountant’s activities, including client lists, notifications, and reminders. The main menu offers quick access to essential tools, such as banking, sales, expenses, and reports.
What should a client account manager do?
QuickBooks Accountant allows accountants to add and manage client accounts efficiently. Accountants can easily add new clients to their database, import client data from other sources, or collaborate with existing QuickBooks users. Each client has a dedicated dashboard where accountants can access client-specific information and perform tasks like invoicing, expense tracking, and bank reconciliation.
How do I use the QuickBooks Online accountant toolbox?
To use the QuickBooks Online Accountant Toolbox, follow these steps:
Log in to your QuickBooks Online Accountant (QBOA) account at accountant.intuit.com using your login credentials.
Once you’re logged in, you’ll be taken to the Accountant Dashboard. In the left navigation menu, click on “Toolbox.”
In the Toolbox, you’ll find various tools and features designed specifically for accountants. Here are some key features you can access:
Client Dashboard: This allows you to view all your clients and access their QuickBooks Online company files in one place. You can click on a client’s name to open their file and perform various accounting tasks.
Accountant Tools: This section provides access to tools that can help you efficiently manage your clients’ books. Some of the tools available include “Reclassify Transactions,” “Fix Unapplied Customer Payments and Credits,” “Merge Vendors,” “Write off Invoices,” and more.
Accountant Reports: This feature provides a range of pre-built reports specifically designed for accountants. You can access reports such as “Trial Balance,” “General Ledger,” “Profit and Loss by Class,” and others. These reports can help you analyze your client’s financial data.
ProAdvisor Benefits: If you are a QuickBooks ProAdvisor, this section provides access to additional benefits and resources available exclusively to ProAdvisors. You can access training materials, certification exams, marketing resources, and more.
Workpapers: This tool allows you to request and organize supporting documents from your clients. You can create new work papers, assign them to clients, and collaborate with your clients on document collection and preparation.
Accountant Toolbox Apps: This section provides access to various third-party apps that integrate with QuickBooks Online and can enhance your accounting workflow. You can explore and install apps that suit your needs. To use any specific tool or feature, simply click on the relevant option within the Toolbox. Each tool will have its own interface and instructions, guiding you on how to perform specific tasks.
Customer collaboration: what it is & why you should do it
Customer collaboration refers to actively involving and engaging customers in the development, improvement, and decision-making processes of a product or service. It goes beyond traditional customer feedback and incorporates customers as valuable contributors to the overall business strategy and product/service development.
Here are a few reasons why customer collaboration is beneficial:
Enhanced customer satisfaction: By involving customers in the development process, you gain valuable insights into their needs, preferences, and pain points. This enables you to create products and services that better meet their expectations, resulting in increased customer satisfaction.
Improved product/service quality: Customer collaboration allows you to gather feedback early on and incorporate it into the product or service design. By involving customers in testing and iteration processes, you can identify and rectify any issues or shortcomings, leading to a higher-quality offering.
Increased customer loyalty: When customers feel valued and have a sense of ownership in the products or services they use, they are more likely to develop loyalty and advocate for your brand. Collaborative relationships foster stronger connections with customers, leading to long-term loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
Market insights and innovation: Customer collaboration provides an opportunity to gain a deeper understanding of market trends, emerging needs, and customer behavior. By involving customers in brainstorming sessions or co-creation activities, you can tap into their creativity and generate innovative ideas that may not have been identified internally.
Early adoption and market validation: Engaging customers in the development process allows you to identify early adopters who are eager to try new products or services. These early adopters can provide valuable feedback and act as ambassadors, helping to validate and promote your offering within their networks.
Competitive advantage: Customer collaboration can differentiate your business from competitors by demonstrating your commitment to customer-centricity. It shows that you value customer input, and this transparency and responsiveness can give you an edge over competitors who are less engaged with their customers.
Co-creation of value: Collaborating with customers allows you to create a mutually beneficial relationship. Customers feel empowered and valued when their input is considered, and they can co-create value with your business. This can lead to long-term partnerships and a shared sense of success.
To foster effective customer collaboration, consider implementing strategies such as customer feedback surveys, focus groups, advisory boards, beta testing programs, online communities, and regular communication channels. By actively involving customers throughout the product or service lifecycle, you can build stronger relationships, improve your offerings, and drive business growth.
How often should I review my new clients?
The frequency of reviewing your new clients can vary depending on several factors, including the size of your client base, the complexity of their financial situations, and your capacity as an accountant or bookkeeper. Here are some general guidelines to consider:
Initial review: Conduct a thorough review of new clients when they onboard to gather essential information about their business, financials, and accounting practices. This review helps you understand their unique needs and challenges, allowing you to set the right expectations and establish a solid foundation for your working relationship.
Regular review: It is generally recommended to review your clients’ accounts on a regular basis, such as quarterly or semi-annually. This review can help identify any potential errors, inconsistencies, or red flags in their financial records. Regular reviews also ensure that you stay updated with your client’s financial situation and can provide timely advice or make necessary adjustments.
Significant events or changes: Review your clients’ accounts whenever significant events or changes occur in their business. This includes changes in ownership, major expansions or contractions, new product or service launches, mergers or acquisitions, or any other event that may impact their financials. Prompt reviews during such events allow you to assess the impact and provide appropriate guidance.
Periodic deep dive: Consider conducting a more in-depth review of your client’s accounts annually or as needed. This comprehensive review involves analyzing key financial statements, assessing financial ratios, identifying trends, and benchmarking their performance against industry standards or previous periods. This deep dive review helps you provide valuable insights, and strategic advice, and identify areas for improvement.
Trigger-based reviews: Implement trigger-based reviews for specific situations. For example, if a client consistently misses their tax deadlines or experiences cash flow issues, it may warrant a more frequent review to address the underlying problems promptly. Similarly, if a client implements new accounting software or undergoes a significant change in their business operations, you may need to conduct a focused review to ensure a smooth transition.
What is the QuickBooks Essentials plan?
As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, QuickBooks offers different subscription plans, including QuickBooks Essentials. However, please note that QuickBooks regularly updates its offerings, so it’s essential to visit the QuickBooks website or contact their customer support for the most up-to-date information. Here is a description of QuickBooks Essentials based on the information available as of September 2021:
QuickBooks Essentials is an online accounting software plan designed for small businesses. It provides essential features to manage your business finances effectively. Here are some key features typically associated with QuickBooks Essentials:
Expense tracking: You can connect your bank accounts and credit cards to automatically import and categorize transactions. This helps you track your business expenses accurately and efficiently.
Invoicing and payments: QuickBooks Essentials allows you to create customized invoices and send them to your customers directly from the software. You can also accept online payments, making it convenient for your customers to pay you.
Bill management: You can easily enter and track bills from vendors and suppliers. QuickBooks Essentials enables you to schedule and automate recurring bills, making it simpler to manage your payables.
Financial reporting: The software provides various financial reports that give you insights into your business’s financial health. You can access reports such as profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Sales tax tracking: QuickBooks Essentials helps you track and calculate sales tax owed on your sales. This feature can be particularly useful if your business is required to collect and remit sales tax.
Integration with third-party apps: QuickBooks Essentials allows integration with a range of third-party applications, expanding its functionality and enabling you to connect with other business tools you may be using.
How do I file a tax return?
Filing a tax return involves reporting your income, deductions, and tax liabilities to the relevant tax authority. The process can vary depending on your country and the specific tax regulations in place. Here is a general guide to help you understand the steps involved in filing a tax return:
Gather necessary documents: Collect all the required documents, including your income statements (e.g., W-2 forms, 1099 forms, or self-employment income records), expense receipts, investment statements, and any other relevant financial records.
Choose the appropriate tax form: Determine the correct tax form to use based on your personal or business situation. In the United States, for example, individuals typically use Form 1040 or one of its variants (such as 1040A or 1040EZ) to file their federal tax returns.
Calculate your income: Calculate your total income for the tax year. This includes wages, salary, self-employment income, rental income, investment income, and any other sources of income.
Determine deductions and credits: Identify eligible deductions and tax credits that you can claim. These may include expenses related to education, homeownership, medical expenses, charitable contributions, or business expenses, among others. Be sure to consult the tax laws and regulations applicable to your situation to understand which deductions and credits you qualify for.
Complete the tax form: Fill out the tax form accurately and completely, providing the required information. Enter your income, deductions, and credits in the appropriate sections of the form. Double-check all the entries to ensure accuracy.
Calculate your tax liability: Calculate your tax liability by applying the applicable tax rates to your taxable income. If you have already had taxes withheld from your income, subtract any applicable tax credits. The resulting amount will be your final tax liability or the amount you are owed as a refund.
Choose your filing method: Decide whether you will file your tax return electronically or by mail. Electronic filing is generally faster and more convenient, and it may also offer features that help reduce errors.
Submit your tax return: If you’re filing electronically, submit your tax return through the designated online platform or software. If you’re filing by mail, print out the completed tax forms, attach any required supporting documents, and send them to the appropriate tax authority’s address.
Pay any taxes owed: If you have a tax liability and owe taxes, make the payment by the tax filing deadline. Various payment options are typically available, such as online payment, check, or money order. If you can’t pay the full amount owed, consider exploring payment plans or requesting an extension.
Keep copies for your records: Make copies of your completed tax return, including all supporting documents, for your personal records. These records are important for future reference and may be necessary for audits or any future inquiries.
Preparing reports and tax filings
QuickBooks Accountant simplifies the process of generating financial reports and preparing tax filings. Accountants can customize reports to meet specific client requirements and generate them with a few clicks. The software also offers tax preparation tools, including tax forms and calculations, which help accountants streamline the tax filing process for their clients.
What are the Quickbook Advanced features and integrations?
QuickBooks Accountant offers advanced features and integrations that further enhance its capabilities. Accountants can take advantage of advanced reporting options, such as creating custom financial statements and graphs, to provide in-depth insights to their clients. The software also integrates with other applications, such as payroll systems and inventory management tools, to streamline data flow and enhance efficiency.
What is Data security and backup?
Data security is crucial when dealing with financial information. QuickBooks Accountant prioritizes data security by providing various options for data backup and protection. Accountants can schedule automatic backups of client files, store data in encrypted formats, and set user permissions to control access levels. These measures ensure that client data remains secure and protected.
Where can I get QuickBooks Accountant support and resources?
QuickBooks Accountant offers comprehensive support and resources to help accountants make the most of the software. The help center provides step-by-step guides, video tutorials, and frequently asked questions to assist users in troubleshooting issues. Additionally, accountants can join online forums and communities to connect with other professionals, share insights, and gain valuable knowledge.
How to add an accountant in QuickBooks?
To add an accountant to your QuickBooks Online account, follow these steps:
Log in to your QuickBooks Online account: Go to the QuickBooks Online login page (qbo.intuit.com) and enter your login credentials to access your account.
Access the Manage Users page: Once you’re logged in, click on the “Settings” (gear) icon in the top-right corner of the screen. From the drop-down menu, select “Manage Users” under the “Your Company” section. This will take you to the Manage Users page.
Invite an accountant: On the Manage Users page, click the “Accounting firms” or “Accountants” tab, depending on the version of QuickBooks Online you are using.
Click on “Invite Accountant”: Look for the “Invite Accountant” button or a similar option on the Accounting Firms or Accountants tab and click on it.
Enter the accountant’s email address: In the invitation window that appears, enter the email address of the accountant you want to invite to access your QuickBooks Online account.
Select the accountant’s access rights: Choose the level of access you want to grant to the accountant. QuickBooks Online provides three levels of access for accountants: “Company administrator,” “Accountant,” and “Reports only.” Select the appropriate level based on the accountant’s role and the level of access they require.
Click on “Invite”: After entering the accountant’s email address and selecting their access rights, click the “Invite” or similar button to send the invitation.
Accountant accepts the invitation: The accountant will receive an email invitation to access your QuickBooks Online account. They need to follow the instructions in the email to accept the invitation and set up their own login credentials.
Once the accountant accepts the invitation, they will be added to your QuickBooks Online account as a user with the specified access rights. They will then be able to log in to your account and access the necessary features and data to provide accounting services.
How do I contact Intuit customer support?
To contact Intuit customer support, you can use the following methods:
Phone support: Intuit offers phone support for its various products and services. The specific phone numbers may vary depending on your location and the product you need assistance with. Visit the Intuit website and navigate to the support section to find the appropriate phone number for your region and product.
Live chat support: Some Intuit products provide live chat support as an option. Visit the Intuit website and look for the support section to see if live chat support is available for the specific product you are using.
Community and online forums: Intuit maintains an active community and online forums where you can find answers to common questions, engage with other users, and seek help from Intuit experts. You can access the community and forums through the Intuit website or by searching for the specific product’s community.
Social media: Intuit has a presence on various social media platforms. You can try reaching out to Intuit customer support through their official social media channels by sending a direct message or posting your query on their public profiles.
Help articles and knowledge base: Intuit provides extensive help articles and a knowledge base for its products and services. Visit the Intuit website and search for the specific product’s support section to access these resources. You can often find step-by-step guides, troubleshooting instructions, and frequently asked questions (FAQs) that may help you resolve your issue.
Email support: While direct email support may not be available for all Intuit products, you can typically find email contact forms or submission options on the Intuit support website. Fill out the form with your inquiry or issue, and the Intuit support team will respond via email.

How Does a Bookkeeper Work with an Accountant?
Introduction
In the realm of finance, two essential roles work in tandem to ensure the smooth operation of businesses and organizations: the bookkeeper and the accountant. While both professionals deal with financial matters, they have distinct responsibilities that complement each other. In this article, we will explore the working relationship between bookkeepers and accountants, their roles and responsibilities, and the benefits of their collaboration.
The Relationship Between a Bookkeeper and an Accountant
It is crucial to understand that bookkeepers and accountants work hand in hand, each playing a vital role in the financial management process. Contrary to popular belief, their duties do not overlap entirely. Rather, they complement and support each other’s work to provide accurate financial information and ensure compliance with regulations.
Bookkeeper’s Role
A bookkeeper is primarily responsible for recording financial transactions and maintaining organized and accurate records. They meticulously enter data into accounting systems, including purchases, sales, payments, and receipts. Bookkeepers also reconcile bank statements and prepare invoices, ensuring that financial records are up-to-date and error-free.
Additionally, bookkeepers prepare financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. These documents provide a snapshot of the company’s financial health and serve as a foundation for further analysis by the accountant.
Accountant’s Role
While the bookkeeper focuses on recording and organizing financial data, the accountant takes on a more analytical and advisory role. Accountants utilize the information provided by bookkeepers to analyze and interpret financial data. They assess the company’s financial performance, identify trends, and offer recommendations to improve profitability and efficiency.
Accountants also play a crucial role in tax planning and preparation. They ensure compliance with tax regulations, prepare tax returns, and help businesses take advantage of tax deductions and credits. Accountants bring a broader perspective to financial matters, providing strategic insights to guide business decisions.
Working Together: How Bookkeepers and Accountants Collaborate
Effective collaboration between bookkeepers and accountants is essential for accurate financial reporting and decision-making. Communication and information sharing are key factors in their working relationship. Bookkeepers must provide accountants with accurate and detailed financial records, enabling them to perform in-depth analyses and provide valuable insights.
Accountants rely on the bookkeeper’s records to identify any discrepancies, reconcile accounts, and prepare accurate financial statements. Regular meetings and open lines of communication ensure that both professionals are aligned and working towards the same financial goals.
Benefits of a Strong Bookkeeper-Accountant Relationship
A strong partnership between a bookkeeper and an accountant brings several benefits to an organization. By working together, they streamline financial processes, minimize errors, and ensure compliance with financial regulations. Accurate and timely financial information enables better decision-making and helps businesses identify opportunities for growth.
Furthermore, the collaboration between a bookkeeper and an accountant reduces the burden on business owners, allowing them to focus on core operations. With the financial aspect in capable hands, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions based on the insights and recommendations provided by their accounting team.
Tips for Effective Collaboration
To foster a successful collaboration between bookkeepers and accountants, consider the following tips:
Regular meetings and communication: Schedule periodic meetings to discuss financial matters, address any discrepancies, and align goals and strategies.
Utilizing technology and accounting software: Embrace accounting software and cloud-based platforms to streamline data sharing, enhance accuracy, and improve efficiency.
Establishing clear expectations and responsibilities: Define the scope of work for each role, establish deadlines, and clarify communication channels to avoid confusion and ensure accountability.
Qualifications and education for bookkeepers and accountants
Qualifications for Bookkeepers: To pursue a career as a bookkeeper, a high school diploma or equivalent qualification is typically the minimum requirement. However, some employers may prefer candidates with additional certifications or formal training in bookkeeping.
There are various certification programs available that can enhance your skills and credibility as a bookkeeper.
Certified Bookkeeper (CB): Offered by the American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers (AIPB), this certification validates your bookkeeping knowledge and skills.
QuickBooks Certified User: This certification focuses on proficiency in using QuickBooks software, a widely used accounting software for small businesses.
National Bookkeepers Association (NBA) Certification: NBA offers certification programs that cover different aspects of bookkeeping, including payroll, financial statements, and more.
Education and Qualifications for Accountants: Accountants typically require a higher level of education and qualifications compared to bookkeepers. The common educational path for accountants is to obtain a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field, such as finance or business administration.
Some of the well-known certifications for accountants include:
Certified Public Accountant (CPA): CPA is a prestigious and highly recognized certification for accountants. It requires meeting specific educational requirements, passing a rigorous exam, and fulfilling experience criteria. CPA certification enables accountants to offer a wide range of services, including auditing and tax preparation.
Certified Management Accountant (CMA): CMA certification is offered by the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA) and focuses on management accounting and financial management skills. This certification is particularly valuable for those interested in managerial roles within organizations.
Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA): While not exclusive to accountants, the CFA certification is highly regarded in the finance industry. It covers a broad range of financial topics, including investment analysis, portfolio management, and ethics.
Do I need an accountant or bookkeeper or both?
Whether you need an accountant, a bookkeeper, or both depends on the complexity and scale of your financial needs. While there is some overlap in their roles, they serve different purposes and can complement each other effectively.
Bookkeeper’s Role: A bookkeeper is responsible for day-to-day financial tasks and maintaining accurate records. They handle tasks such as recording transactions, reconciling bank statements, managing accounts payable and receivable, and organizing financial documents. Bookkeepers ensure that your financial records are up-to-date, accurate, and well-organized. If you have a small business or limited financial transactions, a bookkeeper may be sufficient to handle your financial needs. They can provide you with regular financial reports, help you track expenses, and ensure that you comply with basic accounting practices. A bookkeeper can save you time and ensure that your financial records are in order.
Accountant’s Role: An accountant takes a more strategic and analytical approach to your finances. They analyze and interpret financial data, provide insights and recommendations, and help you make informed decisions for your business. Accountants have a broader understanding of financial concepts, tax laws, and financial planning. If your business has more complex financial needs, such as financial analysis, tax planning, budgeting, or strategic financial guidance, an accountant becomes invaluable. Accountants can assist with financial forecasting, tax preparation, and financial statement analysis, and help you optimize your financial operations.
The Synergy Between Bookkeepers and Accountants: In many cases, businesses benefit from having both a bookkeeper and an accountant. Bookkeepers handle the day-to-day financial tasks and maintain accurate records, providing a solid foundation of financial data. Accountants then utilize this data to analyze, interpret, and provide valuable insights and guidance.
The collaboration between a bookkeeper and an accountant ensures a checks-and-balances system, enhances accuracy and allows for a more comprehensive understanding of your business’s financial health. The bookkeeper provides the accountant with accurate and organized records, enabling them to focus on higher-level analysis and strategic financial planning.
What skills do bookkeepers and accountants need?
Key Skills for Bookkeepers:
Attention to Detail: Bookkeepers must have a meticulous eye for detail to accurately record financial transactions, reconcile accounts, and maintain precise financial records.
Organizational Skills: Strong organizational skills are essential for bookkeepers to keep financial documents and records organized, ensuring easy retrieval and efficient workflow.
Proficiency in Accounting Software: Bookkeepers should be proficient in using accounting software to efficiently record and manage financial transactions. Familiarity with popular accounting software such as QuickBooks, Xero, or Sage is advantageous.
Numerical Aptitude: Bookkeepers need to have a solid understanding of numbers and be comfortable working with numerical data. Strong mathematical skills and the ability to perform accurate calculations are essential.
Time Management: Bookkeepers often handle multiple tasks and deadlines simultaneously. Effective time management skills enable them to prioritize tasks, meet deadlines, and ensure that financial records are up to date.
Key Skills for Accountants:
Analytical Skills: Accountants need strong analytical skills to interpret financial data, identify trends, and analyze financial performance. They should be able to extract meaningful insights from complex financial information.
Financial Reporting and Analysis: Accountants must be proficient in preparing and analyzing financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. They should have a deep understanding of accounting principles and financial reporting standards.
Tax Knowledge: Accountants should possess a comprehensive understanding of tax laws and regulations. They need to stay updated on tax codes, deductions, and credits to ensure compliance and optimize tax planning strategies.
Communication Skills: Accountants often interact with clients, colleagues, and stakeholders. Strong communication skills, both written and verbal, are necessary to explain financial concepts, present reports, and provide financial advice and recommendations.
Ethical Standards: Accountants must adhere to high ethical standards and maintain confidentiality and integrity in handling financial information. Professional ethics and a commitment to accuracy and transparency are essential qualities.
Both bookkeepers and accountants benefit from continuous learning and staying updated with changes in accounting practices, regulations, and technology.
FAQs
What qualifications are necessary to become a bookkeeper or an accountant?
To become a bookkeeper, one typically needs a high school diploma or equivalent qualification, although some employers may require additional certifications or formal training. Accountants, on the other hand, usually require a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field. Professional certifications such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA) can also enhance career prospects for both bookkeepers and accountants.
Can a bookkeeper also perform the tasks of an accountant?
While there may be some overlap in their responsibilities, bookkeepers and accountants have distinct roles. Bookkeepers focus on recording transactions and maintaining financial records, while accountants provide analysis, interpretation, and financial advice. The complexity and scope of the tasks performed by accountants typically require specialized knowledge and qualifications.
How often should a bookkeeper and an accountant collaborate?
The frequency of collaboration depends on the size and nature of the business. Generally, regular communication and collaboration are essential, especially during critical financial periods such as tax season or the end of the fiscal year. It is recommended to establish a regular schedule for meetings and information sharing to ensure accurate and timely financial reporting.
What are some common challenges faced by bookkeepers and accountants in their work?
Bookkeepers and accountants may encounter challenges such as managing large volumes of data, ensuring accuracy, dealing with complex transactions, and staying updated with changing financial regulations. Additionally, effective communication and coordination between the two roles can sometimes be a challenge, emphasizing the importance of establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication.
What are some key skills required for a successful bookkeeper-accountant partnership?
Key skills for a successful partnership include strong attention to detail, proficiency in financial software and tools, excellent organizational skills, effective communication, analytical thinking, and a solid understanding of accounting principles and financial regulations. Collaboration and the ability to work as a team are also vital for a successful bookkeeper-accountant partnership.

Which QuickBooks Function Would Be Most Useful?
Each QuickBooks function serves a specific purpose and provides tools and functionalities to perform related tasks efficiently. For example, the bookkeeping and accounting function allows users to track income and expenses, reconcile bank accounts, and generate financial statements. The invoicing and billing function enables users to create and send professional invoices to clients, track payments, and manage cash flow effectively.
Which QuickBooks Function Would Be Most Useful?
QuickBooks, developed by Intuit, is one of the leading accounting software solutions available in the market today. It offers a wide range of functions and features to streamline bookkeeping, invoicing, financial reporting, payroll management, inventory control, tax preparation, and more. With such versatility, determining the most useful QuickBooks function depends on various factors specific to each business. In this article, we will explore the different functions of QuickBooks and identify which one might be most beneficial for your needs.
Understanding QuickBooks Functions
Bookkeeping and Accounting: QuickBooks excels at automating bookkeeping and accounting tasks. It allows you to track income and expenses, manage bank and credit card transactions, reconcile accounts, and generate financial statements.
Invoicing and Billing: With QuickBooks, you can easily create and send professional invoices to your clients. It enables you to customize invoices, track payments, and send reminders for outstanding payments.
Financial Reporting: QuickBooks provides robust reporting capabilities, allowing you to generate various financial reports, such as profit and loss statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and tax reports. These reports offer valuable insights into your business’s financial health.
Payroll Management: For businesses with employees, QuickBooks offers payroll management features. It helps calculate and track employee salaries, deductions, and tax withholdings and generates pay stubs.
Inventory Management: QuickBooks allows you to efficiently track and manage your inventory. You can monitor stock levels, set reorder points, track sales, and generate reports to optimize inventory control.
Tax Preparation: QuickBooks simplifies tax preparation by organizing your financial data and generating accurate tax reports. It helps you stay compliant with tax regulations and reduces the hassle of tax filing.
Determining the Most Useful QuickBooks Function
The most useful QuickBooks function varies from business to business based on several factors. Consider the following aspects to determine which function will benefit you the most:
Business Type and Size: Different business types have unique requirements. A retail business may prioritize inventory management, while a service-based business may focus on invoicing and billing.
Industry-specific Requirements: Certain industries have specific compliance and reporting needs. Nonprofit organizations may require specialized features for fund accounting, while e-commerce businesses may require integration with online sales platforms.
Business Goals and Objectives: Identify your business goals and objectives to determine which QuickBooks function aligns with your long-term vision. If growth is a priority, payroll management and financial reporting features may be crucial.
Popular QuickBooks Functions for Different Needs
Small Business Owners: Small business owners can benefit from QuickBooks’ comprehensive suite of functions. The invoicing and billing feature helps them manage cash flow, while financial reporting assists in monitoring business performance.
Freelancers and Self-Employed Individuals: For freelancers and self-employed professionals, the invoicing and expense tracking functions are particularly useful. They can easily generate invoices, track payments, and categorize business expenses.
Nonprofit Organizations: QuickBooks offers features tailored for nonprofit organizations. It enables them to manage grants and donations, generate contribution reports, and track expenses based on funding sources.
Retail and E-commerce Businesses: Inventory management is crucial for retail and e-commerce businesses. QuickBooks helps them track stock levels, manage purchase orders, and analyze sales trends.
Service-Based Businesses: Service-based businesses can benefit from QuickBooks’ time-tracking and project management features. They can accurately bill clients based on hours worked and monitor project profitability.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a QuickBooks Function
When selecting the most useful QuickBooks function for your business, consider the following factors:
Ease of Use: Ensure that the chosen function is intuitive and user-friendly, allowing you to navigate through the software effortlessly.
Integration with Other Tools: Check if the function integrates with other tools you use, such as payment gateways, CRM systems, or e-commerce platforms.
Cost and Pricing Plans: Evaluate the pricing plans and determine if they align with your budget and anticipated growth.
Customer Support and Training: Consider the availability of customer support and training resources to help you maximize the benefits of the chosen function.
Advanced Features and Customization Options: Assess whether the function offers advanced features and customization options to cater to your specific business needs.
What is QuickBooks & how does it work?
QuickBooks is an accounting software developed by Intuit that helps businesses manage their financial transactions, track income, and expenses, generate financial reports, and streamline various accounting processes. It is widely used by small and medium-sized businesses to simplify their bookkeeping, invoicing, payroll, and tax-related tasks.
QuickBooks works by providing a user-friendly interface and a range of features to handle different aspects of financial management. Here’s a breakdown of how QuickBooks works:
Setting Up: After installing QuickBooks on your computer or accessing it through the cloud-based version, you’ll need to set up your company profile. This involves entering basic information about your business, such as company name, address, fiscal year, and industry type.
Chart of Accounts: QuickBooks utilizes a chart of accounts, which is a list of different categories to organize your financial transactions. It includes accounts for assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses. You can customize the chart of accounts based on your specific business needs.
Recording Transactions: QuickBooks allows you to record various types of financial transactions. You can enter income from sales, record expenses for purchases or services, track bank and credit card transactions, and reconcile accounts to ensure accuracy.
Invoicing and Billing: With QuickBooks, you can create professional invoices for your customers. You can customize the invoices with your branding, add line items, and calculate taxes. QuickBooks also track outstanding payments and sends reminders to clients for overdue invoices.
Financial Reporting: QuickBooks provides a range of pre-built reports that offer insights into your business’s financial performance. These reports include profit and loss statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and more. You can also customize reports to focus on specific metrics and time periods.
Payroll Management: QuickBooks offers payroll features to help manage employee salaries, deductions, and tax withholdings. It enables you to calculate payroll, generate pay stubs and facilitates direct deposit. It also helps with filing payroll taxes and provides tax forms.
Inventory Management: QuickBooks provides tools for tracking and managing inventory. You can create product listings, set reorder points, and monitor stock levels. QuickBooks also enables you to generate reports to analyze inventory turnover and identify trends.
Tax Preparation: QuickBooks simplifies tax preparation by organizing financial data and generating tax reports. It helps calculate tax liabilities and ensures compliance with tax regulations. It can generate reports required for filing income tax returns.
Integration and Add-Ons: QuickBooks integrates with various third-party applications, such as payment processors, CRM systems, e-commerce platforms, and time-tracking tools. This allows you to streamline workflows and automate data syncing between different systems.
Cloud-Based Access: QuickBooks offers cloud-based versions that allow you to access your financial data securely from any device with an internet connection. Cloud-based access enables collaboration with team members and accountants in real time.
QuickBooks aims to simplify financial management for businesses of all sizes by providing a user-friendly interface, automation features, and comprehensive tools for bookkeeping, invoicing, payroll, reporting, and more. It helps businesses save time, reduce errors, and gain better control over their finances.
FAQs
Can QuickBooks handle multiple currencies?
Yes, QuickBooks supports multiple currencies, allowing you to manage transactions and generate reports in different currencies.
Is QuickBooks suitable for large enterprises?
QuickBooks offers editions designed specifically for small and medium-sized businesses. While it can handle the needs of many large enterprises, some may require more advanced enterprise solutions.
How secure is the data in QuickBooks?
QuickBooks prioritizes data security and employs encryption protocols and secure servers to protect your information. Additionally, regular data backups ensure data integrity.
Can QuickBooks generate tax reports?
Yes, QuickBooks provides built-in tax reporting features that allow you to generate tax reports and simplify the tax filing process.
Does QuickBooks have mobile apps?
Yes, QuickBooks offers mobile apps for iOS and Android devices, enabling you to access and manage your business finances on the go.

What are the Best Bookkeeping Services for Small Businesses?

In today’s fast-paced business environment, small businesses face numerous challenges, and one crucial aspect they need to manage effectively is bookkeeping. Proper bookkeeping ensures accurate financial records, allows businesses to make informed decisions, and enables them to comply with regulatory requirements. However, many small business owners lack the expertise or time to handle bookkeeping themselves, which is where professional bookkeeping services come in. In this article, we will explore the best bookkeeping services available for small businesses and the factors to consider when choosing the right one.
Why is bookkeeping important for businesses?
Accurate bookkeeping is crucial for small businesses for several reasons. Firstly, it allows business owners to have a clear understanding of their financial position. By keeping track of income, expenses, and cash flow, they can identify areas of profitability or financial strain. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions regarding investments, cost-cutting measures, and future business strategies.
Secondly, proper bookkeeping is essential for fulfilling tax obligations. Small businesses need to accurately report their financial information to regulatory authorities, ensuring compliance with tax laws. Having organized and up-to-date financial records simplifies the tax filing process and reduces the risk of errors or penalties.
Lastly, maintaining comprehensive financial records enables small businesses to monitor their financial health and measure their progress over time. By analyzing financial statements and reports, they can identify trends, assess their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Bookkeeping Services
When selecting a bookkeeping service for your small business, there are several factors to consider. Each business has unique requirements, so it’s essential to find a service provider that aligns with your needs. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
Experience and Expertise: Look for bookkeeping services with a proven track record and experience working with small businesses. They should have in-depth knowledge of industry-specific accounting practices and familiarity with relevant software and tools.
Range of Services: Consider the scope of services offered by the bookkeeping service. Some services may only handle basic bookkeeping tasks, while others provide additional services such as payroll management, tax preparation, or financial consulting. Assess your business’s needs and choose a service that can accommodate them.
Scalability: Small businesses have the potential to grow rapidly, so it’s crucial to choose a bookkeeping service that can scale your business. Ensure they have the capacity to handle increased volumes of transactions and adapt to changing business requirements.
Data Security: The confidentiality and security of your financial information are paramount. Inquire about the bookkeeping service’s data security measures, such as encryption, secure servers, and backup systems. They should have robust protocols in place to protect your sensitive information.
Cost: Consider the cost of the bookkeeping service and evaluate it in relation to the value they provide. Compare pricing models, such as hourly rates or monthly packages, and determine which option aligns with your budget and business needs.
Top Bookkeeping Services for Small Businesses
Now that we understand the importance of bookkeeping and the factors to consider, let’s explore some of the top bookkeeping services available for small businesses. These services have gained recognition for their expertise, reliability, and user-friendly approach.
Service 1: X Bookkeeping
X Bookkeeping is a leading provider of bookkeeping services specifically tailored for small businesses. They offer a range of comprehensive solutions that cater to the unique financial needs of small businesses. Here are some key features and benefits of their service:
Feature 1: ABC
X Bookkeeping provides thorough financial record-keeping, ensuring all transactions are accurately recorded and categorized. They use advanced accounting software to streamline the bookkeeping process and maintain real-time financial data.
Feature 2:DEF
With X Bookkeeping, small businesses can benefit from detailed financial reports and statements. These reports provide valuable insights into their financial performance, allowing business owners to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
Benefit 1:GHI
By outsourcing bookkeeping to X Bookkeeping, small businesses can save time and focus on their core operations. The dedicated team at X Bookkeeping handles all bookkeeping tasks, including accounts payable and receivable, bank reconciliation, and financial analysis.
Benefit 2:JKL
X Bookkeeping offers scalable solutions, accommodating businesses of all sizes. As your business grows, it can seamlessly adapt its services to meet your evolving needs, ensuring continuity and accuracy in your financial management.
Service 2:Y Bookkeeping
Y Bookkeeping is a trusted bookkeeping service known for its personalized approach and commitment to client satisfaction. They offer a range of services designed to simplify bookkeeping processes for small businesses. Let’s explore some of their features and benefits:
Feature 1:MNO
Y Bookkeeping provides dedicated account managers who work closely with each client, understanding their unique needs and tailoring their services accordingly. This personalized approach ensures that the bookkeeping service aligns with the specific requirements of the business.
Feature 2: PQR
With Y Bookkeeping, small businesses can benefit from efficient payroll management services. They handle all aspects of payroll, including calculating wages, managing tax withholdings, and generating pay stubs. This alleviates the burden of payroll tasks and ensures compliance with payroll regulations.
Benefit 1: STU
Y Bookkeeping offers advanced reporting capabilities, providing businesses with clear and concise financial reports. These reports help business owners gain a comprehensive understanding of their financial performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
Benefit 2: VWX
By partnering with Y Bookkeeping, small businesses can access expert financial advice and guidance. Their team of experienced professionals can provide insights on optimizing cash flow, improving profitability, and implementing effective financial strategies.
Service 3: Z Bookkeeping
Z Bookkeeping is a well-established bookkeeping service trusted by small businesses for its efficiency and accuracy. They offer a range of services designed to simplify bookkeeping processes and ensure compliance. Let’s explore some of their features and benefits:
Feature 1:YZ
Z Bookkeeping uses cloud-based accounting software that enables real-time collaboration and access to financial data. This allows small businesses to stay up to date with their financial information and make informed decisions based on current data.
Feature 2: AB
With Z Bookkeeping, businesses can rely on accurate and timely financial reporting. They provide regular financial statements, balance sheets, and income statements, enabling small business owners to track their financial performance and identify areas for improvement.
Benefit 1: CD
Z Bookkeeping offers dedicated support from experienced bookkeepers who understand the unique needs of small businesses. They provide personalized assistance, answer queries promptly, and ensure that businesses receive the necessary support to maintain accurate financial records.
Benefit 2: EF
By outsourcing bookkeeping to Z Bookkeeping, small businesses can reduce the risk of errors and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Z Bookkeeping’s expertise in bookkeeping best practices and adherence to accounting standards contribute to the accuracy and reliability of financial records.
Factors to Consider Before Making a Decision

When choosing the best bookkeeping service for your small business, it’s important to consider the following factors:
Business Requirements: Assess your specific bookkeeping needs and ensure the service provider can cater to them effectively. Consider factors such as the volume of transactions, industry-specific requirements, and any additional services you may require, such as tax preparation or financial consulting.
Budget: Evaluate the cost of the bookkeeping services and ensure they align with your budget. Consider the pricing models and compare them based on the value provided by each service. Remember to consider the long-term benefits of accurate bookkeeping in relation to the cost.
Client Reviews and Testimonials: Research the reputation of the bookkeeping service by reading client reviews and testimonials. Pay attention to feedback regarding reliability, accuracy, responsiveness, and overall customer satisfaction. A service with positive reviews is likely to provide a higher level of service.
Communication and Support: Consider the level of communication and support offered by the bookkeeping service. Determine how accessible they are, whether they assign a dedicated account manager, and how responsive they are to queries or concerns. Effective communication is crucial for a successful partnership.
Data Security: Ensure the bookkeeping service prioritizes data security. Inquire about their data encryption methods, secure storage protocols, and backup systems. They should have robust security measures in place to protect your financial information from unauthorized access or breaches.
Why do we make decisions?
We make decisions as a way to navigate through life and choose the course of action that aligns with our goals, desires, and values. Decision-making is an essential cognitive process that helps us select from available options and determine the best course of action in a given situation.
There are several reasons why we make decisions:
Problem-solving: We make decisions to solve problems or address challenges that arise in our personal or professional lives. By analyzing the situation, considering potential solutions, and selecting the most appropriate one, we aim to overcome obstacles and achieve desired outcomes.
Goal attainment: Decisions help us move closer to our goals. By evaluating different options and choosing the one that aligns with our objectives, we can take proactive steps toward achieving what we desire.
Adaptation: Decision-making enables us to adapt to changing circumstances. Life is filled with uncertainties and unexpected events, and making decisions allows us to respond effectively to new information or situations as they arise.
Evaluation of alternatives: We make decisions to compare and evaluate different alternatives. By weighing the pros and cons of each option, we can make informed choices that maximize benefits or minimize potential risks.
Personal satisfaction: Decision-making empowers us to make choices that reflect our personal preferences, values, and aspirations. By exercising autonomy and making decisions that resonate with our individuality, we can experience a sense of fulfillment and satisfaction.
Learning and growth: Decision-making provides opportunities for learning and personal growth. Even if a decision does not yield the desired outcome, we can learn from the experience, gain new insights, and refine our decision-making skills for future situations.
What factors limit the ability to make good decisions?
Several factors can limit the ability to make good decisions. Here are some common ones:
Lack of information: Insufficient or incomplete information can hinder the decision-making process. Without a comprehensive understanding of the situation or available options, it becomes challenging to make well-informed decisions.
Cognitive biases: Human beings are prone to various cognitive biases, which are systematic errors in thinking that can cloud judgment and decision-making. Biases like confirmation bias (favoring information that confirms pre-existing beliefs) or anchoring bias (relying too heavily on initial information) can lead to suboptimal decisions.
Emotional influence: Emotions can significantly impact decision-making. Strong emotions, such as fear, anger, or excitement, can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive or irrational decisions. Emotional attachment to certain outcomes can also hinder the objective evaluation of alternatives.
Time constraints: Making rushed decisions due to time constraints can limit the ability to consider all relevant factors and weigh options adequately. When decisions are made under pressure, there is a higher likelihood of overlooking important information or making hasty choices.
Limited resources: The availability of resources, such as time, money, or expertise, can affect decision-making. When resources are scarce or restricted, individuals may have to make compromises or suboptimal choices due to practical limitations.
Social and cultural influences: Social pressure, norms, and cultural expectations can influence decision-making. Conforming to societal expectations or seeking approval from others may lead to decisions that do not align with personal values or goals.
Overconfidence: Excessive confidence in one’s own judgment and abilities can hinder good decision-making. Overconfidence can lead to underestimating risks, disregarding alternative viewpoints, or failing to seek additional information.
Lack of self-awareness: A lack of self-awareness regarding personal biases, limitations, or blind spots can impede good decision-making. Being unaware of one’s own cognitive or emotional tendencies can prevent individuals from taking steps to mitigate their influence on decisions.
Why should you choose our bookkeeping services?
You should choose our bookkeeping services because we offer accurate, reliable, and efficient bookkeeping solutions tailored to your specific needs, saving you time and resources while ensuring compliance and data security.
What Are Bookkeepers?

What Are Bookkeepers?
Bookkeeping plays a crucial role in any business’s financial management. It involves recording, organizing, and maintaining financial transactions and records accurately. Bookkeepers are the professionals responsible for performing these tasks. They are essential in ensuring the financial stability and success of a business.
Definition
Bookkeepers are professionals who specialize in recording and managing financial transactions. They are responsible for tracking expenses, sales, and payments, organizing receipts and invoices, and ensuring that financial records are accurate and up to date. Bookkeepers play a crucial role in providing businesses with a clear financial picture, enabling informed decision-making, and ensuring compliance with accounting standards.
What skills do you need to become a bookkeeper?
To become a bookkeeper, several skills are essential for success in the role. These skills include:
Attention to Detail: Bookkeepers must have a keen eye for detail to accurately record and track financial transactions. Even small errors can have significant consequences, so meticulousness is crucial.
Organizational Skills: Effective organization is key to maintaining well-structured financial records. Bookkeepers need to categorize and store documents, receipts, and invoices efficiently to ensure easy retrieval and reference.
Mathematical Aptitude: A solid understanding of basic mathematics is vital for bookkeepers. They should be comfortable with numbers, calculations, and performing accurate computations.
Analytical Thinking: Bookkeepers need to analyze financial data and identify patterns, trends, and discrepancies. They must possess the ability to interpret financial information and provide insights for decision-making.
Problem-Solving Abilities: Bookkeepers often encounter discrepancies or inconsistencies in financial records. They must be skilled problem solvers who can investigate issues, identify root causes, and implement corrective measures.
Computer Proficiency: In today’s digital era, bookkeepers must be proficient in using bookkeeping software and accounting systems. Familiarity with tools like QuickBooks, Excel, or other accounting software enhances efficiency and accuracy in managing financial data.
Communication Skills: Bookkeepers may need to interact with colleagues, clients, or external stakeholders to clarify financial matters or resolve discrepancies. Strong communication skills, both written and verbal, are essential for effective collaboration and understanding.
Ethical Conduct: Bookkeepers often have access to sensitive financial information. They must adhere to ethical standards and maintain confidentiality and integrity in handling financial records and data.
Time Management: Bookkeepers deal with multiple tasks and deadlines simultaneously. Effective time management skills enable them to prioritize tasks, meet deadlines, and ensure that financial records are updated and accurate.
Continuous Learning: The field of bookkeeping is constantly evolving, with updates in regulations and advancements in technology. Bookkeepers should have a mindset of continuous learning, staying updated on industry trends, changes in accounting practices, and relevant regulations.
By developing and honing these skills, individuals can enhance their capabilities as bookkeepers and contribute significantly to the financial management of businesses.
Education requirement for bookkeepers
While a formal degree is not always mandatory, aspiring bookkeepers benefit from acquiring relevant education and certifications. Many individuals pursue associate degrees or certification programs in accounting, bookkeeping, or finance to gain foundational knowledge in financial management, accounting principles, and bookkeeping practices. These educational pathways provide a solid foundation for a career in bookkeeping.
Bookkeeper job duties and responsibilities
Bookkeepers undertake various tasks and responsibilities to support a business’s financial operations. They record financial transactions, reconcile bank statements, prepare financial statements, and generate reports. Bookkeepers may also assist in payroll processing, manage accounts payable and receivable, and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Their attention to detail and accuracy are vital to maintaining clean and transparent financial records.
Bookkeeping Systems
With technological advancements, bookkeeping has transitioned from manual processes to computerized systems. Bookkeepers utilize bookkeeping software to streamline their tasks, automate data entry, and generate comprehensive reports. Popular bookkeeping systems include QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks. Familiarity with these systems is increasingly important for bookkeepers to stay competitive in the field.
What is accuracy & precision?
In the context of bookkeeping, accuracy, and precision are two important concepts that relate to the quality and reliability of financial records.
Accuracy refers to the degree of correctness or exactness in recording financial transactions and maintaining financial records. An accurate bookkeeper ensures that the information entered into the books reflects the true nature of the transactions. This involves diligently recording the appropriate amounts, dates, and descriptions of financial activities. Accuracy is crucial to produce reliable financial statements, making informed business decisions, and complying with accounting standards and regulations.
For example, when recording a sale, an accurate bookkeeper would ensure that the sale amount, customer details, and related information are correctly documented without errors or omissions. Any mistakes or inaccuracies could lead to incorrect financial statements, misinterpretation of financial performance, and potential legal or tax compliance issues.
Precision refers to the level of detail and specificity in recording financial transactions. A precise bookkeeper ensures that transactions are categorized and recorded with the appropriate level of granularity. This involves capturing specific details, such as differentiating between various expense categories or accurately allocating costs to specific projects or departments.
Precision is particularly important when generating reports or conducting financial analysis. It allows stakeholders to obtain a clear understanding of where money is being spent, identify cost-saving opportunities, and assess the financial performance of different aspects of the business.
For instance, a precise bookkeeper would record and categorize expenses into detailed categories like office supplies, utilities, travel expenses, and marketing costs. This level of precision provides a comprehensive view of where funds are allocated, enabling more accurate budgeting and financial decision-making.
Both accuracy and precision are critical in bookkeeping because they ensure the integrity and reliability of financial records. By maintaining accurate and precise financial records, businesses can have a solid foundation for financial management, tax compliance, reporting, and strategic planning.
What is a bookkeeper in accounting?
The primary role of a bookkeeper is to record financial transactions, including sales, purchases, expenses, and payments, in the appropriate accounting system or books. They ensure that all transactions are accurately documented, with the correct dates, amounts, and descriptions. This meticulous recording helps track the flow of money and provides a clear audit trail for financial activities.
Bookkeepers are responsible for tasks such as reconciling bank statements, ensuring that the recorded transactions match the bank’s records, and resolving any discrepancies. They also maintain accounts payable and accounts receivable, keeping track of money owed to the business and payments to be collected. Another crucial aspect of a bookkeeper’s role is generating financial reports. They compile information from the financial records and prepare reports such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
These reports provide a snapshot of the organization’s financial health, allowing management, stakeholders, and regulatory authorities to assess its performance and make informed decisions. Bookkeepers may also assist with payroll processing, ensuring that employee salaries, benefits, and tax withholdings are accurately calculated and disbursed. They may help with tax preparations by organizing financial data and providing the necessary documentation to accountants or tax professionals.
With the advent of digital accounting systems, bookkeepers often utilize specialized software or accounting platforms to streamline their tasks. These tools help automate data entry, generate reports, and enhance accuracy and efficiency in financial record-keeping.
What is bookkeeping and why is it important?
Bookkeeping is the process of recording, organizing, and maintaining financial transactions and records for a business or organization. It involves accurately tracking income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity.
Bookkeeping is crucial for several reasons:
Financial Management: Bookkeeping provides a clear and accurate picture of a company’s financial health. It enables business owners and managers to monitor cash flow, track income, and expenses, and make informed financial decisions. By having up-to-date financial records, businesses can identify trends, evaluate profitability, and plan for the future.
Compliance: Proper bookkeeping ensures compliance with accounting standards, tax regulations, and legal requirements. It enables businesses to fulfill their obligations, such as filing accurate tax returns, preparing financial statements, and providing financial information to stakeholders, investors, or regulatory authorities.
Business Analysis: Accurate financial records facilitate effective business analysis. Bookkeeping provides data for generating financial statements, such as balance sheets and income statements, which offer insights into a company’s financial performance, liquidity, and profitability. This information helps identify areas of improvement, assess the viability of projects, and attract potential investors.
Decision-making: Bookkeeping supports informed decision-making by providing financial data and insights. It allows businesses to assess the financial impact of potential investments, evaluate costs and benefits, and make strategic choices. Reliable financial records enable owners and managers to evaluate risks, allocate resources efficiently, and plan for growth.
Tax Preparation: Proper bookkeeping simplifies tax preparation and ensures accurate tax filings. By maintaining organized financial records, businesses can easily track deductible expenses, verify income, and meet reporting deadlines. This helps minimize the risk of errors, penalties, and audits from tax authorities.
Financial Transparency: Bookkeeping promotes transparency within a business. It enables stakeholders, including shareholders, investors, lenders, and employees, to access reliable financial information. Transparent financial records inspire confidence, build trust, and foster good relationships with stakeholders.
What are the different types of bookkeeping?
There are several types of bookkeeping methods that businesses can use based on their needs and preferences. The main types of bookkeeping systems include:
Single-Entry Bookkeeping: This method is relatively simple and suitable for small businesses or individuals with uncomplicated financial transactions. It involves recording transactions in a single column, typically focusing on cash inflows and outflows. While single-entry bookkeeping is straightforward, it may not provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial position.
Double-Entry Bookkeeping: Double-entry bookkeeping is the most widely used method and is considered more accurate and comprehensive. It follows the principle that every financial transaction has two equal and opposite effects. Each transaction is recorded in at least two accounts, with a debit and credit entry. This method provides a complete picture of the company’s financial situation, including assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses.
Manual Bookkeeping: Manual bookkeeping involves recording transactions by hand using journals, ledgers, and spreadsheets. It requires diligent record-keeping and calculations. While manual bookkeeping can be time-consuming and prone to human error, it can be a cost-effective option for small businesses with a limited number of transactions.
Computerized Bookkeeping: With the advent of accounting software, computerized bookkeeping has become the preferred method for many businesses. It involves using specialized software applications, such as QuickBooks, Xero, or Sage, to record and manage financial transactions. Computerized bookkeeping automates tasks, provides real-time data, and offers features like generating financial reports, reconciling accounts, and streamlining processes.
Cash Basis Accounting: Cash basis accounting records transactions based on the actual cash inflows and outflows. Income is recognized when cash is received, and expenses are recognized when cash is paid. This method is straightforward but may not provide an accurate representation of a company’s financial position and performance over time.
Accrual Basis Accounting: Accrual basis accounting records transactions when they occur, regardless of when cash is exchanged. It recognizes revenue when it is earned and expenses when they are incurred, even if the cash is received or paid at a later date. Accrual basis accounting provides a more accurate picture of a business’s financial position and performance, especially for larger companies with complex transactions.
The choice of bookkeeping method depends on factors such as the size of the business, the complexity of transactions, regulatory requirements, and the availability of resources. It’s important for businesses to select a bookkeeping system that suits their needs, ensures accurate financial records, and facilitates effective financial management.
How do I become a bookkeeper?
To become a bookkeeper, you can follow these general steps:
Education and Training: While a formal education is not always required, acquiring a solid foundation in accounting and bookkeeping is beneficial. Consider pursuing a degree or certification program in accounting, bookkeeping, or a related field. This education will provide you with the necessary knowledge and skills to perform bookkeeping tasks accurately.
Gain Experience: Practical experience is essential to become a proficient bookkeeper. Look for opportunities to gain hands-on experience by working as an intern, volunteering, or seeking entry-level positions in bookkeeping or accounting departments. This will help you understand real-world scenarios and sharpen your skills.
Develop Bookkeeping Skills: Enhance your bookkeeping skills by familiarizing yourself with industry-standard bookkeeping practices, software applications (such as QuickBooks or Excel), and accounting principles. Consider taking additional courses or workshops to stay updated on the latest developments in bookkeeping.
Obtain Certification: Although certification is not always mandatory, it can boost your credibility and increase your job prospects. Consider obtaining certifications such as Certified Bookkeeper (CB), Certified Public Bookkeeper (CPB), or other industry-recognized certifications. These certifications demonstrate your proficiency and commitment to professional development.
Stay Updated: The field of bookkeeping is constantly evolving, with updates in regulations, technologies, and best practices. Stay updated on changes in accounting standards, tax laws, and software advancements. Engage in continuous learning through professional development opportunities, workshops, seminars, and networking with other bookkeeping professionals.
Build a Professional Network: Networking is crucial for career growth. Join professional organizations, attend industry events, and connect with other professionals in the field. Building a network can lead to job opportunities, mentorship, and stay informed about industry trends.
Consider Specializing: Bookkeeping offers opportunities for specialization in specific industries or niches. Consider specializing in areas such as payroll, taxes, or industry-specific bookkeeping. Specialization can differentiate you from others and open doors to specialized job roles or clients.
Gain Clients or Employment: Once you feel confident in your bookkeeping skills, start seeking employment opportunities or clients. Update your resume, create an online presence (such as a website or LinkedIn profile), and actively apply for positions or market your services as a freelance bookkeeper.

How Much Tax Does a Small Business Pay?
One of the crucial aspects that small business owners need to understand is the amount of tax they are liable to pay. Taxes play a significant role in the financial operations of any business, and being aware of the tax obligations is essential for proper planning and compliance. In this article, we will delve into the topic of how much tax a small business pays, exploring the factors that influence tax liability and providing insights into strategies to manage and optimize tax payments.
Understanding Small Business Taxes
Small businesses are subject to various types of taxes, and the amount they pay depends on several factors. The structure of the business, such as whether it is a sole proprietorship, partnership, or company, can impact the tax liability. Additionally, the business’s revenue, expenses, and deductions also play a significant role in determining the amount of tax owed.
Types of Taxes for Small Businesses
Small businesses are typically subject to income tax, which is based on the net profit generated by the business. The income tax rate varies depending on the business structure and the total income earned. In addition to income tax, small businesses may also be responsible for paying self-employment tax, which covers Social Security and Medicare taxes for self-employed individuals.
Apart from these federal taxes, small businesses may have state and local tax obligations as well. State taxes vary based on the location and can include sales tax, payroll tax, and franchise tax, among others. Local taxes may include property taxes or municipal taxes, depending on the jurisdiction.
Factors Affecting Tax Liability
Several factors influence the tax liability of a small business. The first is the business’s revenue or income. Generally, higher revenue translates to higher tax liability. However, business expenses and deductions can offset the taxable income, reducing the overall tax burden. It is crucial for small business owners to maintain accurate financial records and keep track of eligible deductions to optimize their tax payments.
Additionally, the business structure plays a role in determining tax liability. Sole proprietors and partnerships may report business income and expenses on their personal tax returns, while companies are subject to separate corporate tax rates. Understanding the tax implications of different business structures is crucial for effective tax planning.
Tax Planning and Optimization Strategies
Small business owners have various strategies at their disposal to manage and optimize their tax payments. Here are some key approaches to consider:
Record Keeping and Documentation: Maintaining accurate and detailed financial records is essential for claiming deductions and ensuring compliance. Effective record-keeping helps small business owners maximize their eligible deductions and minimize the risk of errors during tax filings.
Claiming Eligible Deductions: Small businesses can take advantage of various deductions to reduce their taxable income. Common deductions include business-related expenses, such as office supplies, travel expenses, marketing costs, and professional fees. It is essential to consult with a tax professional to identify all eligible deductions and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Utilizing Tax Credits: Tax credits are a powerful tool for reducing tax liabilities. Small businesses should explore available tax credits, such as research and development credits or energy efficiency credits, to maximize their savings.
Proactive Tax Planning: Small business owners should engage in proactive tax planning throughout the year, rather than waiting until tax season. By monitoring income and expenses, forecasting tax liabilities, and implementing tax-saving strategies, businesses can better manage their tax obligations.
Seeking Professional Advice: Taxes can be complex, and seeking the guidance of a qualified tax professional or accountant is crucial for small business owners. Professionals can provide expert advice, help identify deductions and credits, and ensure compliance with tax laws.
How Do Small Businesses Pay Taxes?

Small businesses have various methods to pay taxes based on their business structure and revenue. Sole proprietors and partnerships typically report their business income and expenses on their personal tax returns using a Schedule C form. They pay taxes on their net profit, which is the income minus deductible expenses. Limited liability companies (LLCs) can choose to be taxed as either a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation. If an LLC elects to be treated as a corporation, it must file a separate corporate tax return and pay taxes on its profits. Corporations, whether they are C corporations or S corporations, must file their own tax returns. C corporations pay taxes on their profits at the corporate level, while S corporations pass their income and losses through to shareholders, who report them on their individual tax returns. Regardless of the business structure, small businesses may be required to make estimated tax payments throughout the year to avoid penalties for underpayment. It is advisable for small business owners to consult with a tax professional or accountant to ensure compliance with tax laws and to optimize their tax strategy.
How Do Small Business Owners Pay Taxes?
Small business owners have several methods to pay taxes depending on their business structure and income. If the business is a sole proprietorship, the owner reports the business income and expenses on their personal tax return using a Schedule C form. They pay taxes on the net profit, which is the income minus deductible expenses. Partnerships follow a similar process, with each partner reporting their share of the business’s income and expenses on their personal tax return. Limited liability companies (LLCs) can choose to be taxed as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation. If treated as a corporation, the owner must file a separate corporate tax return. Corporations, such as C corporations or S corporations, also file their own tax returns. C corporations pay taxes on profits at the corporate level, while S corporations pass income and losses through to shareholders, who report them on their individual tax returns. Small business owners should consult with a tax professional or accountant to ensure compliance with tax regulations and develop an effective tax strategy that minimizes their tax liability.
What Other Taxes Does a Business Pay?
businesses may be subject to various other taxes depending on their location and business activities. One common tax is the employment tax, which includes Social Security and Medicare taxes. Businesses are responsible for withholding these taxes from employees’ wages and also contributing a matching amount. Sales tax is another important tax for businesses that sell goods or services. It is typically collected from customers at the point of sale and remitted to the appropriate tax authority. Property tax is levied on the value of a business’s real estate and personal property. Some jurisdictions also impose excise taxes on specific goods or services, such as fuel, alcohol, or tobacco. Additionally, businesses may be required to pay franchise taxes, which are typically based on their legal structure or income. It’s crucial for business owners to be aware of their tax obligations and consult with tax professionals to ensure compliance and accurate reporting of these various taxes.
Conclusion
Understanding the amount of tax a small business pays is essential for effective financial planning and compliance. By grasping the factors that influence tax liability.

How do you prepare an income statement?
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement or statement of earnings, is a financial document that provides a summary of a company’s revenue, expenses, and net income over a specific period. It is an essential tool for businesses to assess their financial performance and determine their profitability.
What Is An Income Statement?
An income statement is a financial statement that presents the revenues, expenses, gains, and losses incurred by a company during a specific period, typically a fiscal quarter or year. It provides valuable insights into a company’s ability to generate profit by comparing its revenues with the expenses incurred to generate those revenues.
What is the purpose of income?
The primary purpose of an income statement is to determine the profitability of a company. It shows whether a business has made a profit or incurred a loss during a given period. By analyzing the income statement, investors, shareholders, and other stakeholders can evaluate a company’s financial performance and make informed decisions.
What are the components of an income statement?
An income statement consists of several components that reveal different aspects of a company’s financial performance. Let’s explore the key components in detail.
Revenue
Revenue, also referred to as sales or turnover, represents the total amount of money earned from the sale of goods or services. It is the starting point of an income statement and reflects the top line of a company’s financial performance.
Cost of Goods Sold
The cost of goods sold (COGS) represents the direct costs associated with producing or delivering the goods or services sold by the company. It includes the cost of raw materials, labor, and other direct expenses directly related to the production process.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the revenue. It indicates the profitability of a company’s core operations and the efficiency of its production or service delivery.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses include all the costs incurred in running a company’s day-to-day operations. These expenses can include salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, and other administrative costs.
Operating Income
Operating income, also known as operating profit or operating earnings, is obtained by subtracting the operating expenses from the gross profit. It represents the profitability of a company’s core business operations.
Other Income and Expenses
Other income and expenses include non-operating items that are not directly related to a company’s core operations. These can include
interest income, interest expenses, gains or losses from the sale of assets, and other non-operating revenues or expenses.
Net Income
Net income, also called net profit or net earnings, is the final figure on the income statement. It represents the amount of profit or loss generated by a company after accounting for all revenues, expenses, gains, and losses. It is often used as a measure of a company’s overall financial performance.
How do you format an income statement?
An income statement typically follows a standardized format, presenting the components in a specific order. The top section displays the revenue, cost of goods sold, and gross profit. The subsequent section includes the operating expenses, resulting in the operating income. Finally, the other income and expenses are listed, leading to the calculation of net income.
To enhance readability, income statements often use subtotals and bolded headings for each section. The financial amounts are presented in columns, with the most recent period displayed first and the comparative periods following.
Why income statement is Important?
The income statement plays a vital role in assessing the financial health of a company. Here are some key reasons why it is important:
Evaluating Profitability:
The income statement helps determine whether a company is profitable or not. By comparing revenues and expenses, stakeholders can gauge the effectiveness of the company’s operations.
Identifying Trends:
By analyzing income statements over multiple periods, stakeholders can identify trends in revenue, expenses, and profitability. This information helps in making strategic decisions and planning for the future.
Assessing Financial Performance:
Investors and creditors rely on income statements to assess a company’s financial performance and make investment or lending decisions. It provides insights into the company’s ability to generate profits and manage expenses.
Comparing Competitors:
Income statements allow for easy comparison between companies within the same industry. Investors can analyze and compare the financial performance of different companies to identify industry leaders and potential investment opportunities.
How do you analyze an income statement?
Analyzing an income statement involves calculating various financial ratios and metrics to gain deeper insights into a company’s performance. Here are some commonly used measures:
Gross Profit Margin
The gross profit margin is calculated by dividing the gross profit by the revenue and multiplying by 100. It indicates the percentage of revenue that remains after deducting the cost of goods sold. A higher gross profit margin generally signifies better profitability.
Operating Margin
The operating margin is obtained by dividing the operating income by the revenue and multiplying by 100. It measures the percentage of revenue that is left after deducting both the cost of goods sold and operating expenses. It helps assess the efficiency of a company’s operations.
Net Profit Margin
The net profit margin is calculated by dividing the net income by the revenue and multiplying by 100. It represents the percentage of revenue that remains as net profit after considering all expenses and taxes. A higher net profit margin indicates better overall profitability.
Earnings per Share (EPS)
Earnings per Share (EPS) is obtained by dividing the net income by the number of outstanding shares of a company. It is a crucial metric for investors as it shows the portion of a company’s profit allocated to each share. A higher EPS indicates better profitability for shareholders.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on Investment (ROI) measures the efficiency of an investment by comparing the net profit generated to the cost of the investment. It is calculated by dividing the net income by the investment cost and multiplying by 100. A higher ROI indicates a better return on the investment.
What Are the Limitations of Income Statement?
While an income statement provides valuable information about a company’s financial performance, it has certain limitations. Some limitations to consider include:
Subjectivity: The income statement relies on accounting judgments and estimates
, which can introduce subjectivity and potential biases.
Omission of Non-Financial Factors: The income statement focuses solely on financial aspects and does not capture non-financial factors such as customer satisfaction or employee morale.
Limited Timeframe: The income statement reflects the financial performance over a specific period, which may not provide a complete picture of long-term trends or cyclical variations.
Non-Inclusion of Non-Cash Items: Certain transactions and events, such as depreciation or changes in market value, are not reflected in the income statement. This can impact the accuracy of profitability measures.
What are the differences between a balance sheet and an income statement?
While both income statements and balance sheets are essential financial statements, they serve different purposes. The income statement focuses on the company’s financial performance over a specific period, while the balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s financial position at a particular point in time.
The income statement showcases revenues, expenses, and net income, while the balance sheet presents assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. The income statement helps assess profitability, while the balance sheet highlights the company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial health.
Examples of Income Statements
To provide a practical understanding, let’s consider a fictional company, XYZ Corporation, and examine a simplified income statement:

XYZ Corporation
Income Statement
For the Year Ended June 30, 2022
Revenue: $ 586,328,957
Cost of Goods Sold: $ 528,505,416
Gross Profit: $ 57,823,541
Operating Expenses: $ 46,138,825
Operating Income: $250,000
Other Income: $ 24,600,296
Interest Expense: $ 44,738
Net Income: $ 25,730,595
This example demonstrates how the various components of an income statement are presented, ultimately leading to the calculation of net income.
Conclusion
In summary, an income statement is a critical financial statement that provides insights into a company’s revenue, expenses, and profitability. It helps stakeholders evaluate a company’s financial performance, make informed decisions, and compare it to competitors. By understanding the components and analyzing the metrics derived from the income statement, investors and other stakeholders can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial health.

What Is a Balance Sheet in Accounting?
A balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It presents a summary of what a company owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the shareholders’ stake in the company (equity). Understanding a balance sheet is crucial for assessing a company’s financial health, making investment decisions, and managing finances effectively.
Components of a Balance Sheet
A balance sheet consists of three main components: assets, liabilities, and equity. These components provide a detailed overview of a company’s financial position and aid in understanding its financial structure.
Assets
Assets represent what a company owns and controls. They can be categorized into current assets and fixed assets.
Current Assets
Current assets are short-term assets that are expected to be converted into cash within one year or the operating cycle of a business. Examples of current assets include:
- Cash and Cash Equivalents:
This includes cash on hand, checking accounts, and highly liquid investments.
- Accounts Receivable:
Amounts owed to the company by customers who have purchased goods or services on credit.
- Inventory:
Goods held by the company for sale or used in the production process.
Fixed Assets
Fixed assets, also known as non-current assets or property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), are long-term assets with a useful life of more than one year. They are not intended for sale but are essential for the company’s operations. Examples of fixed assets include:
1. Property, Plant, and Equipment:
This includes land, buildings, machinery, vehicles, and other tangible assets.
2. Intangible Assets:
Non-physical assets such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, and goodwill.
Liabilities
Liabilities represent what a company owes to external parties. Similar to assets, liabilities can be divided into current liabilities and long-term liabilities
Current Liabilities
Current liabilities are obligations that are expected to be settled within one year or the operating cycle of a business. They often require the use of current assets to fulfill these obligations. Examples of current liabilities include:
- Accounts Payable:
Amounts owed by the company to suppliers and vendors for goods or services received.
- Short-Term Loans:
Loans that are due within one year.
Long-term Liabilities
Long-term liabilities are obligations that extend beyond one year. They typically include loans, bonds, and other forms of long-term debt. Examples of long-term liabilities include:
1. Bonds Payable: Debt securities issued by the company to raise capital from investors.
2. Mortgages: Long-term loans used to finance the purchase of property or other fixed assets.
Equity
Equity represents the shareholders’ residual interest in the company after deducting liabilities from assets. It consists of two main components: common stock and retained earnings.
Common Stock
Common stock represents the initial capital invested by shareholders in exchange for ownership rights and voting privileges in the company.
Retained Earnings
Retained earnings reflect the accumulated profits or losses retained within the company since its inception. They result from the company reinvesting its profits or incurring net losses over time.
Understanding Assets
Assets are a critical component of a balance sheet and provide insights into a company’s ability to generate future cash flows. By analyzing the different types of assets, investors and financial professionals can gain a better understanding of a company’s operations and potential for growth.
Current Assets Explained
Current assets are highly liquid assets that can be readily converted into cash within a short period, usually within one year. They represent a company’s short-term resources that are necessary for day-to-day operations and fulfilling immediate financial obligations.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid current assets. They include physical currency, funds in checking and savings accounts, and short-term investments that can be quickly converted into cash. These assets provide the company with immediate access to funds, allowing it to meet short-term financial needs.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable are amounts owed to the company by customers who have purchased goods or services on credit. They represent the company’s outstanding invoices that are expected to be collected in the near future. Managing accounts receivable effectively is crucial for maintaining a healthy cash flow and minimizing the risk of bad debts.
Inventory
Inventory consists of goods held by the company for sale or used in the production process. It includes raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. Proper inventory management is essential to ensure efficient operations, prevent stockouts, and control costs.
Fixed Assets Explained
Fixed assets are long-term assets that are necessary for a company’s operations but are not intended for sale. They provide value to the company over an extended period and often require significant investments. Analyzing fixed assets helps assess a company’s growth potential and its ability to generate future cash flows.
Property, Plant, and Equipment
Property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) are tangible assets used in the production, manufacturing, or service delivery process. They include land, buildings, machinery, vehicles, and other physical assets. These assets are critical for a company’s operations and contribute to its ability to generate revenue.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets are non-physical assets that lack physical substance but hold value for a company. They include intellectual property rights such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, and brand recognition. Intangible assets are often crucial for a company’s competitive advantage and long-term success.
Explaining Liabilities
Liabilities on a balance sheet represent the company’s obligations to external parties. They reflect the amounts owed by the company and the timeline for repayment Understanding liabilities helps assess a company’s financial obligations and its ability to meet them.
Current Liabilities Defined
Current liabilities are obligations that are expected to be settled within one year or the operating cycle of the business. They often arise from normal business operations and require the use of current assets to fulfill these obligations.
Accounts Payable
Accounts payable represent the amounts owed by the company to suppliers, vendors, or service providers for goods or services received. It reflects the company’s short-term debts and is a crucial component of managing working capital. Timely payment of accounts payable is essential to maintain good relationships with suppliers and ensure a smooth supply chain.
Short-Term Loans
Short-term loans are borrowings that are due for repayment within one year. They provide companies with temporary financing to meet immediate financial needs, such as funding operating expenses, inventory purchases, or capital investments. Monitoring and managing short-term loans help ensure the company’s liquidity and ability to honor its debt obligations.
Long-term Liabilities Explained
Long-term liabilities are obligations that extend beyond one year or the operating cycle of the business. They represent the company’s long-term financial commitments, usually in the form of loans or bonds.
Bonds Payable
Bonds payable are long-term debt securities issued by the company to raise capital from investors. They represent an agreement to repay the principal amount at a specified future date and pay periodic interest to bondholders. Bonds provide an alternative financing option for companies to fund large-scale projects or expansions.
Mortgages
Mortgages are long-term loans secured by specific assets, typically real estate properties. They enable companies to finance the purchase or development of property or other fixed assets. Mortgages involve regular repayments of principal and interest over an extended period, usually several years or decades.
Unpacking Equity
Equity represents the ownership interest in a company. It reflects the residual value after deducting liabilities from assets. Analyzing equity helps assess a company’s financial stability, ownership structure, and shareholders’ claims on the company’s assets.
Common Stock and Its Significance
Common stock represents the initial capital invested by shareholders in exchange for ownership rights and voting privileges in the company. It represents the ownership stake held by shareholders and provides them with certain rights, such as participating in decision-making processes and receiving dividends.
Retained Earnings and Their Importance
Retained earnings represent the accumulated profits or losses retained within the company since its inception. They reflect the portion of net income that has not been distributed to shareholders as dividends. Retained earnings are reinvested in the company to fund growth opportunities, repay debts, or strengthen the company’s financial position.
How to Read a Balance Sheet
Reading a balance sheet requires understanding its layout and the relationship between its components. By examining the balance sheet, stakeholders can assess a company’s financial health, liquidity, and solvency.
Understanding the Layout
A balance sheet is typically presented in a vertical format, with assets listed on the left side and liabilities and equity on the right side. The equation “Assets = Liabilities + Equity” signifies the fundamental accounting principle of double-entry bookkeeping.
Analyzing the Financial Health of a Company
When analyzing a balance sheet, several key financial ratios and indicators can provide insights into a company’s financial health:
- Current Ratio:
It measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. A higher current ratio indicates better short-term liquidity.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio:
It assesses a company’s leverage and financial risk by comparing its total debt to its equity. A lower ratio suggests lower financial risk.
- Return on Equity (ROE):
It measures the profitability generated by the shareholders’ investment in the company. A higher ROE indicates efficient utilization of equity.
- Working Capital:
It represents the difference between current assets and current liabilities. Positive working capital indicates the company’s ability to cover short-term obligations.
Importance of Balance Sheets for Investors
Balance sheets play a crucial role in investment decision-making. Investors rely on balance sheet analysis to assess a company’s financial position, evaluate its stability, and make informed investment choices.
Assessing a Company’s Financial Position
By examining a company’s balance sheet, investors can gain insights into its asset quality, debt levels, and overall financial stability. This helps in understanding the company’s ability to generate cash flows, meet its obligations, and withstand economic downturns.
Making Informed Investment Decisions
Balance sheets provide valuable information to investors when evaluating investment opportunities. By comparing financial ratios, analyzing trends, and assessing the composition of a company’s assets and liabilities, investors can make informed decisions about investing in a particular company or industry.
Balance Sheets for Financial Management
Balance sheets serve as a valuable tool for financial management within a company. They provide essential information for tracking financial performance, facilitating financial planning, and making strategic decisions.
Tracking Financial Performance
By regularly reviewing balance sheets, companies can monitor their financial performance and identify areas for improvement. It helps in analyzing the company’s revenue generation, asset utilization, and debt management.
Facilitating Financial Planning
Balance sheets provide the necessary data for financial planning and forecasting. By understanding the company’s financial position, management can make informed decisions regarding budgeting, capital allocation, and investment strategies.
Limitations of Balance Sheets
While balance sheets are essential financial statements, they have certain limitations that should be considered.
Historical Nature of the Information
Balance sheets provide a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. They reflect historical data and may not capture the dynamic nature of a company’s financial condition or changes that occurred after the balance sheet date.
Not Capturing Qualitative Aspects
Balance sheets primarily focus on quantitative aspects of a company’s financial position. They do not capture qualitative factors such as management quality, industry trends, or competitive advantages. Therefore, it is important to complement balance sheet analysis with other forms of research and analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a balance sheet is a vital financial statement that provides insights into a company’s financial position, including its assets, liabilities, and equity. It helps stakeholders evaluate a company’s financial health, make investment decisions, and manage finances effectively. Understanding the components of a balance sheet and analyzing its ratios and indicators can provide valuable information for investors, financial professionals, and companies themselves. By leveraging the information provided by balance sheets, stakeholders can make informed decisions and navigate the financial landscape with confidence.
Why Financial Statement Analysis is Important in Business
Financial statement analysis is a critical process that allows businesses to evaluate their financial performance and make informed decisions. By examining various financial statements and using different ratios and metrics, companies gain valuable insights into their financial health, profitability, and overall performance. In this article, we will explore the significance of financial statement analysis in business and understand why it is a crucial tool for assessing the financial well-being of an organization.
Introduction
Financial statement analysis refers to the examination and interpretation of financial statements to gain insights into a company’s financial performance. It involves reviewing various financial documents, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, to assess the company’s financial position, profitability, and cash flow management.
Understanding the financial position of a business is essential for decision-making, strategic planning, and attracting investors and lenders. By analyzing financial statements, companies can identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and patterns, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and improve their overall financial performance.
Purpose of Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis serves several crucial purposes in business:
Assessing the financial health of a company
Financial statements provide a snapshot of a company’s financial health. By analyzing these statements, businesses can determine their liquidity, solvency, and overall stability. This assessment helps stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and management, understand the company’s ability to meet short-term obligations, manage debt, and sustain its operations.
Evaluating Profitability and Performance
Financial statement analysis helps evaluate the profitability and performance of a company. By examining the income statement, businesses can assess their revenue, expenses, and net income. This analysis enables them to identify trends and patterns, assess the efficiency of their operations, and make adjustments to enhance profitability.
Identifying trends and patterns
Financial statement analysis helps identify trends and patterns within a company’s financial data. By comparing financial statements over different periods, businesses can identify areas of growth, decline, or stagnation. This insight is crucial for planning, budgeting, and forecasting future financial performance.
Making informed decisions
Financial statement analysis provides essential information for making informed decisions. Whether it’s evaluating investment opportunities, deciding on expansion plans, or determining pricing strategies, analyzing financial statements helps businesses assess the potential risks and rewards associated with various choices.
Key Components of Financial Statements
Financial statements consist of three primary components:
Balance sheet
The balance sheet presents a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It includes
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Shareholders’ equity.
Analyzing the balance sheet helps evaluate a company’s liquidity, solvency, and net worth.
Income statement
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, provides an overview of a company’s
- Revenues
- Expenses
- Net income
over a specific period. Analyzing the income statement helps assess a company’s profitability, efficiency, and overall financial performance.
Cash flow statement
The cash flow statement reports the inflows and outflows of cash during a specific period. It helps evaluate a company’s cash management,
- Operating activities
- Investing activities
- Financing activities
Analyzing the cash flow statement helps identify the company’s ability to generate and manage cash.
Ratios and Metrics Used in Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis relies on various ratios and metrics to gain insights into a company’s financial performance. Some commonly used ratios include:
Liquidity ratios
Liquidity ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. Examples include the
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
These ratios help assess a company’s liquidity and its ability to handle unexpected financial challenges.
Profitability ratios
Profitability ratios measure a company’s ability to generate profits. Examples include
- Gross profit margin
- Net profit margin
- Return on investment (ROI).
These ratios help assess the efficiency of a company’s operations and its ability to generate returns for its shareholders.
Efficiency ratios
Efficiency ratios measure how effectively a company utilizes its assets and resources to generate revenue. Examples include
- Inventory turnover ratio
- Asset turnover ratio
These ratios help assess the effectiveness of a company’s operations and its ability to manage its assets efficiently.
Solvency ratios
Solvency ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations. Examples include
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Interest coverage ratio
These ratios help assess a company’s financial stability and its ability to repay its long-term debts.
Benefits of Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis offers several benefits to businesses:
Identifying strengths and weaknesses
By analyzing financial statements, businesses can identify their strengths and weaknesses. This insight enables them to capitalize on their strengths and address weaknesses, thereby improving their overall financial performance.
Assessing business risks
Financial statement analysis helps assess the risks associated with a business. By identifying potential risks, such as excessive debt or declining profitability, businesses can take proactive measures to mitigate those risks and safeguard their financial stability.
Planning and budgeting
Financial statement analysis provides essential information for planning and budgeting. By analyzing past financial data and identifying trends, businesses can develop realistic budgets, set achievable goals, and allocate resources effectively.
Attracting investors and lenders
Investors and lenders often rely on financial statements to assess the financial health of a company before making investment or lending decisions. A comprehensive financial statement analysis helps build trust and confidence, attracting potential investors and lenders.
Limitations of Financial Statement Analysis
While financial statement analysis provides valuable insights, it also has certain limitations:
Reliance on historical data
Financial statement analysis relies on historical data, which may not always reflect future performance accurately. Economic conditions, market trends, and other external factors can significantly impact a company’s financial performance in the future.
Subjectivity and estimation
Financial statements involve subjective judgments and estimations, such as asset valuations, bad debt provisions, and useful life estimations. These subjective elements can introduce biases and impact the accuracy of financial statement analysis.
Limited scope
Financial statement analysis provides insights into a company’s financial performance but has limitations in assessing non-financial aspects. Factors like market reputation, customer satisfaction, and employee morale are essential but not captured in financial statements.
Tools and Techniques for Financial Statement Analysis
Several tools and techniques are employed in financial statement analysis:
Vertical analysis
Vertical analysis involves comparing individual items on a financial statement to a base item. It helps assess the proportional relationship between different items and their impact on overall financial performance.
Horizontal analysis
Horizontal analysis involves comparing financial statements over multiple periods. It helps identify trends, changes, and growth rates, providing insights into a company’s performance over time.
Ratio analysis
Ratio analysis involves calculating and analyzing various financial ratios. It helps evaluate a company’s liquidity, profitability, efficiency, and solvency, providing a comprehensive overview of its financial health.
Common-size analysis
Common-size analysis involves expressing financial statement items as a percentage of a common base. It helps compare different companies or different periods, standardizing the analysis and facilitating meaningful comparisons.
Importance of Industry Comparison in Financial Statement Analysis
In addition to analyzing a company’s financial statements, it is crucial to compare its performance with industry benchmarks. Industry comparison provides valuable insights into a company’s market position, competitive advantages, and areas for improvement. By benchmarking against industry peers, businesses can identify industry trends, assess their relative performance, and make informed strategic decisions.
Using Financial Statement Analysis for Decision Making
Financial statement analysis plays a vital role in decision making across various areas of business:
Investment decisions
Financial statement analysis helps investors evaluate investment opportunities. By analyzing a company’s financial performance, growth prospects, and risk factors, investors can make informed decisions about investing in stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments.
Credit decisions
Financial statement analysis assists lenders in assessing creditworthiness. By analyzing a company’s financial health, debt levels, and cash flow, lenders can evaluate the risk of lending money and determine appropriate loan terms.
Strategic planning
Financial statement analysis provides essential information for strategic planning. By understanding a company’s financial position, profitability, and growth potential, businesses can develop effective strategies, set realistic goals, and allocate resources efficiently.
Challenges and Best Practices in Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis comes with its challenges and requires adherence to best practices:
Accuracy and reliability of data
Financial statement analysis heavily relies on accurate and reliable data. It is crucial to ensure that the financial statements are prepared following accounting standards and that the data used for analysis is complete and trustworthy.
Continuous monitoring and updating
Financial statement analysis should be an ongoing process. Companies need to monitor and update their financial statements regularly to reflect changes in their operations, market conditions, and business environment. Outdated or incomplete data can lead to inaccurate analysis and flawed decision-making.
Professional expertise
Financial statement analysis requires expertise in accounting, finance, and data analysis. It is essential to have professionals or consultants with a strong understanding of financial statements, ratios, and industry benchmarks to ensure accurate analysis and interpretation.
Conclusion
Financial statement analysis is a critical tool for businesses to assess their financial health, evaluate performance, and make informed decisions. By examining various financial statements, utilizing ratios and metrics, and comparing industry benchmarks, companies gain valuable insights into their financial position, profitability, and market standing. Financial statement analysis enables businesses to identify strengths and weaknesses, assess risks, plan effectively, and attract investors and lenders. While it has limitations and challenges, proper utilization of financial statement analysis can significantly contribute to the success.


Analysis of Financial Statement of Business
Introduction to Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis involves the systematic examination and interpretation of a company’s financial statements to assess its financial position, performance, and prospects. It enables investors, creditors, management, and other interested parties to make informed decisions about the company’s viability and potential for growth. By analyzing financial statements, stakeholders can identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, helping them mitigate risks and seize opportunities effectively.
Importance of Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis plays a vital role in the decision-making process of investors, creditors, and other stakeholders. It provides valuable information that helps determine the company’s creditworthiness, investment potential, and overall financial health. By assessing key financial ratios, trends, and patterns, stakeholders can evaluate the company’s past performance, assess its current situation, and make predictions about its future prospects. Moreover, financial statement analysis helps in benchmarking the company’s performance against industry standards and competitors, identifying areas for improvement, and optimizing resource allocation.
Key Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are essential tools in financial statement analysis as they provide meaningful insights into a company’s performance. Some of the key financial ratios include:
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. They include the
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
- Cash ratio
These ratios help stakeholders evaluate the company’s liquidity position and its ability to handle unexpected financial challenges.
Solvency Ratios
Solvency ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its long-term obligations.
They include
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Debt ratio
- Interest coverage ratio
. Solvency ratios provide insights into the company’s long-term financial stability and its capacity to repay its debts.
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios evaluate a company’s ability to generate profits relative to its sales, assets, and equity.
They include
- Gross profit Margin
- Return on Assets
- Net Profit Margin
- Return on Equity.
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency ratios measure a company’s ability to utilize its assets and resources effectively.
They include
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
- Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio
. Efficiency ratios help stakeholders evaluate the company’s operational efficiency, asset utilization, and inventory management.
Interpretation of Financial Statement Analysis
Interpreting the results of financial statement analysis requires a comprehensive understanding of the company’s operations, industry dynamics, and economic conditions. Different methods can be used for interpretation, including vertical analysis, horizontal analysis, and comparative analysis.
Vertical Analysis
The vertical analysis involves expressing each item in the financial statements as a percentage of a base figure. It helps stakeholders understand the relative importance of different components within the financial statements and assess their impact on the overall performance.
Horizontal Analysis
Horizontal analysis compares financial data across different periods to identify changes, trends, and growth rates. It helps stakeholders understand the company’s performance over time and identify areas of improvement or concern.
Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis involves benchmarking a company’s financial performance against its competitors or industry standards. It helps stakeholders assess the company’s relative strengths and weaknesses and identify opportunities for improvement.
Limitations of Financial Statement Analysis
While financial statement analysis is a valuable tool, it has certain limitations that should be considered.
These limitations include:
Historical Nature
Financial statement analysis is based on historical data, which may not reflect the current or future conditions accurately.
Quality of Financial Statements
The accuracy and reliability of financial statements can vary, impacting the analysis results.
Limited Scope
Financial statement analysis focuses on quantitative data and may not capture qualitative aspects such as management quality or industry trends.
Subjectivity
Interpretation of financial statement analysis involves subjective judgments and assumptions, which can introduce biases.
Applications of Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis has diverse applications in different contexts:
Investment Decisions
Investors use financial statement analysis to evaluate investment opportunities, assess the potential returns and risks, and make informed investment decisions.
Credit Decisions
Creditors analyze financial statements to determine a company’s creditworthiness and assess the risk of extending credit
Internal Decision-Making
Companies use financial statement analysis to evaluate their own performance, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Financial statement analysis is crucial during mergers and acquisitions to assess the financial viability and synergies of the involved companies.

The Easiest Way to Become a Successful Writer and Authors.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.

There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.
First, solve the problem. Then write the code.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
A programming language is for thinking about programs, not for expressing programs you’ve already thought of. It should be a pencil, not a pen.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Quis ipsum suspendisse ultrices gravida. Risus commodo .
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
The Quickest Way to Deliver Your Message? Make It Visual.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.

There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.
First, solve the problem. Then write the code.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
A programming language is for thinking about programs, not for expressing programs you’ve already thought of. It should be a pencil, not a pen.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Quis ipsum suspendisse ultrices gravida. Risus commodo .
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.

Why We Don’t Have Technical Interviews for Technical Roles at Buffer.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.

There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.
First, solve the problem. Then write the code.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
A programming language is for thinking about programs, not for expressing programs you’ve already thought of. It should be a pencil, not a pen.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Quis ipsum suspendisse ultrices gravida. Risus commodo .
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.

Why Successful People Wear The Same Thing Every Day.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.

There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.
First, solve the problem. Then write the code.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
A programming language is for thinking about programs, not for expressing programs you’ve already thought of. It should be a pencil, not a pen.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Quis ipsum suspendisse ultrices gravida. Risus commodo .
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.

What I Learned From Being a Broke, Unemployed Graduate.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.

There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks.
First, solve the problem. Then write the code.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
A programming language is for thinking about programs, not for expressing programs you’ve already thought of. It should be a pencil, not a pen.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Quis ipsum suspendisse ultrices gravida. Risus commodo .
There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injected humour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable. If you are going to use a passage of Lorem Ipsum. You need to be sure there isn’t anything embarrassing hidden in the middle of text. All the Lorem Ipsum generators on the Internet tend toitrrepeat predefined chunks. Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Necessary, making this the first true generator on the Internet. It re are many variations of passages of Lo rem Ipsum available, but the majority have suffered alteration in some form, by injectedeed eedhumour, or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable.
Hello








